Question
//main.cpp #include using namespace std; // Definition for a binary tree node. struct TreeNode { int val; TreeNode *left; TreeNode *right; TreeNode *parent; TreeNode(int x)
//main.cpp
#include
using namespace std;
// Definition for a binary tree node.
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode *parent;
TreeNode(int x) {
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
parent = NULL;
val = x;
}
};
void rightRotate(TreeNode* root) {
// Your Code Here
return;
}
void leftRotate(TreeNode* root) {
// your code here
return;
}
void deleteTree(TreeNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL) return;
deleteTree(root->left);
deleteTree(root->right);
delete root;
root = NULL;
}
int main() {
TreeNode * n1 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode * n2 = new TreeNode(5);
TreeNode * n3 = new TreeNode(8);
TreeNode * n4 = new TreeNode(10);
TreeNode * n5 = new TreeNode(13);
n4->left = n3;
n3->parent = n4;
n4->right = n5;
n5->parent = n4;
n3->left = n2;
n2->parent = n3;
n2->left = n1;
n1->parent = n2;
// Your Code Here (Right or left rotate to balance above tree? )
cout left)->left)->val left)->val left)->right)->val val right)->val
n1 = new TreeNode(2);
n2 = new TreeNode(5);
n3 = new TreeNode(8);
n4 = new TreeNode(10);
n5 = new TreeNode(13);
n2->right = n3;
n3->parent = n2;
n2->left = n1;
n1->parent = n2;
n3->right = n4;
n4->parent = n3;
n4->right = n5;
n5->parent = n4;
// Your Code Here (Right or left rotate to balance above tree? )
cout left)->val val right)->left)->val right)->val right)->right)->val
deleteTree(n2);
return 0;
}
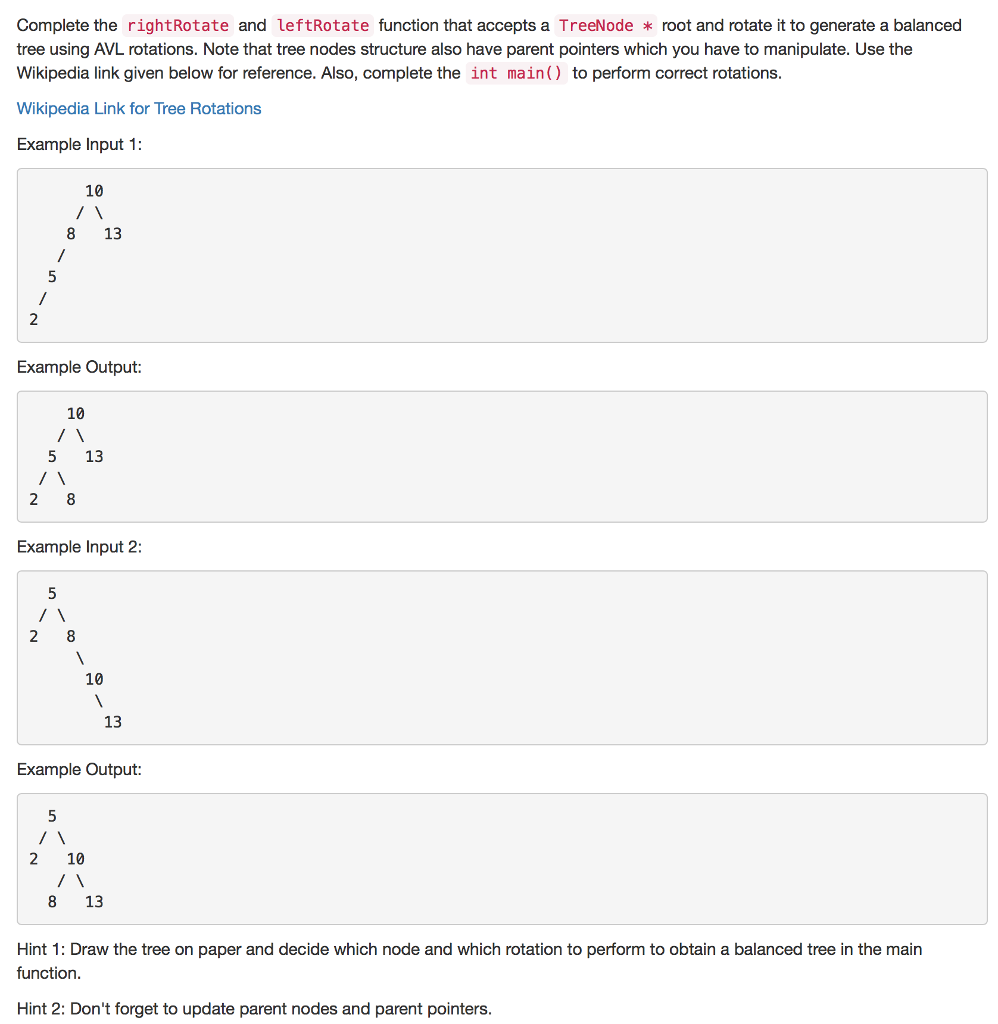
Complete the rightRotate and leftRotate function that accepts a TreeNode root and rotate it to generate a balanced tree using AVL rotations. Note that tree nodes structure also have parent pointers which you have to manipulate. Use the Wikipedia link given below for reference. Also, complete the int main() to perform correct rotations Wikipedia Link for Tree Rotations Example input 1: 10 /N 8 13 Example output: 10 5 13 Example input 2: /N 10 13 Example output /N 2 10 8 13 Hint 1: Draw the tree on paper and decide which node and which rotation to perform to obtain a balanced tree in the main function. Hint 2: Don't forget to update parent nodes and parent pointers. Complete the rightRotate and leftRotate function that accepts a TreeNode root and rotate it to generate a balanced tree using AVL rotations. Note that tree nodes structure also have parent pointers which you have to manipulate. Use the Wikipedia link given below for reference. Also, complete the int main() to perform correct rotations Wikipedia Link for Tree Rotations Example input 1: 10 /N 8 13 Example output: 10 5 13 Example input 2: /N 10 13 Example output /N 2 10 8 13 Hint 1: Draw the tree on paper and decide which node and which rotation to perform to obtain a balanced tree in the main function. Hint 2: Don't forget to update parent nodes and parent pointers
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


