Question: Make a recoomendation for all five projects and Identify a concern with one or more metrics used by Target to make capital budgeting decisions for




 Make a recoomendation for all five projects and Identify a concern with one or more metrics used by Target to make capital budgeting decisions for the specific projects under consideration.
Make a recoomendation for all five projects and Identify a concern with one or more metrics used by Target to make capital budgeting decisions for the specific projects under consideration.
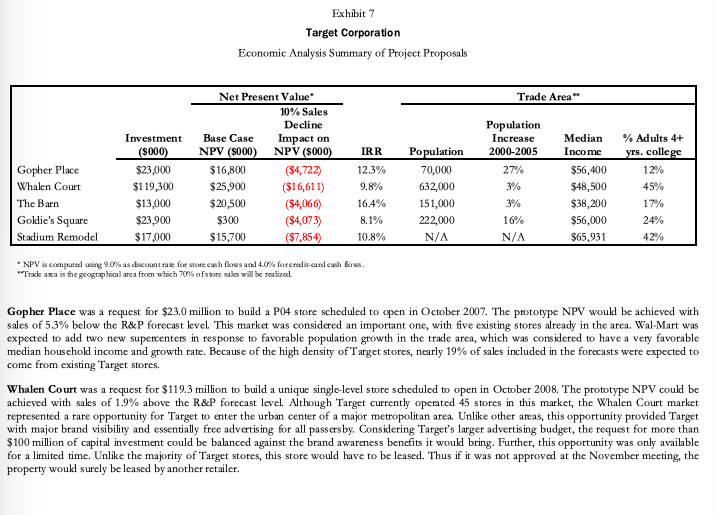
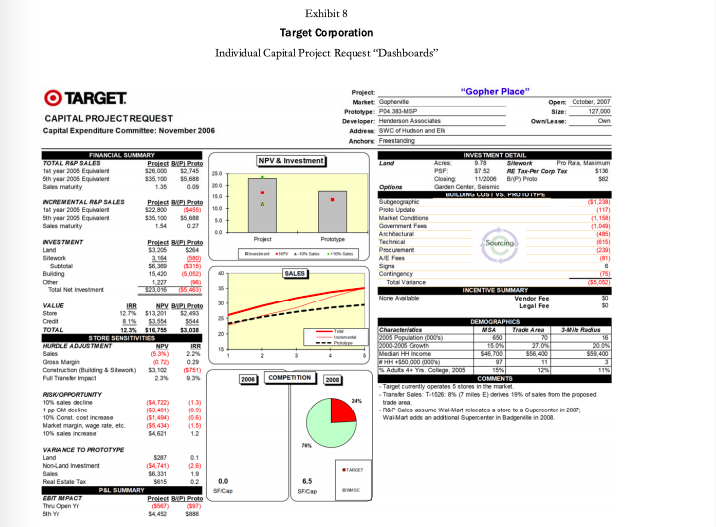
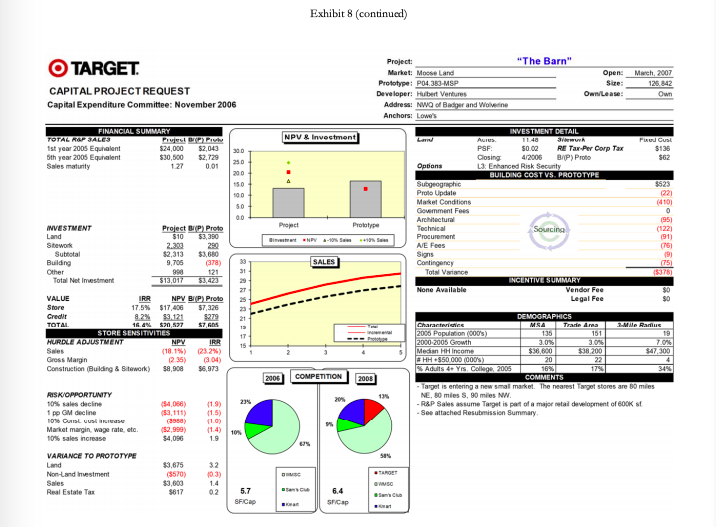
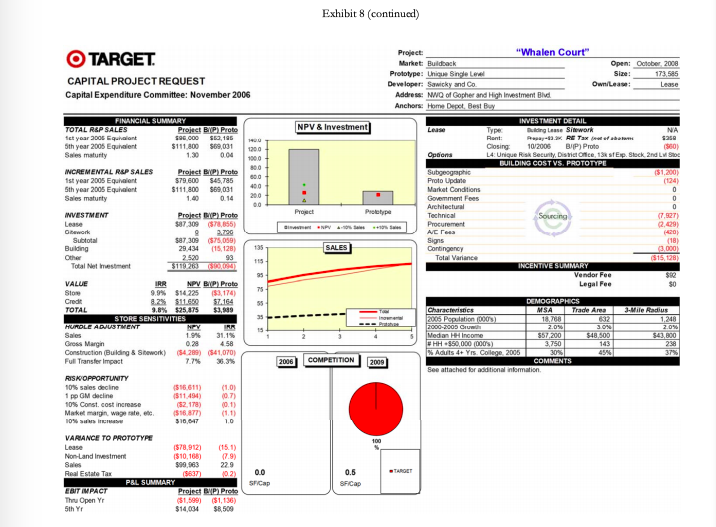
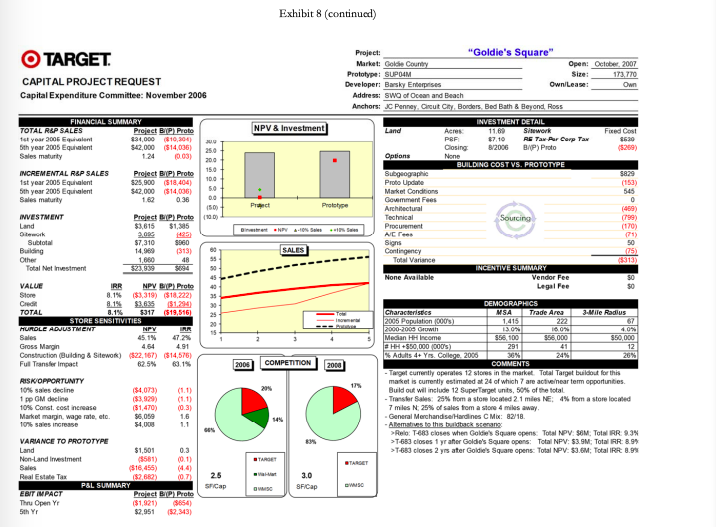
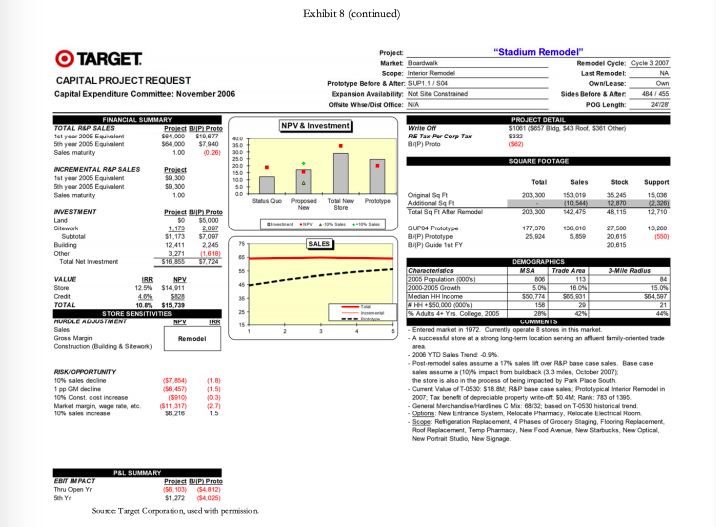
Capital-Expenditure Approval Process The Capital Expenditure Committee was composed of a team of top executives that met monthly to review all capital project requests (CPRs) in excess of $100,000. CPRs were either approved by the CEC, or in the case of projects larger than $50 million, required approval from the board of directors. Project proposals varied widely and included remodeling, relocating, rebuilding, closing an existing store, and building a new store.* A typical CEC meeting involved the review of 10 to 15 CPRs. All of the proposals were considered economically attractive, as any CPRs with questionable economics were normally rejected at the lower levels of review. In the rare instance when a project with a negative net present value (NPV) reached the CEC, the committee was asked to consider the project in light of its strategic importance to the company. CEC meetings lasted several hours as each of the projects received careful scrutiny by the committee members. The process purposefully was designed to be rigorous because the CEC recognized that capital investment could have significant impact on the short-term and long-term profitability of the company. In addition to the large amount of capital at stake, approvals and denials also had the potential to set precedents that would affect future decisions. For example, the committee might choose to reject a remodeling proposal for a store with a positive NPV, if the investment amount requested was much higher than normal and therefore might create a troublesome precedent for all subsequent remodel requests for similar stores. Despite how much the projects differed, the committee was normally able to reach a consensus decision for the vast majority of them. Occasionally however, a project led to such a high degree of disagreement within the committee that the CEO made the final call. Projects typically required 12 to 24 months of development prior to being forwarded to the CEC for consideration. In the case of new store proposals, which represented the majority of the CPRs, a real-estate manager assigned to that geographic region was responsible for the proposal from inception to completion and also for reviewing and presenting the proposal details. The pre-CPR work required a certain amount of expenditures that were not recoverable if the project were ultimately rejected by CEC. More important than these expenditures, however, were the "emotional sunk costs for the real estate managers who believed strongly in the merits of their proposals and felt significant disappointment if any project was not approved. The committee considered several factors in determining whether to accept or reject a project. An overarching objective was to meet the corporate goal of adding about 100 stores a year while maintaining a positive brand image. Projects also needed to meet a variety of financial objectives, starting with providing a suitable financial return as measured by discounted cash-flow metrics: NPV and IRR (internal rate of return). Other financial considerations included projected profit and earnings per share impacts, total investment size, impact on sales of other nearby Target stores, and sensitivity of NPV and IRR to sales variations. Projected sales were determined based on economic trends and demographic shifts but also considered the risks involved with the entrance of new competitors and competition from online retailers. And lastly, the committee attempted to keep the project approvals within the capital budget for the year. If projects were approved in excess of the budgeted amount, Target would likely need to borrow money to fund the shortfall. Adding debt unexpectedly to the balance sheet could raise questions from equity analysts as to the increased risk to the shareholders as well as to the ability of management to accurately project the company's funding needs. Other considerations included tax and real-estate incentives provided by local communities as well as area demographics. Target typically purchased the properties where it built stores, although leasing was considered on occasion. Population growth and affluent communities were attractive to Target, but these factors also invited competition from other retailers. In some cases, new Target stores were strategically located to block other retailers despite marginal short-term returns. When deciding whether to open a new store, the CEC was often asked to consider alternative store formats. For example, the most widely used format was the 2004 version of a Target store prototype called P04, which occupied 125,000 square feet, whereas a Superl'arget format occupied an additional 50,000 square feet to accommodate a full grocery assortment. The desirability of one format over another often centered on whether a store was expected to eventually be upgraded. Smaller stores often offered a higher NPV; but the NPV estimate did not consider the effect of future upgrades or expansions that would be required if the surrounding communities grew, nor the advantage of opening a larger store in an area where it could serve the purpose of blocking competitors from opening stores nearby. The committee members were provided with a capital-project request dashboard" for each project that summarized the critical inputs and assumptions used for the NPV and IRR calculations. The template represented the summary sheet for an elaborate discounted cash flow model. For example, the analysis of a new store included incremental cash flow projections for 60 years, over which time the model included a remodeling of the store every 10 years. Exhibit 6 provides an example of a dashboard with a detailed explanation of the "Store Sensitivities section. The example dashboard shows that