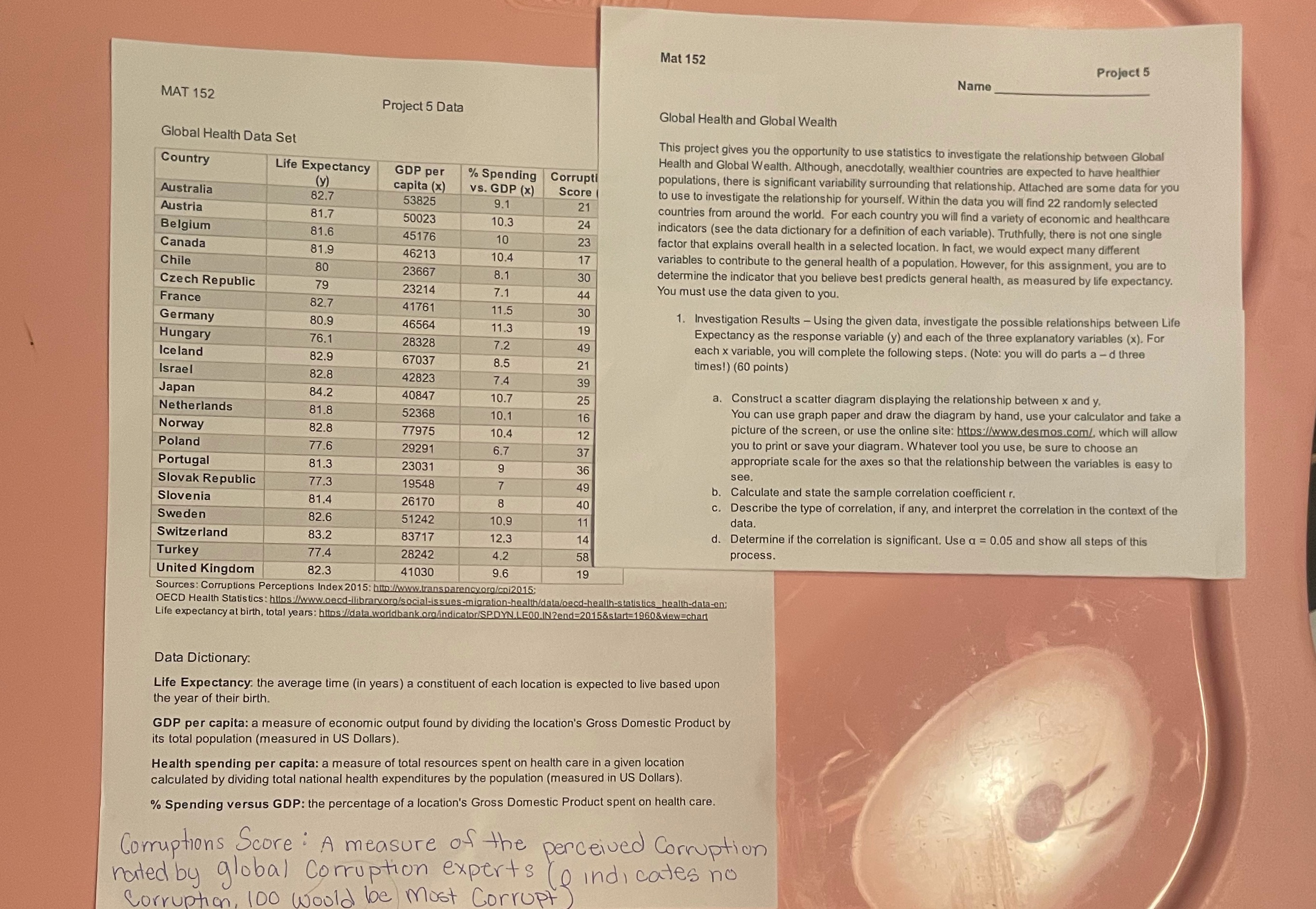
Mat 152 Project 5 Name MAT 152 Project 5 Data Global Health and Global Wealth Global Health Data Set This project gives you the opportunity to use statistics to investigate the relationship between Global Health and Global Wealth. Although, anecdotally, wealthier countries are expected to have healthier Country Life Expectancy GDP per % Spending | Corrupti populations, there is significant variability surrounding that relationship. Attached are some data for you (y) capita (x) VS. GDP (X) Score to use to investigate the relationship for yourself. Within the data you will find 22 randomly selected Australia 82.7 53825 9.1 21 countries from around the world. For each country you will find a variety of economic and healthcare Austria 81.7 50023 10.3 24 indicators (see the data dictionary for a definition of each variable). Truthfully, there is not one single Belgium 81.6 45176 10 23 factor that explains overall health in a selected location. In fact, we would expect many different Canada 81.9 46213 10.4 17 variables to contribute to the general health of a population. However, for this assignment, you are to Chile 80 23667 8.1 30 determine the indicator that you believe best predicts general health, as measured by life expectancy. Czech Republic 79 23214 7.1 44 You must use the data given to you. France 82.7 41761 11.5 30 1. Investigation Results - Using the given data, investigate the possible relationships between Life Germany 80.9 46564 11.3 19 Expectancy as the response variable (y) and each of the three explanatory variables (x). For Hungary 76.1 28328 7.2 49 each x variable, you will complete the following steps. (Note: you will do parts a - d three Iceland 82.9 67037 8.5 21 times!) (60 points) Israel 82.8 4282 7.4 39 a. Construct a scatter diagram displaying the relationship between x and y. Japan 84.2 40847 10.7 25 You can use graph paper and draw the diagram by hand, use your calculator and take a Netherlands 81.8 52368 10.1 16 picture of the screen, or use the online site: https:/www.desmos.com/, which will allow Norway 82.8 77975 10.4 12 you to print or save your diagram. Whatever tool you use, be sure to choose an Poland 77.6 29291 6.7 37 appropriate scale for the axes so that the relationship between the variables is easy to Portugal 81.3 23031 9 36 see. Slovak Republic 77.3 19548 49 b. Calculate and state the sample correlation coefficient r. . Describe the type of correlation, if any, and interpret the correlation in the context of the Slovenia 81.4 26170 8 40 82.6 51242 10.9 11 data. Sweden d. Determine if the correlation is significant. Use a = 0.05 and show all steps of this Switzerland 83.2 83717 12.3 14 Turkey 77.4 28242 4.2 58 process. United Kingdom 82.3 41030 9.6 19 Sources: Corruptions Perceptions Index 2015: http:/www.transparencyorg/col2015 OECD Health Statistics: https./www.oecd-ilibraryorg/social-issues-migration-health/data/oecd-health-statistics_health-data-en; Life expectancy at birth, total years: https/data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.DYN.LF00.IN?end=2015&start=1960&view=chart Data Dictionary: Life Expectancy. the average time (in years) a constituent of each location is expected to live based upon the year of their birth. GDP per capita: a measure of economic output found by dividing the location's Gross Domestic Product by its total population (measured in US Dollars). Health spending per capita: a measure of total resources spent on health care in a given location calculated by dividing total national health expenditures by the population (measured in US Dollars). % Spending versus GDP: the percentage of a location's Gross Domestic Product spent on health care. Corruptions Score : A measure of the perceived Corruption rated by global corruption experts If indicates no Corruption 100 Would be most Corrupt