Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
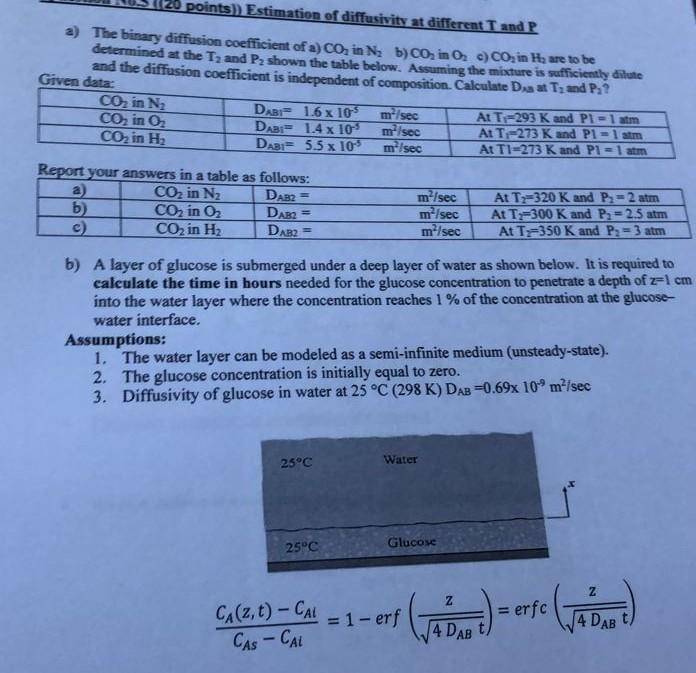
Mass transfer points)) Estimation of diffusivity at different T and P a) The binary diffusion coefficient of a) CO, in N; b) CO, in 0.
Mass transfer
points)) Estimation of diffusivity at different T and P a) The binary diffusion coefficient of a) CO, in N; b) CO, in 0. c) CO, in H, are to be determined at the T, and P2 shown the table below. Assuming the mixture is sufficiently dilute and the diffusion coefficient is independent of composition. Calculate Dsa at Tand P. ? Given data CO2 in N2 DAB 1.6 x 10 m/sec At T-293 K and PI = 1 sm CO, in O. DAB = 1.4 x 10 m/sec At T-273 K and P1 = 1 atm CO, in H DAB= 5.5 x 10 m/sec At TI-273 K and P1 - 1 atm Report your answers in a table as follows: CO2 in N2 DAB2= b) CO2 in 02 DAR2 = c) CO2 in H2 DAB2= m-/sec m Isec m/sec At T2=320 K and P. = 2 atm At T=300 K and Pa = 2.5 atm At T=350 K and P. = 3 atm b) A layer of glucose is submerged under a deep layer of water as shown below. It is required to calculate the time in hours needed for the glucose concentration to penetrate a depth of 21 cm into the water layer where the concentration reaches 1% of the concentration at the glucose- water interface. Assumptions: 1. The water layer can be modeled as a semi-infinite medium (unsteady-state). 2. The glucose concentration is initially equal to zero. 3. Diffusivity of glucose in water at 25 C (298 K) DAB=0.69x 10 m Isec 25C Water 1 25C Glucose Z z = CA(z,t) - CAL CASCAL : 1- erf (a bw) -erfe (babwe = 4 DAB 4 DAB t)Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