incremental sales group. The R&P group used demographic and other data to make site-specific forecasts. Incremental sales were computed as total sales less those cannibalized from other Target stores. The resulting NPV and IRR metrics were divided between value created by store sales and credit card activity. NPV calculations used a 9.0% discount rate for cash flows related to the store cash flows and a 4.0% discount rate for credit card cash flows. The different discount rates were chosen to represent the different costs of capital for funding store operations versus funding credit card receivables. The dashboards also presented a variety of demographic information, investment-cost details and sensitivity analyses. An important sensitivity feature was the comparison of the project's NPV and IRR to the prototype. For example, the P04 store had an NPV of about $10 million and an IRR of 13%. The sensitivity calculations answered the question of how much a certain cost or revenue item needed to change in order for the project to achieve the same NPV or IRR that would be experienced for the typical P04 or SuperTarget store. The November Meeting Of the 10 projects under consideration for the November CEC meeting, Doug Scovanner recognized that five would be easily accepted, but that the remaining five CPRs were likely to be difficult choices for the committee. These projects included four new store openings (Gopher Place, Whalen Court, The Barn, and Goldie's Square) and one remodeling of an existing store into a Super Target format (Stadium Remodel). Exhibit 7 contains a summary of the five projects, and Exhibit 8 contains the CPR dashboards for the individual projects. As was normally the case, all five of the CPRs had positive NPVs, but Scovanner wondered if the projected NPVs were high enough to justify the required investment. Further, with stiff competition from other large retailers looking to get footholds in major growth areas, how much consideration should be given to short-term versus long-term sales opportunities? For example, Whalen Court represented a massive investment with relatively uncertain sales returns. Should Scovanner take the stance that the CEC should worry less about Whalen Court's uncertain sales and focus more on the project as a means to increase Target's brand awareness in an area with dense foot traffic and high-fashion appeal? Goldie's Square represented a more typical investment level of $24 million for a SuperTarget. The NPV, however, was small at $317,000, well below the expected NPV of a SuperTarget prototype, and would be negative without the value contribution of credit card sales. As CFO, Scovanner was also aware that Target shareholders had experienced a lackluster year in 2006, given that Target's stock price had remained essentially flat Exhibit 9). Stock analysts were generally pleased with Target's stated growth policy and were looking for decisions from management regarding investments that were consistent with the company maintaining its growth trajectory. In that regard, Scovanner recognized that each of the projects represented a growth opportunity for Target. The question, however, was whether capital was better spent on one project or another to create the most value and the most growth for Target shareholders. Thus Scovanner believed that he needed to rank the five projects in order to be able to recommend which ones to keep and which ones to reject during the CEC meeting the next day. Exhibit 7 Target Corporation Economic Analysis Summary of Project Proposals Trade Area IRR Gopher Place Whalen Court The Barn Goldie's Square Stadium Remodel Investment (5000) $23,000 $119,300 $13,000 $23,900 $17,000 Net Present Value 10% Sales Decline Base Case Impact on NPV (5000) NPV (5000) $16,800 (34,722) $25,900 ($16,611) $20,500 (34,066) $300 (34,073) $15,700 (37,854) 12.3% 9.8% 16.4% 8.1% 10.8% Population 70,000 632,000 151,000 222,000 N/A Population Increase 2000-2005 27% 3% 3% 16% N/A Median Income $56,400 $48,500 $38,200 $56,000 $65,931 % Adults 4+ yrs. college 12% 45% 17% 24% 42% NPV is compated using 9.0% as discount rate for store cash flores and 4.0% forcrediscard cash fous. "Track ana is the geographical area from which 70% of store sales will be realized. Gopher Place was a request for $23.0 million to build a PO4 store scheduled to open in October 2007. The prototype NPV would be achieved with sales of 5.3% below the R&P forecast level. This market was considered an important one, with five existing stores already in the area. Wal-Mart was expected to add two new supercenters in response to favorable population growth in the trade area, which was considered to have a very favorable median household income and growth rate. Because of the high density of Target stores, nearly 19% of sales included in the forecasts were expected to come from existing Target stores. Whalen Court was a request for $119.3 million to build a unique single-level store scheduled to open in October 2008. The prototype NPV could be achieved with sales of 1.9% above the R&P forecast level. Although Target currently operated 45 stores in this market, the Whalen Court market represented a rare opportunity for Target to enter the urban center of a major metropolitan area. Unlike other areas, this opportunity provided Target with major brand visibility and essentially free advertising for all passers by. Considering Target's larger advertising budget, the request for more than $100 million of capital investment could be balanced against the brand awareness benefits it would bring. Further, this opportunity was only available for a limited time. Unlike the majority of Target stores, this store would have to be leased. Thus if it was not approved at the November meeting, the property would surely be leased by another retailer. Exhibit 7 (continued) The Barn was a request for $13.0 million to build a PO4 store scheduled to open in March 2007. The prototype NPV was achievable with sales of 18.1% below the R&P forecast level. This project was being resubmitted after initial development efforts failed because of a disagreement with the developer. This small rural area was an extreme contrast to Whalen Court. The small initial investment allowed for a large retum on investment even if sales growth turned out to be less than expected. This investment represented a new market for Target as the two nearest Target stores were 80 and 90 miles away. Goldie's Square was a request for $23.9 million to build a SuperTarget store scheduled to open in October 