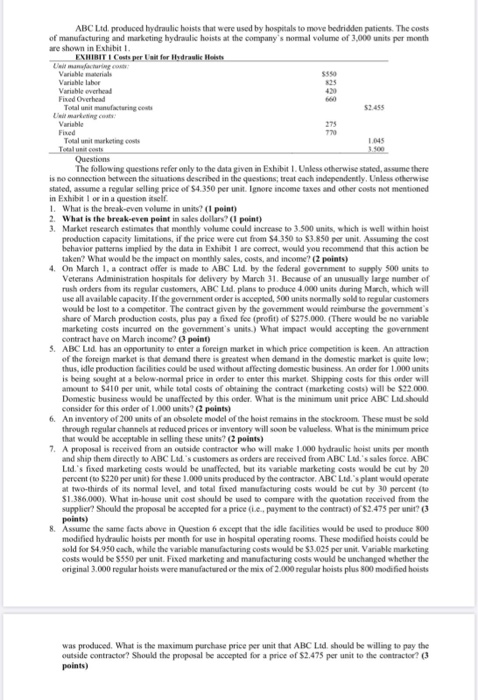
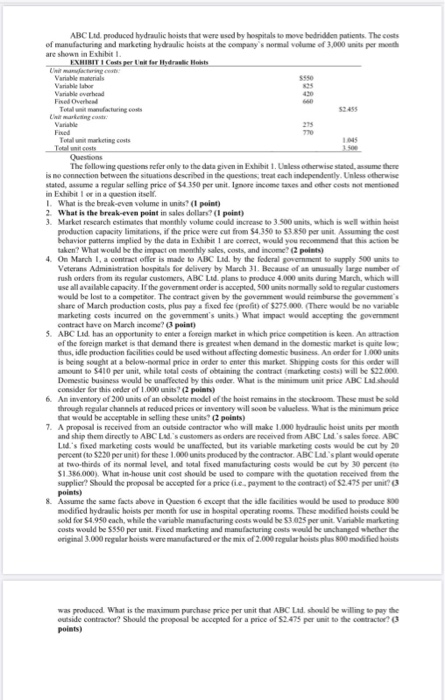
Ltd. produced hydraulic hoists that were used by hospitals to move bedridden patients. The costs of manufacturing and marketing hydraulic hoists at the company`s normal volume of 3,000 units per month are shown in Exhibit 1.
EXHIBIT 1 Costs per Unit for Hydraulic Hoists
Unit manufacturing costs:
Variable materials $550 Variable labor 825 Variable overhead 420 Fixed Overhead 660
Total unit manufacturing costs
Unit marketing costs:
Variable 275 Fixed 770
Total unit marketing costs Total unit costs
Questions
$2.455
1.045 3.500
The following questions refer only to the data given in Exhibit 1. Unless otherwise stated, assume there is no connection between the situations described in the questions; treat each independently. Unless otherwise stated, assume a regular selling price of $4.350 per unit. Ignore income taxes and other costs not mentioned in Exhibit 1 or in a question itself.
1. What is the break-even volume in units? (1 point)
2. What is the break-even point in sales dollars? (1 point)
3. Market research estimates that monthly volume could increase to 3.500 units, which is well within hoist
production capacity limitations, if the price were cut from $4.350 to $3.850 per unit. Assuming the cost behavior patterns implied by the data in Exhibit 1 are correct, would you recommend that this action be taken? What would be the impact on monthly sales, costs, and income? (2 points)
4. On March 1, a contract offer is made to ABC Ltd. by the federal government to supply 500 units to Veterans Administration hospitals for delivery by March 31. Because of an unusually large number of rush orders from its regular customers, ABC Ltd. plans to produce 4.000 units during March, which will use all available capacity. If the government order is accepted, 500 units normally sold to regular customers would be lost to a competitor. The contract given by the government would reimburse the government`s share of March production costs, plus pay a fixed fee (profit) of $275.000. (There would be no variable marketing costs incurred on the government`s units.) What impact would accepting the government contract have on March income? (3 point)
5. ABC Ltd. has an opportunity to enter a foreign market in which price competition is keen. An attraction of the foreign market is that demand there is greatest when demand in the domestic market is quite low; thus, idle production facilities could be used without affecting domestic business. An order for 1.000 units is being sought at a below-normal price in order to enter this market. Shipping costs for this order will amount to $410 per unit, while total costs of obtaining the contract (marketing costs) will be $22.000. Domestic business would be unaffected by this order. What is the minimum unit price ABC Ltd.should consider for this order of 1.000 units? (2 points)
6. An inventory of 200 units of an obsolete model of the hoist remains in the stockroom. These must be sold through regular channels at reduced prices or inventory will soon be valueless. What is the minimum price that would be acceptable in selling these units? (2 points)
7. A proposal is received from an outside contractor who will make 1.000 hydraulic hoist units per month and ship them directly to ABC Ltd.`s customers as orders are received from ABC Ltd.`s sales force. ABC Ltd.`s fixed marketing costs would be unaffected, but its variable marketing costs would be cut by 20 percent (to $220 per unit) for these 1.000 units produced by the contractor. ABC Ltd.`s plant would operate at two-thirds of its normal level, and total fixed manufacturing costs would be cut by 30 percent (to $1.386.000). What in-house unit cost should be used to compare with the quotation received from the supplier? Should the proposal be accepted for a price (i.e., payment to the contract) of $2.475 per unit? (3 points)
8. Assume the same facts above in Question 6 except that the idle facilities would be used to produce 800 modified hydraulic hoists per month for use in hospital operating rooms. These modified hoists could be sold for $4.950 each, while the variable manufacturing costs would be $3.025 per unit. Variable marketing costs would be $550 per unit. Fixed marketing and manufacturing costs would be unchanged whether the original 3.000 regular hoists were manufactured or the mix of 2.000 regular hoists plus 800 modified hoists
