Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
manufacturing plant uses paints in two coating operation units. These units produce fumes containing VOCs. As part of the air pollution control system used by
manufacturing plant uses paints in two coating operation units. These units produce fumes containing VOCs.
As part of the air pollution control system used by this plant, the two streams A and B, are first mixed before
passing the combined stream into the air pollution control device. The characteristics of the two gaseous
waste streams are as follows: Stream A has a pressure of 725 mm Hg, a temperature of 30oC and flows at 5.0
acm/min carrying 2.0 mg/acm of VOC-a. Stream B has a pressure of 770 mmHg, a temperature of 80oC and
flows at 7.5 acm/min carrying 3.0 mg/acm of VOC-b. The combined flow from the two units is then diluted in a
chamber with a flow of 1 std-m3/min of air to lower the concentration of the VOCs before conveying the gas to
a VOC incinerator unit. All gaseous streams have thermophysical properties similar to air
1. Draw a diagram representing the mass balance around the mixing unit and around the dilution chamber.
2. Find the volumetric flow rate of the mixed stream A+B, in standard-cm/min.
3. Find the mass flow rate of the mixed stream A+B, in lb/min.
4. Find the volumetric flow rate of the final diluted stream in standard-cm/min.
5. Find the mass flow rate of the final diluted stream, in lb/min.
6. After the dilution, the gas stream is incinerated at 1200oC. Assuming zero heat losses and all enthalpy
transferred from fuel to gas, what is the necessary heat input in Btu/lb?
use these tables
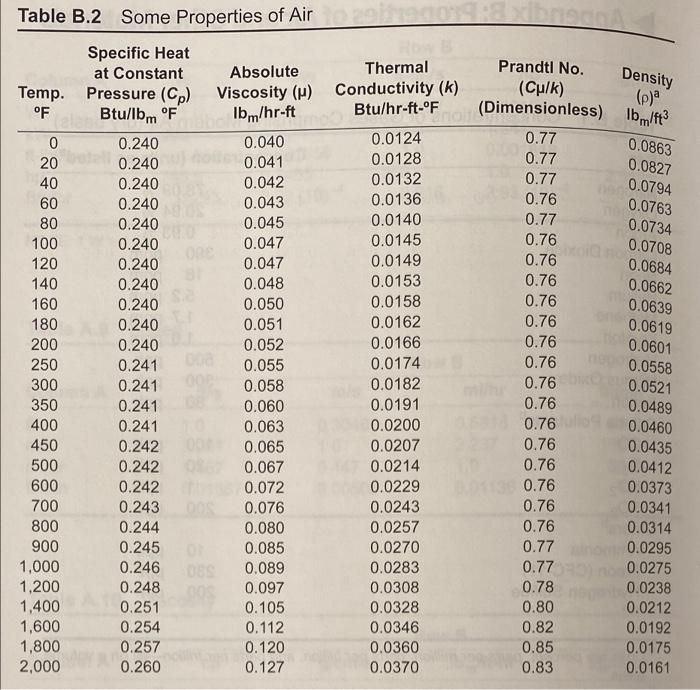
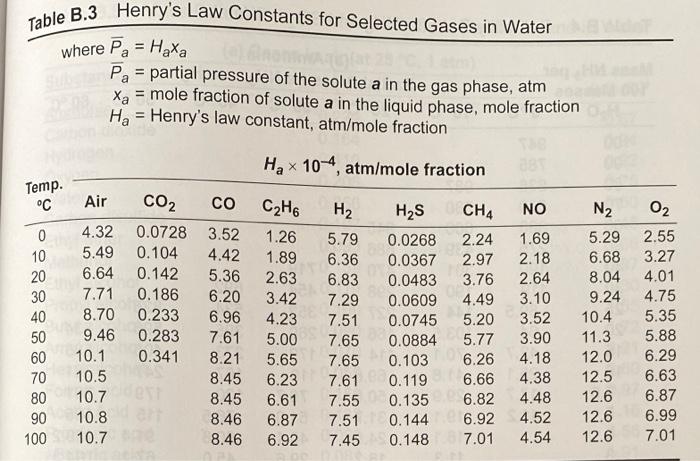
use table b2 and 7 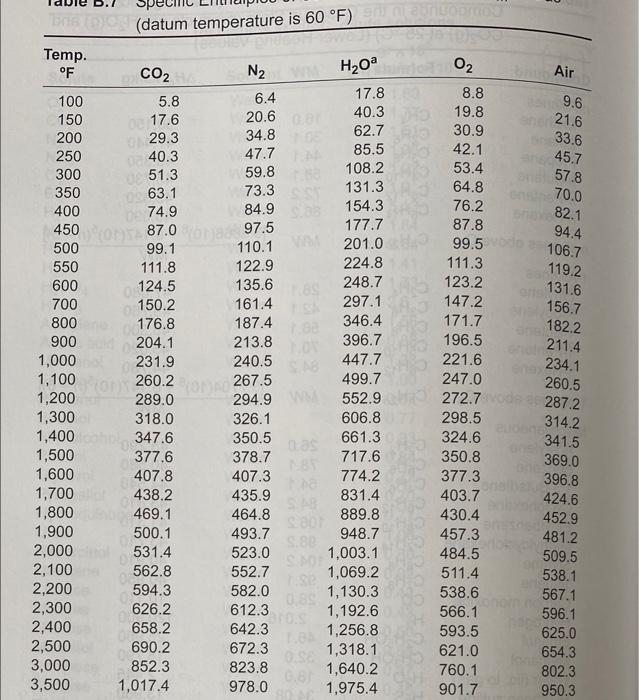

Density Thermal Conductivity (k) Btu/hr-ft-OF (p) OF Table B.2 Some Properties of Air Specific Heat at Constant Absolute Temp. Pressure (Cp) Viscosity (H) Btu/bm OF Ibm/hr-ft 0 0.240 0.040 20 0.240 0.041 40 0.240 0.042 60 0.240 0.043 80 0.240 0.045 100 0.240 0.047 120 0.240 0.047 140 0.240 0.048 160 0.240 0.050 180 0.240 0.051 200 0.240 0.052 250 0.241 0.055 300 