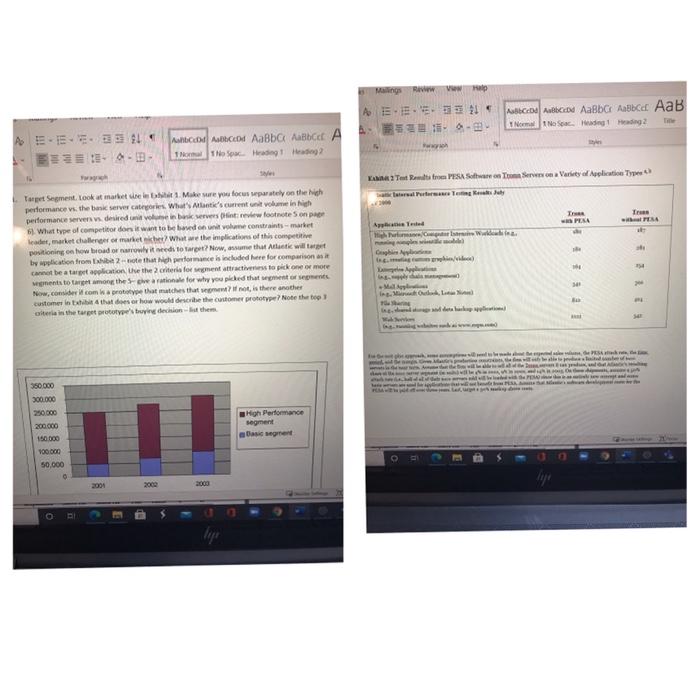
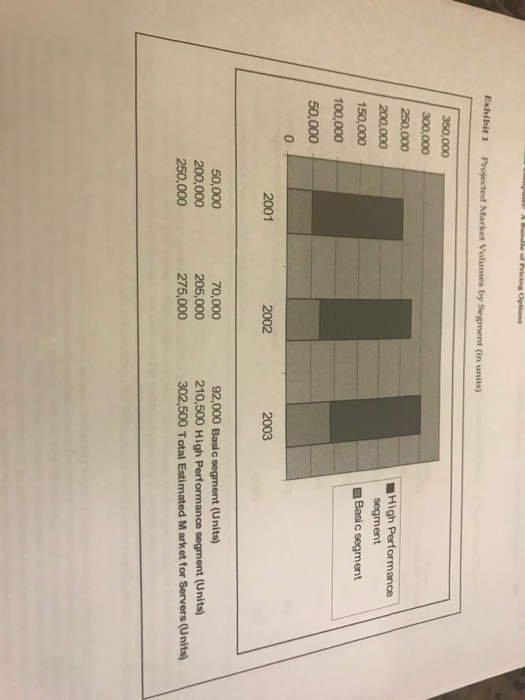
Malings VW Help A ... 1 tec ABCD Aabba Abbce A. 1. - 1 Normal 1 No Spec. Heading Heading 2 wich c I Nomad No Spac. Heading 1 Heading 2 Title Por Fak? Test Rewalts from PESA Seca Tron Servers ce Variety of Application Types lateral Performance Trg Res July Trus PESA 18 Hilor. Com Wwe. Target Segment. Look at market sie in bit 1. Make sure you focus separately on the high performance vs. the basic server categories. What's Atlantie's current unit volume in high performance servers vs. desired unit volume in bas verslind review footnotes on page 6) What type of competitor does it want to be based on unit volume constraints - market leader, market challenger or market het What are the implications of this competitive positioning on how broad or owly it needs to target? Now, assume that Atlantic will target by application from the note that high performance is included here for comparison as it cannot be a target application. Use the criteria for segment attractiveness to pick one or more wegments to target among the 5-gwea rationale for why you picked that segment or segments Now, consideri.com is a prototype that matches that woment? If not, is there another customer in Exhibit that does or how would describe the customer prototype Note the top 3 criteria in the target prototype's buying decision-them. Cengi 354 341 Map no. MON rober 350.000 300.000 250.000 200.000 150 000 1 High Performance segment Basic segment 100.000 50,000 lipo 2005 2000 2000 lige Exhibit 2 Test Results from PESA Software on Tronn Servers on a variety of Application Types Ab Atlantic Internal Performance Testing Results July 22 2000 Tronn with PESA 180 Tronn without PESA 187 280 281 264 254 Application Tested High Performance/Computer Intensive Workloads (e.g., running complex scientific models) Graphics Applications (e.g, creating custom graphics/videos) Enterprise Applications (e.g., supply chain management) e-Mail Applications (e.g., Microsoft Outlook, Lotus Notes) File Sharing (e.g., shared storage and data backup applications) Web Services (e.g., running websites such as www.espn.com) 341 300 812 404 2222 542 ding Options Exhibit 1 Projected Market Volumes by Segment (in units) 350,000 300,000 250.000 High Performance segment Basic segment 200.000 150,000 100,000 50,000 0 2001 2002 2003 50,000 200,000 250,000 70,000 205,000 275,000 92,000 Basic segment (Units) 210,500 High Performance segment (Units) 302,500 Total Estimated Market for Servers (Units) this customer. This would require him to not only convey the pricing strategy that would optimize value capture for Atlantic, but also describe any implementation inues that could possibly aris. Por example, he recalled that the industry norm was to give away software tools The were to recommend one of the other alternatives, he'd better be ready to answer how he could break from what was already a well-established tradition in the industry. In addition, he knew that he would have to think more broadly about the top-line revenue implications from each of the four alternative pricing strategies. He knew that he could undertake a quick "back of the envelope" calculation utilizing the total estimated sales for the Atlantic Bundle over the upcoming three years to effectively convey the gains from his recommended pricing strategy 4 Please see "Customer Value Propositions in Business Markets" appearing in the March (2006) issue of Harvard Business Review. In that article, Anderson, Narus, and van Rossum outline the importance of being able to demonstrate and articulate the savings to the customer from a vendor's offering and provide a means by which to do so. They offer that a value word equation "expresses in words and simple mathematical operators (for example, + and ) how to mess the differences in functionality or performance between a supplier's offering and the next best alternative and how to convert those differences into dollars." (p. 96) For the cost-plus approach, some assumptions will need to be made about the expected sales volume, the PESA attach rate, the time period, and the margin. Given Atlantic's production constraints, the firm will only be able to produce a limited number of basic servers in the near term. Assume that the firm will be able to sell all of the Tronn servers it can produce, and that Atlantic's resulting share of the basic server segment in units) will be 4% in 2001, 9% in 2002, and 14% in 2003. On these shipments, assume a 50% attach rate (.e., half of all of their basic servers sold will be loaded with the PESA) since this is an entirely new concept and some basic servers are used for applications that will not benefit from PESA. Assume that Atlantic's software development costs for the PESA will be paid off over three years. Last, target a 30% markup above costs. 