was produced. What is the maximum purchase price per unit that ABC Ltd. should be willing to pay the outside contractor? Should the proposal be accepted for a price of $2.475 per unit to the contractor? (3
Fred ABC Ltd, produced hydraulic hoists that were used by hospitals to move bedridden patients. The costs of manufacturing and marketing hydraulic hoists at the company's normal volume of 3,000 units per month are shown in Exhibiti EXHIBITI Costs per alt for bedral Hots Variable was 5550 Variable laber Variable overhead 430 Fixed Overhead 60 Total unit manufacturing costs Le ring Variable 275 770 Total unit marketing costs Questions The following questions refer only to the data given in Exhibit 1. Unless otherwise stated, assume there is no connection between the situations described in the questions, treat each independently. Unless otherwise stated, assume a regular selling price of $4.350 per unit. Ignore income taxes and other costs not mentioned in Exhibit I or in a question itself 1. What is the break-even volume in units? (l point) 2. What is the break-even point in sales dollars? (1 point) 3. Market research estimates that monthly volume could increase to 3.500 units, which is well within hoist production capacity limitations, if the price were cut from $4.350 to $3.850 per unit. Assuming the cost behavior patterns implied by the data in Exhibit I are correct, would you recommend that this action be taken? What would be the impact on monthly sales, costs, and income? (2 points) 4. On March 1, a contract offer is made to ABC Ltd. by the federal government to supply 500 units to Veterans Administration hospitals for delivery by March 31. Because of an unusually large number of rush orders from its regular customers, ABC Lad plans to produce 4.000 units during March, which will use all available capacity. If the government order is accepted, 500 units normally sold to regular customers would be lost to a competitor. The contract given by the government would reimburse the government's share of March production costs, plus pay a fixed fee (profit) of S275.000. (There would be no variable marketing costs incurred on the government's units.) What impact would accepting the government contract have on March income? 3 point) 5. ABC Lid. has an opportunity to enter a foreign market in which price competition is keen. An attraction of the foreign market is that demand there is greatest when demand in the domestic market is quite low; thus, idle production facilities could be used without affecting domestic business. An order for 1.000 units is being sought at a below-normal price in order to enter this market. Shipping costs for this order will amount to $410 per unit, while total costs of obtaining the contract (marketing costs) will be $22.000 Domestic business would be unaffected by this order. What is the minimum unit price ABC Lid.should consider for this order of 1.000 units? (2 points) 6. An inventory of 200 units of an obsolete model of the hoist remains in the stockroom. These must be sold through regular channels at reduced prices or inventory will soon be valueless. What is the minimum price that would be acceptable in selling these units? (2 points) 7. A proposal is received from an outside contractor who will make 1.000 hydraulic heist units per month and ship them directly to ABC Lid's customers as orders are received from ABC Lid's sales force. ABC Lid's fixed marketing costs would be unaffected, but its variable marketing costs would be cut by 20 percent to $220 per unit) for these 1.000 units produced by the contractor, ABC Lid's plant would operate at two-thirds of its normal level, and total fixed manufacturing costs would be cut by 30 percent (to $1.386.000). What in-house unit cost should be used to compare with the quotation received from the supplier? Should the proposal be accepted for a price (i.c., payment to the contract) of S2.475 per unit? (3 points) 8. Assume the same facts above in Question 6 except that the idle facilities would be used to produce 800 modified hydraulic hoists per month for use in hospital operating rooms. These modified hoists could be sold for 54.950 cach, while the variable manufacturing costs would be $3.025 per unit. Variable marketing costs would be $550 per unit. Fixed marketing and manufacturing costs would be unchanged whether the original 3.000 regular hoists were manufactured or the mix of 2.000 regular hoists plus 800 modified hoists was produced. What is the maximum purchase price per unit that ABC Ltd. should be willing to pay the outside contractor? Should