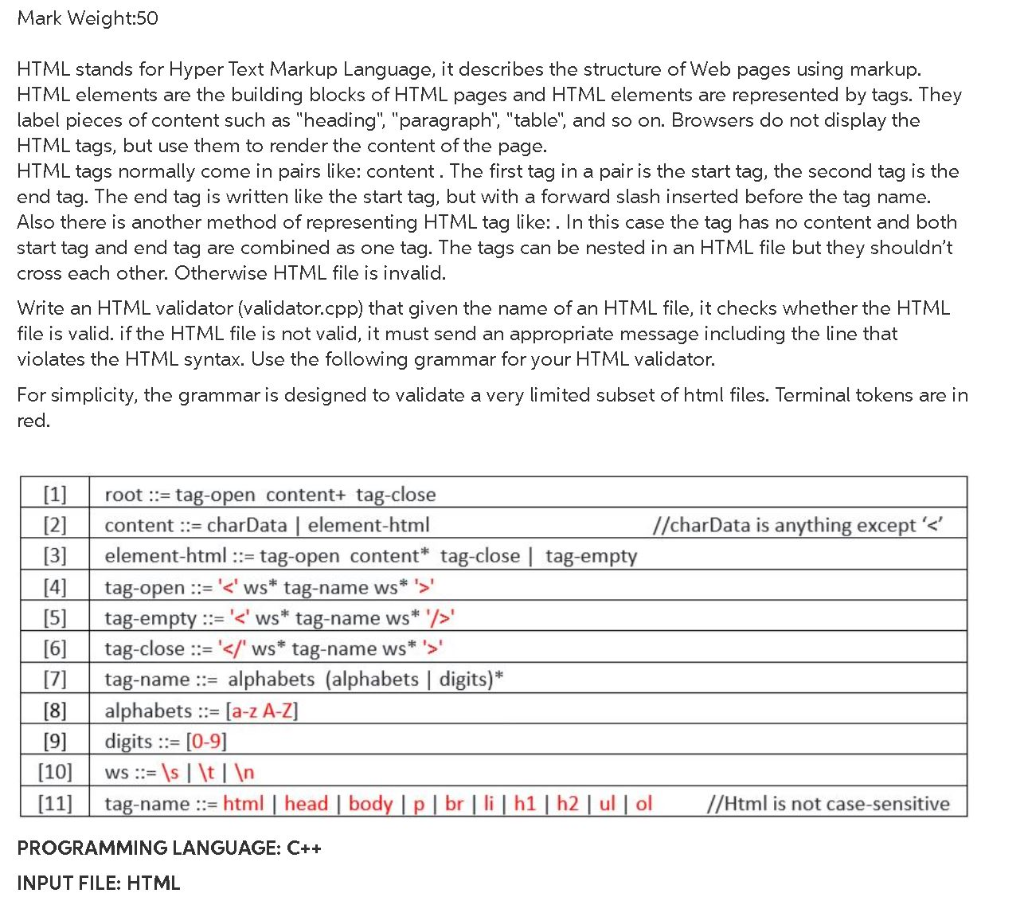
Mark Weight:50 HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language, it describes the structure of Web pages using markup. HTML elements are the building blocks of HTML pages and HTML elements are represented by tags. They label pieces of content such as "heading", "paragraph", "table", and so on. Browsers do not display the HTML tags, but use them to render the content of the page. HTML tags normally come in pairs like: content. The first tag in a pair is the start tag, the second tag is the end tag. The end tag is written like the start tag, but with a forward slash inserted before the tag name. Also there is another method of representing HTML tag like:. In this case the tag has no content and both start tag and end tag are combined as one tag. The tags can be nested in an HTML file but they shouldn't cross each other. Otherwise HTML file is invalid. Write an HTML validator (validator.cpp) that given the name of an HTML file, it checks whether the HTML file is valid. if the HTML file is not valid, it must send an appropriate message including the line that violates the HTML syntax. Use the following grammar for your HTML validator. For simplicity, the grammar is designed to validate a very limited subset of html files. Terminal tokens are in red. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] root ::= tag-open content+ tag-close content ::= charData element-html //charData is anything except' tag-empty :=' tag-close ::= '' ws* tag-name ws* > tag-name ::= alphabets (alphabets | digits)* alphabets := [a-zA-Z] digits ::= [0-9] Ws ::= \s \t tag-name ::= htmlhead body lpbrlih1|h2|ul|ol // Html is not case-sensitive [7] [8] [9] (10) [11] PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE: C++ INPUT FILE: HTML Mark Weight:50 HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language, it describes the structure of Web pages using markup. HTML elements are the building blocks of HTML pages and HTML elements are represented by tags. They label pieces of content such as "heading", "paragraph", "table", and so on. Browsers do not display the HTML tags, but use them to render the content of the page. HTML tags normally come in pairs like: content. The first tag in a pair is the start tag, the second tag is the end tag. The end tag is written like the start tag, but with a forward slash inserted before the tag name. Also there is another method of representing HTML tag like:. In this case the tag has no content and both start tag and end tag are combined as one tag. The tags can be nested in an HTML file but they shouldn't cross each other. Otherwise HTML file is invalid. Write an HTML validator (validator.cpp) that given the name of an HTML file, it checks whether the HTML file is valid. if the HTML file is not valid, it must send an appropriate message including the line that violates the HTML syntax. Use the following grammar for your HTML validator. For simplicity, the grammar is designed to validate a very limited subset of html files. Terminal tokens are in red. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] root ::= tag-open content+ tag-close content ::= charData element-html //charData is anything except' tag-empty :=' tag-close ::= '' ws* tag-name ws* > tag-name ::= alphabets (alphabets | digits)* alphabets := [a-zA-Z] digits ::= [0-9] Ws ::= \s \t tag-name ::= htmlhead body lpbrlih1|h2|ul|ol // Html is not case-sensitive [7] [8] [9] (10) [11] PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE: C++ INPUT FILE: HTML