2007. The prototype NPV required sales 45.1% above the R&P forecast level. This area was considered a key strategic anchor for many retailers. The Goldie's Square center included Bed Bath & Beyond, JCPenney, Circuit City, and Borders. Target currently operated 12 stores in the area and was expected to have 24 eventually. Despite the relatively weak NPV figures, this was a hotly contested area with an affluent and fast growing population, which could afford good brand awareness should the growth materialize. Stadium Remodel was a request for $17.0 million to remodel a Super Target store opening March 2007. As a remodel, there was no prototype NPV for comparison. The recent sales decline and deteriorating facilities at this location could lead to tarnishing the brand image. This trade area had supported Target stores since 1972 and had already been remodeled twice previously. The $17 million investment would certainly give a lift to the lagging sales. Source: Target Corporation, sed with permission Exhibit 8 Target Corporation Individual Capital Project Request Dashboards TARGET CAPITAL PROJECT REQUEST Capital Expenditure Committee: November 2006 Option Project "Gopher Place" Market Gopherve Open Cetober 2007 Prototype: PO 30 MSP Size: 127.000 Developer: Henderson Associates Owne: On Address: SWC of Hudson and ER Anchors Freestanding NPV & Investment INVESTMENT DETAIL Land ACT 9270 Sidework Pro Minum PSF S752 RE Tar Per Carp To $130 Closing 11/2008 BAP) Proto SO Garden Center Seismi BULUS LUSIVS. PATUITE Bugeographie Proto Update 11171 Market Conditions Government Fees Prot Architectural Prototype 405 Technical Sourcing Best PVN Procurement Art Sigu SALES Cortingency Total Vatance ( (55.CORT INCENTIVE SUMMARY None obble Vender Fee Legal Fee DEMOGRAPHICS Characteristics Trade Area -Wes 2005 Population 1000 10 2000-2005 Growth 15701 2070 Median Hicone 356 39,400 HH +850 000 000 97 11 Adults do Y Coleg 2305 158 115 2004 COMPETITION 2008 COMMENTS Target currently operates 5 stores in the market Transfer Sales T-15268 miles E) derives 19% of sales from the proposed 245 trade area -nar Colcs asume Wal-Mart cloccatore to upgroenter in 2007 Walmart adds an additional Supercenter in Badgende in 2008 15.30 VALUE FINANCIAL SUMMARY TOTAL RAP SALES Protest P. Proto 1st year 2005 Equivalent 528.000 $2.745 250 5th year 2006 Equivalent 335.100 56686 Sales maturity 135 0.00 15.0 NCREMENTAL RAP SALES Project API Prote 1st year 2005 Equivalent $22.000 5455) 100 Sth year 2005 Equiler $35100 $5660 Sales may 154 0.27 00 NVESTMENT Project BP Proto Land $264 Stwork a 164 56.300 Building 40 1.221 Total Net investment 2016 30 IRR NPV BAP. Proto Store 12.7% $13.201 52.493 8.1984 5544 -- TOTAL 12.3% 516 TES 53038 STORE SENSITIVITIES HURELE ADJUSTMENT NPV IRR 15 Sales Gross Main 0.29 Construction Building & Stwork) 100 (5751) Mars met RISK OPPORTUNITY 10% sales decline 154.722) 1 pp CM decine 10% Const. cost increase 10.6) Market marginwage sale, etc. (1.5) 10% sales increase 54021 12 VARANCE TO PROTOTYPE Land 5.287 0.1 Norland Investment 154.741) (26) Sales $8.331 1.9 Real Estate Tax $815 0.0 PEL SUMMARY Siap FRIT IMPACT Proiect BPI Proto Thu Open Y (556 5th $4452 $836 Cinder 28 STARE 6.5 SF Cap OWS Exhibit 8 (continued) O TARGET CAPITAL PROJECT REQUEST Capital Expenditure Committee: November 2006 March 2007 126.842 Own FINANCIAL SUMMARY TOTAL ROP SALES 1st year 2005 Equhalent $24,000 5th year 2005 Equivalent $30,500 Sales maturity $2,043 $2.729 0.01 Fed Cust 5136 $62 300 250 200 150 190 Project: "The Barn" Market: Moose Land Open: Prototype : P04.383 MSP Size: Developer: Hubert Ventures Own/Lease: Address: NWO of Badger and Wolverine Anchors: Lowe's INVESTMENT DETAIL NPV & Investment La Aures: 11.40 31 PSF S002 RE Tax-Per Corp Tax Closing 4/2006 BAP) Proto Options L3 Enhanced Risk Security BUILDING COST VS. PROTOTYPE Sugeographic Proto Update Market Conditions Goverment Fees Architectural Project Prototype Technical Sourcing Procurement instant NPV-10. Siis NE Fees Signs SALES Contingency Total Variance INCENTIVE SUMMARY None Available Vendor Fee Legal Fee 50 $523 (221 (410) 0 (95) (122) (91) (75) 9 75 5378) 33 31 INVESTMENT Project BAP) Proto Land $10 $3,350 Sitework 2.300 299 Subtotal $2,313 $3,680 Building 9,706 (378) Other 990 120 Total Net Imestment $13,017 $3,423 VALUE IRR NPV BIP) Proto Store 17.5% $17,406 $7,326 Credit 8.2% 3.121 $279 TOTAL 16.0% 520 527 $7 STORE SENSITIVITIES HURDLE ADJUSTMENT NPV IRR Sales (18.1%) (23.2%) Gross Margin (235) (304) Construction (Building & Sitework) $8.900 56,973 30 23 13 17 15 DEMOGRAPHICS Characteristics MSA Trade Area ZIMA 2006 Population (0005 135 11 2000-2005 Growth 3.09 Median HH Income $38,600 $38.200 $47.300 HH$50 000 0005) 20 22 Adults 4+ Yes College, 2005 16% 3496 COMMENTS Target is entering a new smal market. The nearest Target stores are 80 miles NE, 80 miles S, 90 miles NW. - R&P Sales assume Target is part of a major tal development of BOOKS - See attached Resubmission Summary 2006 COMPETITION 2008 13 234 RISK OPPORTUNITY 10% sales decline 1 pp GM decline 10% SLEVA Market margin, wage rate, etc. 10% sales increase (34.068) (53,111) (8580) (52,999) $4,096 (19) (15) (1.0) 10 1.9 SIS VARIANCE TO PROTOTYPE Land Non-Land Investment Sales Real Estate Tax $3,675 (5570) $3,603 $617 32 10.3) 1.4 02 5.7 SF Cup 6.4 SF Cap OWO Sense . Exhibit 8 (continued) Project: "Whalen Court" Market Buldback Open: October 2008 Prototype: Unique Single Level Size: 173 585 Developer: Sawicky and Co. Own/Lease: Lease Address: NWQ of Gopher and High Investment Blvd Anchors: Home Depot, Best Buy NPV & Investment INVESTMENT DETAIL Lease Type Buting lane Sitwork NA Rant Ray-13. RC Tax sasa Closing 10/2006 BHP) Proto (860) Options L4: Unique Risk Security District Office, 13 st Exp. Stock 2nd L Stoe BUILDING COSTVS. PROTOTYPE Subgeographic (51,200) Proto Update (124) Market Conditions Government Fees 0 Architectural 0 Project Prototype Technical Sourcing (7.521) BERRY Procurement 2,229) Ne fe Signs (18) SALES Contingency 3.000 Total Variance $15.00 INCENTIVE SUMMARY Vendor Fee $ Legal Fee 50 O TARGET CAPITAL PROJECT REQUEST Capital Expenditure Committee: November 2006 FINANCIAL SUMMARY TOTAL R&P SALES Project BIP) Proto fet year 2005 Equhalant 596.000 $63, 196 5th year 2005 Equivalent $111.800 $69,031 1200 Sales maturity 1.30 0.04 1000+ 80.0 INCREMENTAL RAP SALES Project BYP) Proto 1st year 2005 Equivalent 579.600 545,785 5th year 2005 Equivalent $111.800 S69,031 Sales maturty 0.14 00 INVESTMENT Project HP) Proto Lease $37,309 (878,655) work 2.790 Subtotal SBT 309 (75,050) Building 29 434 (15,128) 135 Other 2.520 93 115 Total Net mestment 3119263.00 VALUE IRR NPV BYP) Proto Store 75 9.9% $14.225 153,174) Crede 8.2% $11.650 55 TOTAL 3.8% $25.875 $3,899 HUOLE ADJUSTMENT STORE SENSITIVITIES NEY IRA Sales 1.9% 31.15 Gross Margin 0.28 458 Construction (Building & Stework) 54.289) (541,070) Full Transfer Impact 7.7% RISK OPPORTUNITY 10% sales decline ($16.611) (1.0) 1 pp OM decline ($11.494) (0.7) 10% Const cost increase (52.178) (0.1) Market marginwagte, et ($16.877) (1.1) 10% 310,647 10 VARIANCE TO PROTOTYPE Lease 1878,912) (15.1) Non Land Investment ($10,168) 7.9) Sales 390063 229 Real Estate Tax (5637 10.2) 0.0 PBL SUMMARY SF Cap EBIT IMPACT Project ByP Prote Thu Open Yr ($1,599) ($1,136) 5th Yr $14.034 S8.500 SS 57.164 15 DEMOGRAPHICS Characteristics MSA Trade Ares 2005 Population (0000 18,788 632 2000-2005 GIU 2.0% 3.09 Medan Income 557200 $48,500 HH$50.000000 3.750 143 % Adults 4+ Yrs. College. 