the proposal be accepted for a price of $2.475 per unit to the contractor? (3 points) Variable materials ABC Ltd. produced hydraulic hoists that were used by hospitals to move bedridden patients. The costs of manufacturing and marketing hydraulic hoists at the company's normal volume of 3,000 units per month are shown in Exhibiti EXHIBITI Costs per l'alt for Hydraulic Hobh 5550 Variable labor Variable overhead Fred Own Total manufacturing costs 52.455 Variable 770 Totalni marketing costs Totale Questions The following questions refer only to the data given in Exhibit 1. Unless otherwise stated assume there is no connection between the situations described in the questions, treat each independently. Unless otherwise stated, assume a regular selling price of 54350 per unit. Ignore income taxes and other costs not mentioned in Exhibitor in a question itself 1. What is the break-even volume in units? (point) 2. What is the break-even point in sales dollars? (1 point) 3. Market rescarch estimates that monthly volume could increase to 3.500 units, which is well within his production capacity limitations, if the price were cut from 54.350 to 53.850 per unit. Assuming the cost behavior patterns implied by the data in Exhibit I are correct, would you recommend that this action be taken? What would be the impact on monthly sales, costs, and income points) 4. On March 1, a contract offer is made to ABC Lid. by the federal government to supply 500 units to Veterans Administration hospitals for delivery by March 31. Because of an unusually large number of rush orders from its regular customers, ABC Led plans to produce 4.000 units during March, which will use all available capacity. If the government order is accepted, 500 units normally sold to regular customers would be lost to a competitor. The contract given by the goverment would reimburse the govermene's share of March production costs, plus pay a fixed foe (profit) of 5275.000. (There would be no variable marketing costs incurred on the goverment's units) What impact would accepting the government contract have on March income? 3 point) 5. ABC Lid. has an opportunity to enter a foreign market in which price competition is keen. An attraction of the foreign market is that demand there is greatest when demand in the domestic market is quite low thus, idle production facilities could be used without affecting domestic business. An order for 1.000 units is being sought at a blow-normal price in order to enter this market. Shipping costs for this order will amount to 5410 per unit, while total costs of obtaining the contract (marketing costs) will be $22.000 Domestic business would be unaffected by this order. What is the minimum unit price ABC Lad should consider for this order of 1.000 units points) 6. An inventory of 200 units of an obsolete model of the horist remains in the stockroom. These must be sold through regular channels at reduced prices or inventory will soon be valueless. What is the minimum price that would be acceptable in selling these units! points) 7. A proposal is received from an outside contractor who will make 1.000 hydraulic hoist units per month and ship them directly to ABC Lad's customers as orders are received from ABC Lad's salesforce ABC Lod's fixed marketing costs would be unaffected, but its variable marketing costs would be cut by 20 percent (to S220 per unit) for these 1.000 units produced by the contractor. ABC Lad's plant would operate at two-thirds of its normal level and total fixed manufacturing costs would be cut by 30 percent to 51.386.000). What in-house unit cost should be used to compare with the quotation received from the supplier? Should the proposal be accepted for a price (ie.payment to the contract) of S2.475 per unit? points) & Assume the same facts above in Question 6 except that the idle facilities would be used to produce 800 modified hydraulic hoists per month for use in hospital operating rooms. These modified hoists could be sold for $4.950 each, while the variable manufacturing costs would be 53.025 per unit. Variable marketing costs would be $550 per unit. Fixed marketing and manufacturing costs would be unchanged whether the original 3.000 regular hoists were manufactured or the mix of 2.000 regular hoists plus 800 modified hoists was produced. What is the maximum purchase price per unit that ABC Lad should be willing to pay the outside contractor? Should the proposal be accepted for a price of $2.475 per unit to the contractor (3 points)