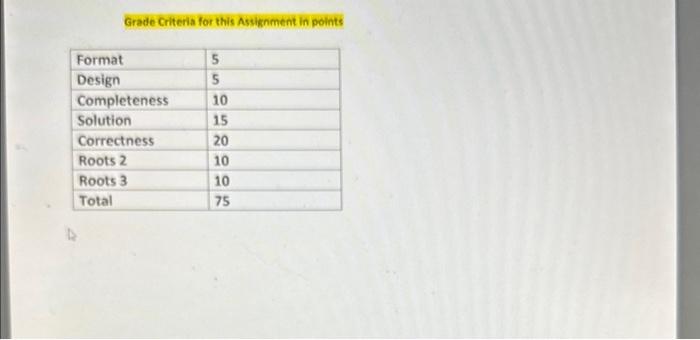
Make a business model from the case below. Write your name in the file properties of the file so that you have ownership of it. ROOTS CLOTHING COMPANY The Roots Clothing Company, owned by Juliet Austrich, produces scarf, sweater, shirts and pants. The clothing requirements are: for the scarf it requires 1.25 square yards of cloth, 2.4 square yards of cloth for the sweater, 2 square yards of cloth for the shirt and 3 square yards of cloth for the pants. During the next 4 months the following demands for scarf, sweater, shirts and pants must be met (on time): month \# 1, 150 scarf, 400 sweaters, 1000 shirts and 1500 pants; month H 2, 160 scarf, 300 sweaters, 800 shirts and 1200 pants; month H 3, 50 scarf, 100 sweaters, 1000 shirts and 600 pants; month \#4, 450 scarf, 700 sweaters, 3000 shirts and 2500 pants. The company operates at optimum capacity to meet the demands. During each month the following resources are available: month \# 1, 25,000 square yards; month #2,5000 square yards; month #3,6,000 square yards; month #4,5,000 square yards. Cloth that is available during month 1 and is not used can be used during month 2 . Same apply to the succeeding months. For labor cost during each month it cost $14 to make an article of scarf, $28 for sweater, $7 for shirt and $28 for pants. The cost of each square yard of cloth is $6.25 for the 1 and 2Nd month. There is an increase of 6% in the cost of cloth for month 3 and 5% for month 4 because of the suppliers' control of the market. It is expected that the supplies of cloth will dwindle or may even hit zero at the end of the year because of the ongoing crisis in the textile industry all over the world. Cost for resources/materials are computed based on used. Thus, for the first month, only the used square yards of cloth will be reflected in the materials cost and not for the entire 25,000 square yards. This is a common practice in price determination among manufacturers. There are monthly costs which are as follows: rent which is $5,000, office supplies $300, utilities at $275 and salary of employees $12,000. These monthly costs will be the fixed cost for the production Cost for resources/materials are computed based on used. Thus, for the first month, only the used square yards of cloth will be reflected in the materials cost and not for the entire 25,000 square yards. This is a common practice in price determination among manufacturers. There are monthly costs which are as follows: rent which is $5,000, office supplies $300, utilities at $275 and salary of employees $12,000. These monthly costs will be the fixed cost for the production of all the products per month. To arrive at the fixed cost per product, divide the fixed cost by the proportion of the variable cost per product over the total variable cost in producing all the products per month. The variable cost per product is the sum of labor cost and materials cost of producing the product. Selling price per product type is equal to mark up plus average cost. Average Cost is equal to Total Cost per product per month divided by quantity of the product type produced for the month, Total cost per product is equal to fixed cost plus variable cost of the product. The mark up are 38%,56%,28% and 75% respectively for scarf, sweater, shirt and pants. If the price of the product is lower than the previous month because of the inconsistency of the average cost, then the price of the previous month is adopted. The Multi Period production Scheduling is the guide model for the above cose to start with. 1. What is the monthly price for each product? 2. What is the monthly profit for each product? 3. What is the total profit in four months? 4. What is the remaining inventory of cloth per month? 5. Can you forecast a shortage or surplus of cloth for the future given a certain demand and available materials? Duplicate your Roots model. Name the new sheet as Roots 2. Using trendline, forecast the profit for the Sthth month in relation to the used resources (cloth) per month. Use 18000 yards of used cloth for the 5 th month. Do not include the polynomial and power curve trendine in your choices of best fit. Show the trendline graph with the corresponding equation and RSQ of your best fit prediction. (A recording on forecasting will be posted in Moodle) Duplicate your Roots model. Name the sheet as Roots 3. Create a fifth month using the given variables of the fourth month. Copy and adjust your model to fifth month until profit. The cost of cloth for the 5 th month should be the same as the fourth month. Using Solver, find the optimum profit for the month by distributing the remaining materials to cover the demand. The production for month 5 for each product should not be greater than the production for each product in month 4. Your ending inventory should be zero. Instead of Simplex LP as your solving method use GRG Non Linear. Grade Criteria for this Assignment in points Grade Criteria for this Assiknment in points