2005 30% 45961 COMMENTS See attached for additional information -White Radius 1,248 2.09 $43,800 238 37% 2006 COMPETITION 2009 100 TARGET 0.5 SF Cap Exhibit 8 (continued) O TARGET CAPITAL PROJECT REQUEST Capital Expenditure Committee: November 2006 25.0 200 15.0 100 50 0.0 15.00 (10) 1494 FINANCIAL SUMMARY TOTAL REP SALES Project BIP Proto 1st year 2006 834,000 10,304) 5th year 2005 Equivalent $42.000 $14,006) Sales maturity 1.24 10.00) INCREMENTAL R&P SALES Project BIP) Proto 1st year 2005 Equivalent $25.900 (518,404) 5th year 2005 Equivalent $42.000 $14,006) Sales maturity 0.36 INVESTMENT Project BIP) Proto Land $3,615 $1,385 Otwork 2,090 Subtotal 87,310 8960 Building (313) Other 1,660 48 Total Netrestment 327939 5894 VALUE IRR NPV BYP) Proto Store 8.1% ($3,319) (18,222) 8.1% $26.95 51.286 TOTAL 8.1% 5317 ($19,516 STORE SENSITIVITIES MUROLE ADJUSTMENT NPV IRR Sales 45.1% 472 Gross Margin 4.64 4.91 Construction (Building & Sitework) ($22,167) ($14,576) Ful Transfer Impact 62.5% 63.1% RISK OPPORTUNITY 10% sales decline (84,073) 1 pp GM decline (3.929) 10% Const. cost increase (51,470) (0.3) Market margin, wage rate ato 56,050 1.6 10% sales increase $4,000 1.1 VARIANCE TO PROTOTYPE Land $1,501 0.3 Non-Land Investment (5581) (0.1) (516,455) Real Estate Tax ($2,682) (0.7) P&L SUMMARY EBIT IMPACT Project Proto Thu Open Yr ($1.921) $654) 5th Y $2,951 (52,343) 60 55 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 Project: "Goldie's Square" Market: Gold County Open: October 2007 Prototype SUPDAM Size: 173,770 Developer: Barsky Enterprises Own/Lease: Own Address: Swo of Ocean and Beach Anchors: JC Penney. Circut Cay Borders. Bed Bath & Beyond, Ross INVESTMENT DETAIL NPV & Investment Land Acres 11.60 Siswork Fixed Cost PRE 67.10 RS Tax Aer Carp Tax 8630 Closing 8/2006 BAP) Proto (5269) Options BUILDING COST VS. PROTOTYPE Sulgeographie 5823 Proto Update (153) Market Conditions 545 Goviment Fees 0 Pro Prototype Architectural (459) Technical Sourcing (799) Procurement Bent NPV A. Selle (170) ACT (71) Signs 50 SALES Contingency 25) Total Variance 3313) INCENTIVE SUMMARY None Available Vendor Fee 50 Legal Fee 50 DEMOGRAPHICS Characteristics MSA Trade Area 3.Wire Radius 2005 Population (00032 1.415 222 2000-2005 Gruwih 130 16.00 40% Median HH Income $56,100 $56,000 $50,000 HH +$50,0000005) 291 12 Adults 4+ Yos. College. 2006 36% 24% 26% 2006 COMPETITION 2008 COMMENTS Target currently operates 12 stores in the market. Total Target buldout for this market is currently estimated at 24 of which are active near term opportunities. 205 Build out will include 12 Super Target units, 50% of the total - Transfer Sales: 25% from a store located 21 miles NE 4% from a store located 7 miles N 25% of sales from a store 4 miles away 14% General Merchandise Hardlines CM: 82/18 - Alematies to this balduck senang > Relo: T-483 closes when Goldie's Square opens: Total NPV:58MTotal IRR 9.34 >T-683 closes 1 yr after Goldie's Square opens: Total NPV: $3.9M; Total RR: 8.9% >T-68 closes 2 yrs ater Goldies Square opens: Total NPV: 53.6M; Total IRR 8.99 TARGET STARGET 3.0 OSC SF Cap DISC 2.5 SFICA Exhibit 8 (continued) TARGET CAPITAL PROJECT REQUEST Capital Expenditure Committee: November 2006 NA Project Market Boardwalk Scope: Interior Remodel Prototype Before & After SUP 1.1/SO4 Expansion Availability: No Se Contained Offsite Whise/Dist Office: NA "Stadium Remodel Remodel Cycle: Cycle 3 2007 Last Remodel: Own Lease: Own Sides Before & After 484655 POG Length: 24/25 PROJECT DETAIL 5100186 Bldg 343 Root. 5381 Other) 120 19621 SQUARE FOOTAGE NPV & Investment Write of RETax Pur Cory Tax BAP) Proto 350 300 250 200 100 50 Status Que Proposed Town Prototype New Best Pero FINANCIAL SUMMARY TOTAL REP SALES Projet BIP Prote styw 2006 giunt 04.000 10.077 Sth year 2005 Equivalent $84.000 $7.940 Sales maturity 1.00 (0.28) INCREMENTAL RAP SALES Project 1st year 2005 Equivalent $0 300 Sth year 2005 Equivalent 50 300 Sales many 1.00 INVESTMENT Project P) Proto Land $0 $5,000 Dilework 1.179 2007 Subtotal $1,173 $7,087 Building 12 411 2.245 3.271 (1.618 Total Net imestment 516855 57724 IRR NPV Store 12.5% $14.911 Credit 5828 TOTAL 10,0 $15.739 STORE SENSITIVITIES PURIAE ALUSTMENT NPV INS Sales Gross Margin Remodel Construction (Building & Stework) SALES Other 65 55 VALUE 4 45 o Total Sales Stock Support Original 203.300 153019 35.245 15,000 Adonal Sq (10.544) 12.870 12.3261 Total Sq Ft Ater Remodel 142,475 48. 115 12/10 OUP Prototype 177,370 130010 27.500 19,200 BAP) Prototype 25,824 5.850 20.615 1550) BIP Guides FY 20 615 DEMOGRAPHICS Characteristics MSA Trade Area 3-M Me Radius 2005 Population 000 006 113 2000-2005 Growth 5.0% 18.09 15.04 Median HH Income $50,774 566.901 564, $50.00051 156 20 21 Aduts 4+ Yis. College, 2005 284 LUMMENIS -Entered market in 1972. Currently operate stores in this market. - A success store a strong long-term location sering an att bumily-oriented trade area - 2008 YTD Sales Trend 0.9% Post-remodel sales assume a 17% sales litt over R&P base case sales. Base case sales assume a 10% impact from bulduck (3.3 miles October 2007 the store is also in the process of being impacted by Park Place South - Curent Value of T-0530 $18.8M R&P base case sales Prototypical Interior Remodelin 2007: Tax benefit of depreciable property write-oft $0.4M; Rank: 783 of 1395 General Merchandise Hardines Mix: 88/52based on T-0530 historical trend Options New Entrance System Halocate Pharmacy, Helocate Electrical Room Scope Retigeration Replacement, 4 Phases of Grocery Staging, Flooring Replacement, Roof Replacement, Temp Pharmacy, New Food Avenue, New Starbucks, New Optical New Portrait Studio, New Signage ONT RISK OPPORTUNTY 10% sales decline pp GM decline 10% Const. cost increase Market marginwage rate, etc 10% alene 38 457 (5910) ($11,317) 8.216 (1.3) (1,5) 10.31 27 15 P&L SUMMARY EBIT PACY Proin UP Proto Thru Open Yr (56.103 (54.312) Sth Y $1.272 (54,025) Souxe Target Corporation, used with permission Capital-Expenditure Approval Process The Capital Expenditure Committee was composed of a team of top executives that met monthly to review all capital project requests (CPRs) in excess of $100,000. CPRs were either approved by the CEC, or in the case of projects larger than $50 million, required approval from the board of directors. Project proposals varied widely and included remodeling, relocating, rebuilding, closing an existing store, and building a new store.