0.241 0.058 350 0.241 0.060 400 0.241 0.063 450 0.242 0.065 500 0.242 0.067 600 0.242 0.072 700 0.243 0.076 800 0.244 0.080 900 0.245 0.085 1,000 0.246 0.089 1,200 0.248 0.097 1,400 0.251 0.105 1,600 0.254 0.112 1,800 0.257 0.120 2,000 0.260 0.127 0.0863 0.0827 0.0794 0.0763 0.0734 0.0708 0.0684 0.0662 0.0639 0.0619 0.0601 0.0124 0.0128 0.0132 0.0136 0.0140 0.0145 0.0149 0.0153 0.0158 0.0162 0.0166 0.0174 0.0182 0.0191 0.0200 0.0207 0.0214 0.0229 0.0243 0.0257 0.0270 0.0283 0.0308 0.0328 0.0346 0.0360 0.0370 Prandtl No. (Culk) (Dimensionless) 1bm/ft3 0.77 0.77 0.77 0.76 0.77 0.76 0.76 0.76 0.76 0.76 0.76 0.76 0.0558 0.76 0.0521 0.76 0.0489 0.76 0.0460 0.76 0.0435 0.76 0.0412 0.76 0.0373 0.76 0.0341 0.76 0.0314 0.77 0.0295 0.77 0.0275 0.78 0.0238 0.80 0.0212 0.82 0.0192 0.85 0.0175 0.83 0.0161 Henry's Law Constants for Selected Gases in Water Table B.3 where Pa = Haxa Pa = partial pressure of the solute a in the gas phase, atm = mole fraction of solute a in the liquid phase, mole fraction Ha = Henry's law constant, atm/mole fraction Hax 10-4, atm/mole fraction - Temp. C CH4 NO Air CO2 CO CH6 0 4.32 0.0728 3.52 1.26 10 5.49 0.104 4.42 1.89 20 6.64 0.142 5.36 2.63 30 7.71 0.186 6.20 3.42 40 8.70 0.2336.96 4.23 50 9.46 0.283 7.61 5.00 60 10.1 0.341 8.21 5.65 70 10.5 8.45 6.23 80 10.7 8.45 6.61 90 10.8 8.46 6.87 10.7 8.46 6.92 H2 H2S 5.79 0.0268 6.36 0.0367 6.83 0.0483 7.29 0.0609 7.51 0.0745 7.65 0.0884 7.65 0.103 7.61 0.119 7.55 0.135 7.51 0.144 7.45 0.148 2.24 2.97 3.76 4.49 5.20 5.77 6.26 6.66 6.82 6.92 7.01 1.69 2.18 2.64 3.10 3.52 3.90 4.18 4.38 4.48 4.52 4.54 N O2 5.29 2.55 6.68 3.27 8.04 4.01 9.24 4.75 10.4 5.35 11.3 5.88 12.06.29 12.5 6.63 12.6 6.87 12.6 6.99 12.6 7.01 100 02 CO2 W H0 Air 20.6 17.6 29.3 40.3 51.3 63.1 BORDIC (datum temperature is 60 F) Temp. OF N2 100 6.4 17.8 5.8 150 40.3 62.7 200 34.8 250 47.7 85.5 300 59.8 108.2 350 73.3 131.3 400 74.9 84.9 154.3 450 97.5 177.7 87.0 500 99.1 110.1 201.0 550 111.8 122.9 224.8 600 124.5 135.6 248.7 700 150.2 161.4 297.1 800 176.8 187.4 346.4 900 204.1 213.8 396.7 1,000 231.9 240.5 447.7 1,100 260.2 267.5 499.7 1,200 289.0 294.9 552.9 1,300 318.0 326.1 606.8 