6 Value-in-use pricing is a method of setting prices in which an attempt is made to capture a portion of what a customer WOC save by buying a firm's product. For this case, please assume a 50-50 sharing of the savings gain with the customer. A please base your calculations on one year of savings (e.g., annual electricity savings equal $250 (Exhibit 3)). Although average life of an Atlantic basic server is estimated to be three years, please use the conservative per annum estimate. BRIEFCASES HARVARD BUSINESS SC 6 Your Case Assignment: 1. Target Segment. Look at market size in Exhibit 1. Make sure you focus separately on the high performance vs. the basic server categories. What's Atlantic's current unit volume in high performance servers vs. desired unit volume in basic servers (Hint: review footnote 5 on page 6). What type of competitor does it want to be based on unit volume constraints - market leader, market challenger or market nicher? What are the implications of this competitive positioning on how broad or narrowly it needs to target? Now, assume that Atlantic will target by application from Exhibit 2 - note that high performance is included here for comparison as it cannot be a target application. Use the 2 criteria for segment attractiveness to pick one or more segments to target among the 5- give a rationale for why you picked that segment or segments. Now, consider if com is a prototype that matches that segment? If not, is there another customer in Exhibit 4 that does or how would describe the customer prototype? Note the top 3 criteria in the target prototype's buying decision - list them. Malings VW Help A ... 1 tec ABCD Aabba Abbce A. 1. - 1 Normal 1 No Spec. Heading Heading 2 wich c I Nomad No Spac. Heading 1 Heading 2 Title Por Fak? Test Rewalts from PESA Seca Tron Servers ce Variety of Application Types lateral Performance Trg Res July Trus PESA 18 Hilor. Com Wwe. Target Segment. Look at market sie in bit 1. Make sure you focus separately on the high performance vs. the basic server categories. What's Atlantie's current unit volume in high performance servers vs. desired unit volume in bas verslind review footnotes on page 6) What type of competitor does it want to be based on unit volume constraints - market leader, market challenger or market het What are the implications of this competitive positioning on how broad or owly it needs to target? Now, assume that Atlantic will target by application from the note that high performance is included here for comparison as it cannot be a target application. Use the criteria for segment attractiveness to pick one or more wegments to target among the 5-gwea rationale for why you picked that segment or segments Now, consideri.com is a prototype that matches that woment? If not, is there another customer in Exhibit that does or how would describe the customer prototype Note the top 3 criteria in the target prototype's buying decision-them. Cengi 354 341 Map no. MON rober 350.000 300.000 250.000 200.000 150 000 1 High Performance segment Basic segment 100.000 50,000 lipo 2005 2000 2000 lige Exhibit 2 Test Results from PESA Software on Tronn Servers on a variety of Application Types Ab Atlantic Internal Performance Testing Results July 22 2000 Tronn with PESA 180 Tronn without PESA 187 280 281 264 254 Application Tested High Performance/Computer Intensive Workloads (e.g., running complex scientific models) Graphics Applications (e.g, creating custom graphics/videos) Enterprise Applications (e.g., supply chain management) e-Mail Applications (e.g., Microsoft Outlook, Lotus Notes) File Sharing (e.g., shared storage and data backup applications) Web Services (e.g., running websites such as www.espn.com) 341 300 812 404 2222 