* A typical CEC meeting involved the review of 10 to 15 CPRs. All of the proposals were considered economically attractive, as any CPRs with questionable economics were normally rejected at the lower levels of review. In the rare instance when a project with a negative net present value (NPV) reached the CEC, the committee was asked to consider the project in light of its strategic importance to the company. CEC meetings lasted several hours as each of the projects received careful scrutiny by the committee members. The process purposefully was designed to be rigorous because the CEC recognized that capital investment could have significant impact on the short-term and long-term profitability of the company. In addition to the large amount of capital at stake, approvals and denials also had the potential to set precedents that would affect future decisions. For example, the committee might choose to reject a remodeling proposal for a store with a positive NPV, if the investment amount requested was much higher than normal and therefore might create a troublesome precedent for all subsequent remodel requests for similar stores. Despite how much the projects differed, the committee was normally able to reach a consensus decision for the vast majority of them. Occasionally however, a project led to such a high degree of disagreement within the committee that the CEO made the final call. Projects typically required 12 to 24 months of development prior to being forwarded to the CEC for consideration. In the case of new store proposals, which represented the majority of the CPRs, a real-estate manager assigned to that geographic region was responsible for the proposal from inception to completion and also for reviewing and presenting the proposal details. The pre-CPR work required a certain amount of expenditures that were not recoverable if the project were ultimately rejected by CEC. More important than these expenditures, however, were the "emotional sunk costs for the real estate managers who believed strongly in the merits of their proposals and felt significant disappointment if any project was not approved. The committee considered several factors in determining whether to accept or reject a project. An overarching objective was to meet the corporate goal of adding about 100 stores a year while maintaining a positive brand image. Projects also needed to meet a variety of financial objectives, starting with providing a suitable financial return as measured by discounted cash-flow metrics: NPV and IRR (internal rate of return). Other financial considerations included projected profit and earnings per share impacts, total investment size, impact on sales of other nearby Target stores, and sensitivity of NPV and IRR to sales variations. Projected sales were determined based on economic trends and demographic shifts but also considered the risks involved with the entrance of new competitors and competition from online retailers. And lastly, the committee attempted to keep the project approvals within the capital budget for the year. If projects were approved in excess of the budgeted amount, Target would likely need to borrow money to fund the shortfall. Adding debt unexpectedly to the balance sheet could raise questions from equity analysts as to the increased risk to the shareholders as well as to the ability of management to accurately project the company's funding needs. Other considerations included tax and real-estate incentives provided by local communities as well as area demographics. Target typically purchased the properties where it built stores, although leasing was considered on occasion. Population growth and affluent communities were attractive to Target, but these factors also invited competition from other retailers. In some cases, new Target stores were strategically located to block other retailers despite marginal short-term returns. When deciding whether to open a new store, the CEC was often asked to consider alternative store formats. For example, the most widely used format was the 2004 version of a Target store prototype called P04, which occupied 125,000 square feet, whereas a Superl'arget format occupied an additional 50,000 square feet to accommodate a full grocery assortment. The desirability of one format over another often centered on whether a store was expected to eventually be upgraded. Smaller stores often offered a higher NPV; but the NPV estimate did not consider the effect of future upgrades or expansions that would be required if the surrounding communities grew, nor the advantage of opening a larger store in an area where it could serve the purpose of blocking competitors from opening stores nearby. The committee members were provided with a capital-project request dashboard" for each project that summarized the critical inputs and assumptions used for the NPV and IRR calculations. The template represented the summary sheet for an elaborate discounted cash flow model. For example, the analysis of a new store included incremental cash flow projections for 60 years, over which time the model included a remodeling of the store every 10 years. Exhibit 6 provides an example of a dashboard with a detailed explanation of the "Store Sensitivities section. The example dashboard shows that incremental sales group. The R&P group used demographic and other data to make site-specific forecasts. Incremental sales were computed as total sales less those cannibalized from other Target stores. The resulting NPV and IRR metrics were divided between value created by store sales and credit card activity. NPV calculations used a 9.0% discount rate for cash flows related to the store cash flows and a 4.0% discount