Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Match the numbers to the responses Firms can grow profitably in the international arena by entering new markets where indigenous competitors have inadequate skills and
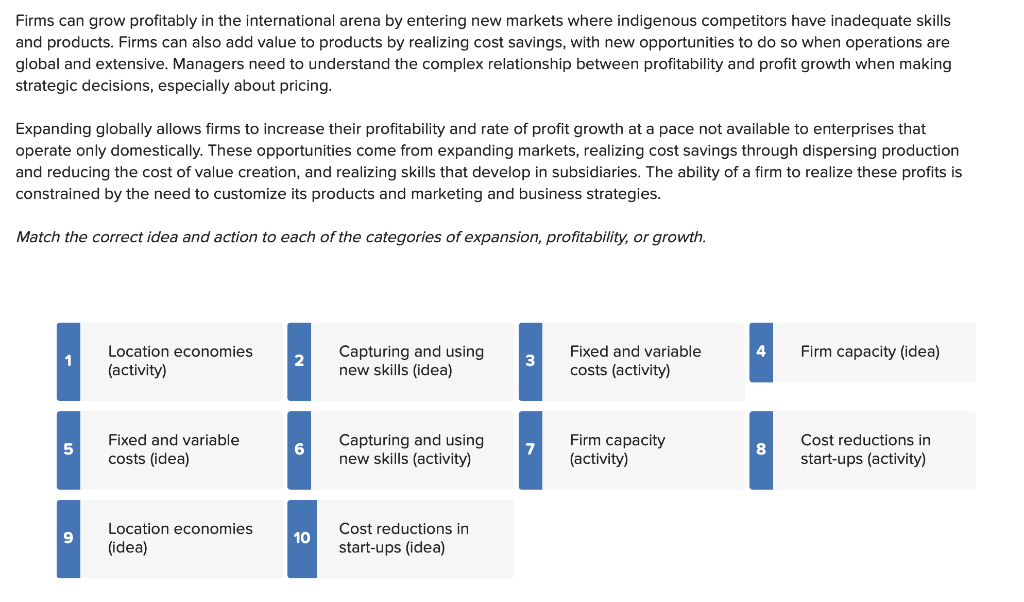
Match the numbers to the responses
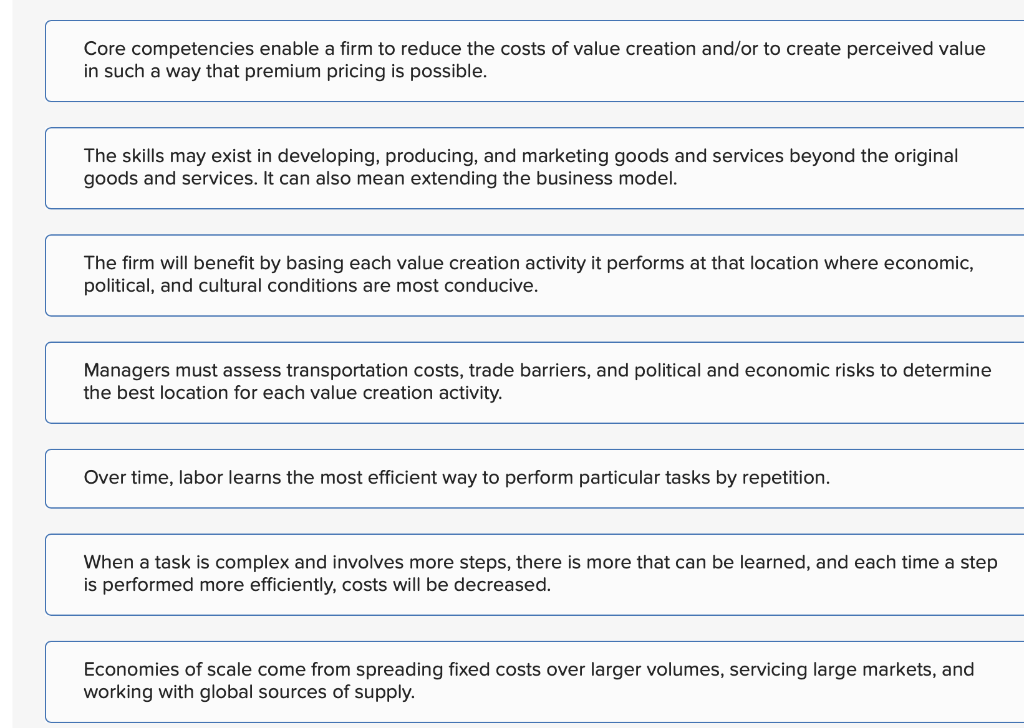

Firms can grow profitably in the international arena by entering new markets where indigenous competitors have inadequate skills and products. Firms can also add value to products by realizing cost savings, with new opportunities to do so when operations are global and extensive. Managers need to understand the complex relationship between profitability and profit growth when making strategic decisions, especially about pricing. Expanding globally allows firms to increase their profitability and rate of profit growth at a pace not available to enterprises that operate only domestically. These opportunities come from expanding markets, realizing cost savings through dispersing production and reducing the cost of value creation, and realizing skills that develop in subsidiaries. The ability of a firm to realize these profits is constrained by the need to customize its products and marketing and business strategies. Match the correct idea and action to each of the categories of expansion, profitability, or growth. Core competencies enable a firm to reduce the costs of value creation and/or to create perceived value in such a way that premium pricing is possible. The skills may exist in developing, producing, and marketing goods and services beyond the original goods and services. It can also mean extending the business model. The firm will benefit by basing each value creation activity it performs at that location where economic, political, and cultural conditions are most conducive. Managers must assess transportation costs, trade barriers, and political and economic risks to determine the best location for each value creation activity. Over time, labor learns the most efficient way to perform particular tasks by repetition. When a task is complex and involves more steps, there is more that can be learned, and each time a step is performed more efficiently, costs will be decreased. Economies of scale come from spreading fixed costs over larger volumes, servicing large markets, and working with global sources of supply. The way to recoup development costs and achieve leverage with suppliers is to expand into global markets, as domestic markets may not produce sufficient volumes. Mature multinational enterprises have been successful, but skills to lower costs of production and enhance perceived value may come from other