1,400 347.6 350.5 661.3 DO 1,500 377.6 378.7 717.6 1,600 407.8 407.3 774.2 1,700 438.2 435.9 831.4 1,800 469.1 464.8 889.8 SD 1,900 500.1 493.7 948.7 3 2,000 531.4 523.0 1,003.1 2,100 S 562.8 552.7 1,069.2 2,200 594.3 582.0 03 1,130.3 2,300 626.2 612.3 1,192.6 2,400 658.2 642.3 1,256.8 2,500 690.2 672.3 1,318.1 3,000 852.3 823.8 1,640.2 3,500 1,017.4 978.0 1,975.4 8.8 19.8 30.9 42.1 53.4 64.8 76.2 87.8 99.5 111.3 123.2 147.2 171.7 196.5 221.6 247.0 272.7 298.5 324.6 350.8 377.3 403.7 430.4 457.3 484.5 511.4 538.6 566.1 593.5 621.0 760.1 901.7 9.6 21.6 33.6 45.7 57.8 70.0 82.1 94.4 106.7 119.2 131.6 156.7 182.2 211.4 234.1 260.5 2872 314.2 341.5 369.0 396.8 424.6 452.9 481.2 509.5 538.1 567.1 596.1 625.0 654.3 802.3 950.3 acm=actual cubic meter std-cm=std-mp=standard cubic meter (1 atm, 20C) 1 m3 = 35.3147 ft 1 lb = 453.592 g K = C + 273 TP2 V = V . P . Iz Density Thermal Conductivity (k) Btu/hr-ft-OF (p) OF Table B.2 Some Properties of Air Specific Heat at Constant Absolute Temp. Pressure (Cp) Viscosity (H) Btu/bm OF Ibm/hr-ft 0 0.240 0.040 20 0.240 0.041 40 0.240 0.042 60 0.240 0.043 80 0.240 0.045 100 0.240 0.047 120 0.240 0.047 140 0.240 0.048 160 0.240 0.050 180 0.240 0.051 200 0.240 0.052 250 0.241 0.055 300 0.241 0.058 350 0.241 0.060 400 0.241 0.063 450 0.242 0.065 500 0.242 0.067 600 0.242 0.072 700 0.243 0.076 800 0.244 0.080 900 0.245 0.085 1,000 0.246 0.089 1,200 0.248 0.097 1,400 0.251 0.105 1,600 0.254 0.112 1,800 0.257 0.120 2,000 0.260 0.127 0.0863 0.0827 0.0794 0.0763 0.0734 0.0708 0.0684 0.0662 0.0639 0.0619 0.0601 0.0124 0.0128 0.0132 0.0136 0.0140 0.0145 0.0149 0.0153 0.0158 0.0162 0.0166 0.0174 0.0182 0.0191 0.0200 0.0207 0.0214 0.0229 0.0243 0.0257 0.0270 0.0283 0.0308 0.0328 0.0346 0.0360 0.0370 Prandtl No. (Culk) (Dimensionless) 1bm/ft3 0.77 0.77 0.77 0.76 0.77 0.76 0.76 0.76 0.76 0.76 0.76 0.76 0.0558 0.76 0.0521 0.76 0.0489 0.76 0.0460 0.76 0.0435 0.76 0.0412 0.76 0.0373 0.76 0.0341 0.76 0.0314 0.77 0.0295 0.77 0.0275 0.78 0.0238 0.80 0.0212 0.82 0.0192 0.85 0.0175 0.83 0.0161 Henry's Law Constants for Selected Gases in Water Table B.3 where Pa = Haxa Pa = partial pressure of the solute a in