Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
(looks long) In C code please, I am super lost with this topic and assignment got super complicated very fast, HELP 8.31 (Text Analysis) The
(looks long) In C code please, I am super lost with this topic and assignment got super complicated very fast, HELP




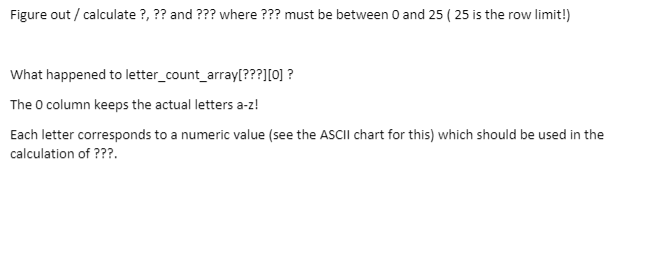
8.31 (Text Analysis) The availability of computers with string-manipulation capabilities has re- sulted in some rather interesting approaches to analyzing the writings of great authors. Much atten- tion has been focused on whether William Shakespeare ever lived. Some scholars find substantial evidence that Christopher Marlowe actually penned the masterpieces attributed to Shakespeare. Re- searchers have used computers to find similarities in the writings of these two authors. This exercise examines three methods for analyzing texts with a computer. a) Write a program that reads several lines of text and prints a table indicating the number of occurrences of each letter of the alphabet in the text. For example, the phrase To be, or not to be that is the question: contains one "a," two "b's," no "c's," and so on. b) Write a program that reads several lines of text and prints a table indicating the number of one-letter words, two-letter words, three-letter words, and so on, appearing in the text. For example, the phrase Whether 'tis nobler in the mind to suffer contains Word length Occurrences 1 0 2 2 3 1 4 2 (including tis) 5 0 6 2 7 1 Page of 6 ZOOM + 8.31 (Text Analysis. The availability of computers with string-manipulation capabilities has re- sulted in some rather interesting approaches to analyzing the writings of great authors . Much atten- tion has been focused on whether William Shakespeare ever lived. Some scholars find substantial evidence that Christopher Marlowe actually penned the masterpieces attributed to Shakespeare. Re- searchers have used computers to find similarities in the writings of these two authors. This exercise examines three methods for analyzing texts with a computer. a) Write a program that reads several lines of text and prints a table indicating the number of occurrences of each letter of the alphabet in the For example, the phrase To be, or not to be that is the question: contains one","two "b's," no "C's," and so on. b) Write a program that reads several lines of text and prints a table indicating the number of one-letter words, two-letter words, three-letter words, and so on, appearing in the text. For example, the phrase Whether 'tis nobler in the mind to suffer contains Word length Occurrences 1 0 2 3 1 2 (including tis) 4 0 2 1 Text book : "C How to program 8th Edition" Amendments 1) Instead of reading several lines of text, just hard-code the following text in the program a. myString= "The quick Brown? Fox ? jumps over the Lazy Dog and the !##! LAZY DOG IS still sleeping" b. The program should work with any value assigned to myString. Use a very small set of text (like "Ab#C#d") to test/debug your program first. C. 2) The program should make use of a function that converts the text to lower case (need to create your own conversion logic) and then perform the analysis in the main function. Ignore any numbers, symbols or special characters, etc in the text if any. Note: It's easier to create a new string for the result instead of modifying the original string. 3) Instead of the three methods outlined in the original question, complete only part a and part b. Assume maximum length is 10 for part b. 4) Turn in one program that contains part a and b. Output 3 Original text: The quick Brown? Fox ? jumps over the Lazy Dog and the !##! LAZY DOG is still sleeping Modified text: the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog and the lazy dog is still sleeping Letter Count 2 b 1 a Word length Occurrences 1 2 0 1 Required: Use two 2 dimensional arrays to emulate the tables that will capture the result of the analysis. One for part a and another for part b. Use loops to initialize the array values. Indent your code/ provide comments when implementing somethings that require some logic. Do not use 26 if statements to check for each letter. Use range of the alphabet (like between the starting and ending ASCII value of the letters). Create a function that will a) Accept two strings: target and source b) Copy from source to target; consume only A-Z, a-z and space, converting all upper case letters to lower case and ignoring everything else. Hints: Part a. Since we have 26 letters, then we can use an array with 26 rows. Each row can hold value for the actual letter and another value for the count. // Create an two dimensional array like below. You can use char instead of int to keep track of count too! char letter_count_array[26][2]; // 26 rows & 2 columns The following statements assign to the first row, the letter 'a' to the first column and 5 to the second column. This represents the letter 'a' was used 5 times in the sentence. letter_count_array[0][0]='a'; letter_count_array[0][1]=5; The following statements assign to the last row, the letter 'z' to the first column and 3 to the second column. This represents the letter 'z' was used 3 times in the sentence. letter_count_array[25][0]='z'; letter_count_array[25][1]=3; When populating the table a) with letters and table b) with word length, use loops. Use the loop iterator, the ASCII value of the letter and some mathematical operation to determine which bucket (row) of the array needs to updated. Do not use 26 comparison and/or assignment statements like shown below. When trying to figure out the letter occurrences, consider the following. Assuming array word contains the modified sentence and the second column of letter_count_array is used to keep of the letter occurrences (count). if (word[i] == 'a') letter_count_array[0][1]++; else if (word[i] == 'b') letter_count_array[1][1] ++; else if (word[i] == 'c') letter_count_array[2][1]++; else if (word[i] == '2') letter_count_array[25][1]++; Avoid the above mentioned technique. Instead of the 26 conditional/assignment statements, the replacement code segment should look like the following 1 conditional/assignment statement. if (word[i] >= ? && word[i]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