locations. Managers must have a way to identify new and good ideas and skills and provide incentives to share and experiment with these ideas. Firms can grow profitably in the international arena by entering new markets where indigenous competitors have inadequate skills and products. Firms can also add value to products by realizing cost savings, with new opportunities to do so when operations are global and extensive. Managers need to understand the complex relationship between profitability and profit growth when making strategic decisions, especially about pricing. Expanding globally allows firms to increase their profitability and rate of profit growth at a pace not available to enterprises that operate only domestically. These opportunities come from expanding markets, realizing cost savings through dispersing production and reducing the cost of value creation, and realizing skills that develop in subsidiaries. The ability of a firm to realize these profits is constrained by the need to customize its products and marketing and business strategies. Match the correct idea and action to each of the categories of expansion, profitability, or growth. Core competencies enable a firm to reduce the costs of value creation and/or to create perceived value in such a way that premium pricing is possible. The skills may exist in developing, producing, and marketing goods and services beyond the original goods and services. It can also mean extending the business model. The firm will benefit by basing each value creation activity it performs at that location where economic, political, and cultural conditions are most conducive. Managers must assess transportation costs, trade barriers, and political and economic risks to determine the best location for each value creation activity. Over time, labor learns the most efficient way to perform particular tasks by repetition. When a task is complex and involves more steps, there is more that can be learned, and each time a step is performed more efficiently, costs will be decreased. Economies of scale come from spreading fixed costs over larger volumes, servicing large markets, and working with global sources of supply. The way to recoup development costs and achieve leverage with suppliers is to expand into global markets, as domestic markets may not produce sufficient volumes. Mature multinational enterprises have been successful, but skills to lower costs of production and enhance perceived value may come from other locations. Managers must have a way to identify new and good ideas and skills and provide incentives to share and experiment with these ideas
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