rate for credit card cash flows. The different discount rates were chosen to represent the different costs of capital for funding store operations versus funding credit card receivables. The dashboards also presented a variety of demographic information, investment-cost details and sensitivity analyses. An important sensitivity feature was the comparison of the project's NPV and IRR to the prototype. For example, the P04 store had an NPV of about $10 million and an IRR of 13%. The sensitivity calculations answered the question of how much a certain cost or revenue item needed to change in order for the project to achieve the same NPV or IRR that would be experienced for the typical P04 or SuperTarget store. The November Meeting Of the 10 projects under consideration for the November CEC meeting, Doug Scovanner recognized that five would be easily accepted, but that the remaining five CPRs were likely to be difficult choices for the committee. These projects included four new store openings (Gopher Place, Whalen Court, The Barn, and Goldie's Square) and one remodeling of an existing store into a Super Target format (Stadium Remodel). Exhibit 7 contains a summary of the five projects, and Exhibit 8 contains the CPR dashboards for the individual projects. As was normally the case, all five of the CPRs had positive NPVs, but Scovanner wondered if the projected NPVs were high enough to justify the required investment. Further, with stiff competition from other large retailers looking to get footholds in major growth areas, how much consideration should be given to short-term versus long-term sales opportunities? For example, Whalen Court represented a massive investment with relatively uncertain sales returns. Should Scovanner take the stance that the CEC should worry less about Whalen Court's uncertain sales and focus more on the project as a means to increase Target's brand awareness in an area with dense foot traffic and high-fashion appeal? Goldie's Square represented a more typical investment level of $24 million for a SuperTarget. The NPV, however, was small at $317,000, well below the expected NPV of a SuperTarget prototype, and would be negative without the value contribution of credit card sales. As CFO, Scovanner was also aware that Target shareholders had experienced a lackluster year in 2006, given that Target's stock price had remained essentially flat Exhibit 9). Stock analysts were generally pleased with Target's stated growth policy and were looking for decisions from management regarding investments that were consistent with the company maintaining its growth trajectory. In that regard, Scovanner recognized that each of the projects represented a growth opportunity for Target. The question, however, was whether capital was better spent on one project or another to create the most value and the most growth for Target shareholders. Thus Scovanner believed that he needed to rank the five projects in order to be able to recommend which ones to keep and which ones to reject during the CEC meeting the next day. Exhibit 7 Target Corporation Economic Analysis Summary of Project Proposals Trade Area IRR Gopher Place Whalen Court The Barn Goldie's Square Stadium Remodel Investment (5000) $23,000 $119,300 $13,000 $23,900 $17,000 Net Present Value 10% Sales Decline Base Case Impact on NPV (5000) NPV (5000) $16,800 (34,722) $25,900 ($16,611) $20,500 (34,066) $300 (34,073) $15,700 (37,854) 12.3% 9.8% 16.4% 8.1% 10.8% Population 70,000 632,000 151,000 222,000 N/A Population Increase 2000-2005 27% 3% 3% 16% N/A Median Income $56,400 $48,500 $38,200 $56,000 $65,931 % Adults 4+ yrs. college 12% 45% 17% 24% 42% NPV is compated using 9.0% as discount rate for store cash flores and 4.0% forcrediscard cash fous. "Track ana is the geographical area from which 70% of store sales will be realized. Gopher Place was a request for $23.0 million to build a PO4 store scheduled to open in October 2007. The prototype NPV would be achieved with sales of 5.3% below the R&P forecast level. This market was considered an important one, with five existing stores already in the area. Wal-Mart was expected to add two new supercenters in response to favorable population growth in the trade area, which was considered to have a very favorable median household income and growth rate. Because of the high density of Target stores, nearly 19% of sales included in the forecasts were expected to come from existing Target stores. Whalen Court was a request for $119.3 million to build a unique single-level store scheduled to open in October 2008. The prototype NPV could be achieved with sales of 1.9% above the R&P forecast level. Although Target currently operated 45 stores in this market, the Whalen Court market represented a rare opportunity for Target to enter the urban center of a major metropolitan area. Unlike other areas, this opportunity provided Target with major brand visibility and essentially free advertising for all passers by. Considering Target's larger advertising budget, the request for more than $100 million of capital investment could be balanced against the brand awareness benefits it would bring. Further, this opportunity was only available for a limited time. Unlike the majority of Target stores, this store would have to be leased. Thus if it was not approved at the November meeting, the property would surely be leased by another retailer. Exhibit 7 (continued) The Barn was a request for $13.0 million to build a PO4 store scheduled to open in March 2007. The prototype NPV was achievable with sales of 18.1% below the R&P forecast level. This project was being resubmitted after initial development efforts failed because of a disagreement with the developer. This small rural area was an extreme contrast to Whalen Court. The small initial investment allowed for a large retum on investment even if sales growth turned out to be less than expected. This investment represented a new market for Target as the two nearest Target stores were 80 and 90 miles away. Goldie's Square was a request for $23.9 million to build a SuperTarget store scheduled to open in October 2007. The prototype NPV required sales 45.1% above the R&P forecast level. This area was considered a key strategic anchor for many retailers. The Goldie's Square center included Bed Bath & Beyond, JCPenney, Circuit City, and Borders. Target currently operated 12 stores in the area and was expected to have 24 eventually. Despite the relatively weak NPV figures, this was a hotly contested area with an affluent and