542 ding Options Exhibit 1 Projected Market Volumes by Segment (in units) 350,000 300,000 250.000 High Performance segment Basic segment 200.000 150,000 100,000 50,000 0 2001 2002 2003 50,000 200,000 250,000 70,000 205,000 275,000 92,000 Basic segment (Units) 210,500 High Performance segment (Units) 302,500 Total Estimated Market for Servers (Units) this customer. This would require him to not only convey the pricing strategy that would optimize value capture for Atlantic, but also describe any implementation inues that could possibly aris. Por example, he recalled that the industry norm was to give away software tools The were to recommend one of the other alternatives, he'd better be ready to answer how he could break from what was already a well-established tradition in the industry. In addition, he knew that he would have to think more broadly about the top-line revenue implications from each of the four alternative pricing strategies. He knew that he could undertake a quick "back of the envelope" calculation utilizing the total estimated sales for the Atlantic Bundle over the upcoming three years to effectively convey the gains from his recommended pricing strategy 4 Please see "Customer Value Propositions in Business Markets" appearing in the March (2006) issue of Harvard Business Review. In that article, Anderson, Narus, and van Rossum outline the importance of being able to demonstrate and articulate the savings to the customer from a vendor's offering and provide a means by which to do so. They offer that a value word equation "expresses in words and simple mathematical operators (for example, + and ) how to mess the differences in functionality or performance between a supplier's offering and the next best alternative and how to convert those differences into dollars." (p. 96) For the cost-plus approach, some assumptions will need to be made about the expected sales volume, the PESA attach rate, the time period, and the margin. Given Atlantic's production constraints, the firm will only be able to produce a limited number of basic servers in the near term. Assume that the firm will be able to sell all of the Tronn servers it can produce, and that Atlantic's resulting share of the basic server segment in units) will be 4% in 2001, 9% in 2002, and 14% in 2003. On these shipments, assume a 50% attach rate (.e., half of all of their basic servers sold will be loaded with the PESA) since this is an entirely new concept and some basic servers are used for applications that will not benefit from PESA. Assume that Atlantic's software development costs for the PESA will be paid off over three years. Last, target a 30% markup above costs. 6 Value-in-use pricing is a method of setting prices in which an attempt is made to capture a portion of what a customer WOC save by buying a firm's product. For this case, please assume a 50-50 sharing of the savings gain with the customer. A please base your calculations on one year of savings (e.g., annual electricity savings equal $250 (Exhibit 3)). Although average life of an Atlantic basic server is estimated to be three years, please use the conservative per annum estimate. BRIEFCASES HARVARD BUSINESS SC 6 Your Case Assignment: 1. Target Segment. Look at market size in Exhibit 1. Make sure you focus separately on the high performance vs. the basic server categories. What's Atlantic's current unit volume in high performance servers vs. desired unit volume in basic servers (Hint: review footnote 5 on page 6). What type of competitor does it want to be based on unit volume constraints - market leader, market challenger or market nicher? What are the implications of this competitive positioning on how broad or narrowly it needs to target? Now, assume that Atlantic will target by application from Exhibit 2 - note that high performance is included here for comparison as it cannot be a target application. Use the 2 criteria for segment attractiveness to pick one or more segments to target among the 5- give a rationale for why you picked that segment or segments. Now, consider if com is a prototype that matches that segment? If not, is there another customer in Exhibit 4 that does or how would describe the customer prototype? Note the top 3 criteria in the target prototype's buying decision - list them