the gas phase, atm = mole fraction of solute a in the liquid phase, mole fraction Ha = Henry's law constant, atm/mole fraction Hax 10-4, atm/mole fraction - Temp. C CH4 NO Air CO2 CO CH6 0 4.32 0.0728 3.52 1.26 10 5.49 0.104 4.42 1.89 20 6.64 0.142 5.36 2.63 30 7.71 0.186 6.20 3.42 40 8.70 0.2336.96 4.23 50 9.46 0.283 7.61 5.00 60 10.1 0.341 8.21 5.65 70 10.5 8.45 6.23 80 10.7 8.45 6.61 90 10.8 8.46 6.87 10.7 8.46 6.92 H2 H2S 5.79 0.0268 6.36 0.0367 6.83 0.0483 7.29 0.0609 7.51 0.0745 7.65 0.0884 7.65 0.103 7.61 0.119 7.55 0.135 7.51 0.144 7.45 0.148 2.24 2.97 3.76 4.49 5.20 5.77 6.26 6.66 6.82 6.92 7.01 1.69 2.18 2.64 3.10 3.52 3.90 4.18 4.38 4.48 4.52 4.54 N O2 5.29 2.55 6.68 3.27 8.04 4.01 9.24 4.75 10.4 5.35 11.3 5.88 12.06.29 12.5 6.63 12.6 6.87 12.6 6.99 12.6 7.01 100 02 CO2 W H0 Air 20.6 17.6 29.3 40.3 51.3 63.1 BORDIC (datum temperature is 60 F) Temp. OF N2 100 6.4 17.8 5.8 150 40.3 62.7 200 34.8 250 47.7 85.5 300 59.8 108.2 350 73.3 131.3 400 74.9 84.9 154.3 450 97.5 177.7 87.0 500 99.1 110.1 201.0 550 111.8 122.9 224.8 600 124.5 135.6 248.7 700 150.2 161.4 297.1 800 176.8 187.4 346.4 900 204.1 213.8 396.7 1,000 231.9 240.5 447.7 1,100 260.2 267.5 499.7 1,200 289.0 294.9 552.9 1,300 318.0 326.1 606.8 1,400 347.6 350.5 661.3 DO 1,500 377.6 378.7 717.6 1,600 407.8 407.3 774.2 1,700 438.2 435.9 831.4 1,800 469.1 464.8 889.8 SD 1,900 500.1 493.7 948.7 3 2,000 531.4 523.0 1,003.1 2,100 S 562.8 552.7 1,069.2 2,200 594.3 582.0 03 1,130.3 2,300 626.2 612.3 1,192.6 2,400 658.2 642.3 1,256.8 2,500 690.2 672.3 1,318.1 3,000 852.3 823.8 1,640.2 3,500 1,017.4 978.0 1,975.4 8.8 19.8 30.9 42.1 53.4 64.8 76.2 87.8 99.5 111.3 123.2 147.2 171.7 196.5 221.6 247.0 272.7 298.5 324.6 350.8 377.3 403.7 430.4 457.3 484.5 511.4 538.6 566.1 593.5 621.0 760.1 901.7 9.6 21.6 33.6 45.7 57.8 70.0 82.1 94.4 106.7 119.2 131.6 156.7 182.2 211.4 234.1 260.5 2872 314.2 341.5 369.0 396.8 424.6 452.9 481.2 509.5 538.1 567.1 596.1 625.0 654.3 802.3 950.3 acm=actual cubic meter std-cm=std-mp=standard cubic meter (1 atm, 20C) 1 m3 = 35.3147 ft 1 lb = 453.592 g K = C + 273 TP2 V = V . P . Iz 

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