fast growing population, which could afford good brand awareness should the growth materialize. Stadium Remodel was a request for $17.0 million to remodel a Super Target store opening March 2007. As a remodel, there was no prototype NPV for comparison. The recent sales decline and deteriorating facilities at this location could lead to tarnishing the brand image. This trade area had supported Target stores since 1972 and had already been remodeled twice previously. The $17 million investment would certainly give a lift to the lagging sales. Source: Target Corporation, sed with permission Exhibit 8 Target Corporation Individual Capital Project Request Dashboards TARGET CAPITAL PROJECT REQUEST Capital Expenditure Committee: November 2006 Option Project "Gopher Place" Market Gopherve Open Cetober 2007 Prototype: PO 30 MSP Size: 127.000 Developer: Henderson Associates Owne: On Address: SWC of Hudson and ER Anchors Freestanding NPV & Investment INVESTMENT DETAIL Land ACT 9270 Sidework Pro Minum PSF S752 RE Tar Per Carp To $130 Closing 11/2008 BAP) Proto SO Garden Center Seismi BULUS LUSIVS. PATUITE Bugeographie Proto Update 11171 Market Conditions Government Fees Prot Architectural Prototype 405 Technical Sourcing Best PVN Procurement Art Sigu SALES Cortingency Total Vatance ( (55.CORT INCENTIVE SUMMARY None obble Vender Fee Legal Fee DEMOGRAPHICS Characteristics Trade Area -Wes 2005 Population 1000 10 2000-2005 Growth 15701 2070 Median Hicone 356 39,400 HH +850 000 000 97 11 Adults do Y Coleg 2305 158 115 2004 COMPETITION 2008 COMMENTS Target currently operates 5 stores in the market Transfer Sales T-15268 miles E) derives 19% of sales from the proposed 245 trade area -nar Colcs asume Wal-Mart cloccatore to upgroenter in 2007 Walmart adds an additional Supercenter in Badgende in 2008 15.30 VALUE FINANCIAL SUMMARY TOTAL RAP SALES Protest P. Proto 1st year 2005 Equivalent 528.000 $2.745 250 5th year 2006 Equivalent 335.100 56686 Sales maturity 135 0.00 15.0 NCREMENTAL RAP SALES Project API Prote 1st year 2005 Equivalent $22.000 5455) 100 Sth year 2005 Equiler $35100 $5660 Sales may 154 0.27 00 NVESTMENT Project BP Proto Land $264 Stwork a 164 56.300 Building 40 1.221 Total Net investment 2016 30 IRR NPV BAP. Proto Store 12.7% $13.201 52.493 8.1984 5544 -- TOTAL 12.3% 516 TES 53038 STORE SENSITIVITIES HURELE ADJUSTMENT NPV IRR 15 Sales Gross Main 0.29 Construction Building & Stwork) 100 (5751) Mars met RISK OPPORTUNITY 10% sales decline 154.722) 1 pp CM decine 10% Const. cost increase 10.6) Market marginwage sale, etc. (1.5) 10% sales increase 54021 12 VARANCE TO PROTOTYPE Land 5.287 0.1 Norland Investment 154.741) (26) Sales $8.331 1.9 Real Estate Tax $815 0.0 PEL SUMMARY Siap FRIT IMPACT Proiect BPI Proto Thu Open Y (556 5th $4452 $836 Cinder 28 STARE 6.5 SF Cap OWS Exhibit 8 (continued) O TARGET CAPITAL PROJECT REQUEST Capital Expenditure Committee: November 2006 March 2007 126.842 Own FINANCIAL SUMMARY TOTAL ROP SALES 1st year 2005 Equhalent $24,000 5th year 2005 Equivalent $30,500 Sales maturity $2,043 $2.729 0.01 Fed Cust 5136 $62 300 250 200 150 190 Project: "The Barn" Market: Moose Land Open: Prototype : P04.383 MSP Size: Developer: Hubert Ventures Own/Lease: Address: NWO of Badger and Wolverine Anchors: Lowe's INVESTMENT DETAIL NPV & Investment La Aures: 11.40 31 PSF S002 RE Tax-Per Corp Tax Closing 4/2006 BAP) Proto Options L3 Enhanced Risk Security BUILDING COST VS. PROTOTYPE Sugeographic Proto Update Market Conditions Goverment Fees Architectural Project Prototype Technical Sourcing Procurement instant NPV-10. Siis NE Fees Signs SALES Contingency Total Variance INCENTIVE SUMMARY None Available Vendor Fee Legal Fee 50 $523 (221 (410) 0 (95) (122) (91) (75) 9 75 5378) 33 31 INVESTMENT Project BAP) Proto Land $10 $3,350 Sitework 2.300 299 Subtotal $2,313 $3,680 Building 9,706 (378) Other 990 120 Total Net Imestment $13,017 $3,423 VALUE IRR NPV BIP) Proto Store 17.5% $17,406 $7,326 Credit 8.2% 3.121 $279 TOTAL 16.0% 520 527 $7 STORE SENSITIVITIES HURDLE ADJUSTMENT NPV IRR Sales (18.1%) (23.2%) Gross Margin (235) (304) Construction (Building & Sitework) $8.900 56,973 30 23 13 17 15 DEMOGRAPHICS Characteristics MSA Trade Area ZIMA 2006 Population (0005 135 11 2000-2005 Growth 3.09 Median HH Income $38,600 $38.200 $47.300 HH$50 000 0005) 20 22 Adults 4+ Yes College, 2005 16% 3496 COMMENTS Target is entering a new smal market. The nearest Target stores are 80 miles NE, 80 miles S, 90 miles NW. - R&P Sales assume Target is part of a major tal development of BOOKS - See attached Resubmission Summary 2006 COMPETITION 2008 13 234 RISK OPPORTUNITY 10% sales decline 1 pp GM decline 10% SLEVA Market margin, wage rate, etc. 10% sales increase (34.068) (53,111) (8580) (52,999) $4,096 (19) (15) (1.0) 10 1.9 SIS VARIANCE TO PROTOTYPE Land Non-Land Investment Sales Real Estate Tax $3,675 (5570) $3,603 $617 32 10.3) 1.4 02 5.7 SF Cup 6.4 SF Cap OWO Sense . Exhibit 8 (continued) Project: "Whalen Court" Market Buldback Open: October 2008 Prototype: Unique Single Level Size: 173 585 Developer: Sawicky and Co. Own/Lease: Lease Address: NWQ of Gopher and High Investment Blvd Anchors: Home Depot, Best Buy NPV & Investment INVESTMENT DETAIL Lease Type Buting lane Sitwork NA Rant Ray-13. RC Tax sasa Closing 10/2006 BHP) Proto (860) Options L4: Unique Risk Security District Office, 13 st Exp. Stock 2nd L Stoe BUILDING COSTVS. PROTOTYPE Subgeographic (51,200) Proto Update (124) Market Conditions Government Fees 0 Architectural 0 Project Prototype Technical Sourcing (7.521) BERRY Procurement 2,229) Ne fe Signs (18) SALES Contingency 3.000 Total Variance $15.00 INCENTIVE SUMMARY Vendor Fee $ Legal Fee 50 O TARGET CAPITAL PROJECT REQUEST Capital Expenditure Committee: November 2006 FINANCIAL SUMMARY TOTAL R&P SALES Project BIP) Proto fet year 2005 Equhalant 596.000 $63, 196 5th year 2005 Equivalent $111.800 $69,031 1200 Sales maturity 1.30 0.04 1000+ 80.0 INCREMENTAL RAP SALES Project BYP) Proto 1st year 2005 Equivalent 579.600 545,785 5th year 2005 Equivalent $111.800 S69,031 Sales maturty 0.14 00 INVESTMENT Project HP) Proto Lease $37,309 (878,655) work 2.790 Subtotal SBT 309 (75,050) Building 29 434 (15,128) 135 Other 2.520 93 115 Total Net mestment 3119263.00 VALUE IRR NPV BYP) Proto Store 75 9.9% $14.225 153,174) Crede 8.2% $11.650 55 TOTAL 3.8% $25.875 $3,899 HUOLE ADJUSTMENT STORE SENSITIVITIES NEY IRA Sales 1.9% 31.15 Gross Margin 0.28 458 Construction (Building & Stework) 54.289) (541,070) Full Transfer Impact 7.7% RISK OPPORTUNITY 10% sales decline ($16.611) (1.0) 1 pp OM decline ($11.494) (0.7) 10% Const cost increase (52.178) (0.1) Market marginwagte, et ($16.877) (1.1) 10% 310,647 10 VARIANCE TO PROTOTYPE Lease 1878,912) (15.1) Non Land Investment ($10,168) 7.9) Sales 390063 229 Real Estate Tax (5637 10.2) 0.0 PBL SUMMARY SF Cap EBIT IMPACT Project ByP Prote Thu Open Yr ($1,599) ($1,136) 5th Yr $14.034 S8.500 SS 57.164 15 DEMOGRAPHICS Characteristics MSA Trade Ares 2005 Population (0000 18,788 632 2000-2005 GIU 2.0% 3.09 Medan Income 557200 $48,500 HH$50.000000 3.750 143 % Adults 4+ Yrs. College. 2005 30% 45961 COMMENTS See attached for additional information -White Radius 1,248 2.09 $43,800 238 37% 2006 COMPETITION 2009 100 TARGET 0.5 SF Cap Exhibit 8 (continued) O TARGET CAPITAL PROJECT REQUEST Capital Expenditure Committee: November 2006 25.0 200 15.0 100 50 0.0 15.00 (10) 1494 FINANCIAL SUMMARY TOTAL REP SALES Project BIP Proto 1st year 2006 834,000 10,304) 5th year 2005 Equivalent $42.000 $14,006) Sales maturity 1.24 10.00) INCREMENTAL R&P SALES Project BIP) Proto 1st year 2005 Equivalent $25.900 (518,404) 5th year 2005 Equivalent $42.000 $14,006) Sales maturity 0.36 INVESTMENT Project BIP) Proto Land $3,615 $1,385 Otwork 2,090 Subtotal 87,310 8960 Building (313) Other 1,660 48 Total Netrestment 327939 5894 VALUE IRR NPV BYP) Proto Store 8.1% ($3,319) (18,222) 8.1% $26.95 51.286 TOTAL 8.1% 5317 ($19,516 STORE SENSITIVITIES MUROLE ADJUSTMENT NPV IRR Sales 45.1% 472 Gross Margin 4.64 4.91 Construction (Building & Sitework) ($22,167) ($14,576) Ful Transfer Impact 62.5% 63.1% RISK OPPORTUNITY 10% sales decline (84,073) 1 pp GM decline (3.929) 10% Const. cost increase (51,470) (0.3) Market margin, wage rate ato 56,050 1.6 10% sales increase $4,000 1.1 VARIANCE TO PROTOTYPE Land $1,501 0.3 Non-Land Investment (5581) (0.1) (516,455) Real Estate Tax ($2,682) (0.7) P&L SUMMARY EBIT IMPACT Project Proto Thu Open Yr ($1.921) $654) 5th Y $2,951 (52,343) 60 55 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 Project: "Goldie's Square" Market: Gold County Open: October 2007 Prototype SUPDAM Size: 173,770 Developer: Barsky Enterprises Own/Lease: Own Address: Swo of Ocean and Beach Anchors: JC Penney. Circut Cay Borders. Bed Bath & Beyond, Ross INVESTMENT DETAIL NPV & Investment Land Acres 11.60 Siswork Fixed Cost PRE 67.10 RS Tax Aer Carp Tax 8630 Closing 8/2006 BAP) Proto (5269) Options BUILDING COST VS. PROTOTYPE Sulgeographie 5823 Proto Update (153) Market Conditions 545 Goviment Fees 0 Pro Prototype Architectural (459) Technical Sourcing (799) Procurement Bent NPV A. Selle (170) ACT (71) Signs 50 SALES Contingency 25) Total Variance 3313) INCENTIVE SUMMARY None Available Vendor Fee 50 Legal Fee 50 DEMOGRAPHICS Characteristics MSA Trade Area 3.Wire Radius 2005 Population (00032 1.415 222 2000-2005 Gruwih 130 16.00 40% Median HH Income $56,100 $56,000 $50,000 HH +$50,0000005) 291 12 Adults 4+ Yos. College. 2006 36% 24% 26% 2006 COMPETITION 2008 COMMENTS Target currently operates 12 stores in the market. Total Target buldout for this market is currently estimated at 24 of which are active near term opportunities. 205 Build out will include 12 Super Target units, 50% of the total - Transfer Sales: 25% from a store located 21 miles NE 4% from a store located 7 miles N 25% of sales from a store 4 miles away 14% General Merchandise Hardlines CM: 82/18 - Alematies to this balduck senang > Relo: T-483 closes when Goldie's Square opens: Total NPV:58MTotal IRR 9.34 >T-683 closes 1 yr after Goldie's Square opens: Total NPV: $3.9M; Total RR: 8.9% >T-68 closes 2 yrs ater Goldies Square opens: Total NPV: 53.6M; Total IRR 8.99 TARGET STARGET 3.0 OSC SF Cap DISC 2.5 SFICA Exhibit 8 (continued) TARGET CAPITAL PROJECT REQUEST Capital Expenditure Committee: November 2006 NA Project Market Boardwalk Scope: Interior Remodel Prototype Before & After SUP 1.1/SO4 Expansion Availability: No Se Contained Offsite Whise/Dist Office: NA "Stadium Remodel Remodel Cycle: Cycle 3 2007 Last Remodel: Own Lease: Own Sides Before & After 484655 POG Length: 24/25 PROJECT DETAIL 5100186 Bldg 343 Root. 5381 Other) 120 19621 SQUARE FOOTAGE NPV & Investment Write of RETax Pur Cory Tax BAP) Proto 350 300 250 200 100 50 Status Que Proposed Town Prototype New Best Pero FINANCIAL SUMMARY TOTAL REP SALES Projet BIP Prote styw 2006 giunt 04.000 10.077 Sth year 2005 Equivalent $84.000 $7.940 Sales maturity 1.00 (0.28) INCREMENTAL RAP SALES Project 1st year 2005 Equivalent $0 300 Sth year 2005 Equivalent 50 300 Sales many 1.00 INVESTMENT Project P) Proto Land $0 $5,000 Dilework 1.179 2007 Subtotal $1,173 $7,087 Building 12 411 2.245 3.271 (1.618 Total Net imestment 516855 57724 IRR NPV Store 12.5% $14.911 Credit 5828 TOTAL 10,0 $15.739 STORE SENSITIVITIES PURIAE ALUSTMENT NPV INS Sales Gross Margin Remodel Construction (Building & Stework) SALES Other 65 55 VALUE 4 45 o Total Sales Stock Support Original 203.300 153019 35.245 15,000 Adonal Sq (10.544) 12.870 12.3261 Total Sq Ft Ater Remodel 142,475 48. 115 12/10 OUP Prototype 177,370 130010 27.500 19,200 BAP) Prototype 25,824 5.850 20.615 1550) BIP Guides FY 20 615 DEMOGRAPHICS Characteristics MSA Trade Area 3-M Me Radius 2005 Population 000 006 113 2000-2005 Growth 5.0% 18.09 15.04 Median HH Income $50,774 566.901 564, $50.00051 156 20 21 Aduts 4+ Yis. College, 2005 284 LUMMENIS -Entered market in 1972. Currently operate stores in this market. - A success store a strong long-term location sering an att bumily-oriented trade area - 2008 YTD Sales Trend 0.9% Post-remodel sales assume a 17% sales litt over R&P base case sales. Base case sales assume a 10% impact from bulduck (3.3 miles October 2007 the store is also in the process of being impacted by Park Place South - Curent Value of T-0530 $18.8M R&P base case sales Prototypical Interior Remodelin 2007: Tax benefit of depreciable property write-oft $0.4M; Rank: 783 of 1395 General Merchandise Hardines Mix: 88/52based on T-0530 historical trend Options New Entrance System Halocate Pharmacy, Helocate Electrical Room Scope Retigeration Replacement, 4 Phases of Grocery Staging, Flooring Replacement, Roof Replacement, Temp Pharmacy, New Food Avenue, New Starbucks, New Optical New Portrait Studio, New Signage ONT RISK OPPORTUNTY 10% sales decline pp GM decline 10% Const. cost increase Market marginwage rate, etc 10% alene 38 457 (5910) ($11,317) 8.216 (1.3) (1,5) 10.31 27 15 P&L SUMMARY EBIT PACY Proin UP Proto Thru Open Yr (56.103 (54.312) Sth Y $1.272 (54,025) Souxe Target Corporation, used with permission
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


