matching
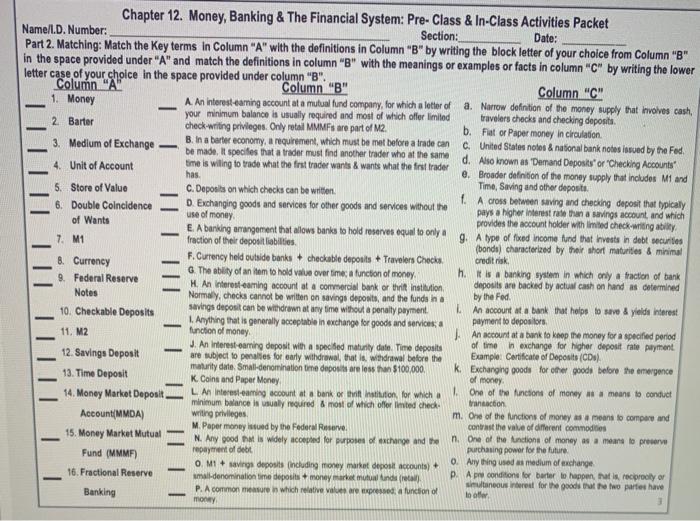
Date: Chapter 12. Money, Banking & The Financial System: Pre-Class & In-Class Activities Packet Name/l.D. Number: Section: Part 2. Matching: Match the Key terms in Column "A" with the definitions in Column "B" by writing the block letter of your choice from Column "B" in the space provided under "A" and match the definitions in column "B" with the meanings or examples or facts in column "C" by writing the lower letter case of your choice in the space provided under column "B". Column. A Column "B" Column "C" 1. Money A. An interest-earning account at a mutual fund company, for which a letter of a. Narrow definition of the money supply that involves cash, your minimum balance is usually required and most of which offer limited travelers checks and checking deposits 2 Barter check writing privileges. Only retail MMMFs are part of M2. b. Fiat or Paper money in circulation 3. Medium of Exchange B. In a barter economy, a requirement, which must be met before a trade can C. United States notes & national banknotes issued by the Fed. be made. It specifies that a trader must find another trader who at the same d. Also known as Demand Deposits' or 'Checking Accounts 4 Unit of Account time is willing to rade what the first trader wants & wants what the first trader has. e. Broader definition of the money supply that includes M1 and 5. Store of Value C. Deposits on which checks can be written. Time, Saving and other deposits A cross between saving and checking deposit that typically 6. Double Coincidence D. Exchanging goods and services for other goods and services without the pays a higher interest rate than a savings account and which use of money of Wants provides the account holder with limited check writing ability E. A banking unangement that allows banks to hold reserves equal to only a 7 M1 fraction of their deposit liabilities g. A type of fixed income fund that invest in debt securities (bonda) characterized by their short maturities & minimal 8. Currency F. Currency held outside banks + checkable deposits + Travelers Checks credit risk G. The ability of an em to hold value over time, a function of money h. a banking system in which only a fraction of bank 9. Federal Reserve H. An Interesteaming account at a commercial bank or thrilt Institution deposits are backed by actual cash on hand as determined Notes Normaly checks cannot be written on savings deposits, and the funds in a by the Fed 10. Checkable Deposits savings deposit can be withdrawn at any time without a penalty payment An account at a bank that helps to save & yields interest I. Anything that is generally acceptable in exchange for goods and services a payment to depositors 11. M2 function of money An account at a bank to keep the money for a specified period J. An Interest-earning deposit with a specified maturity date. Time deposits of time in exchange for higher deposit rate payment 12. Savings Deposit are subject to penales for early withdrawal, that is withdrawal before the Example: Certificate of Deposits (CD) maturity date Small-denomination time deposits are less than $100,000, k. Exchanging good for the goods before the emergence 13. Time Deposit K. Coins and Paper Money 14. Money Market Deposit LA Interesteaming account at a bank of thrination for which a One of the function of money # means to conduct minimum balance is usually required most of which offer limited check transaction Account(MMDA) witing privileges m. One of the functions of money as a means to compare and M. Paper Money issued by the Federal Reserve contrast the value of different commodities 15. Money Market Mutual N. Any good is widely accepted for purpose of exchange and the n. One of the functions of money as a means to preserve Fund (MMMF) repayment of debt purchasing power for the future 0 Anything used as medium of exchange O MI + savings deposits including money market deposit accounts) 16. Fractional Reserve mall.denomination time deposits + money market mutlindreta). D. A conditions for barter to happen a reciprooly or multaneous roul for the goods that the two partes have P. A common measure in which relative values are pressed a function of Banking low money of money - - TI Chapter 12. Money, Banking & The Financial System: Pre-Class & In-Class Activities Packet Name/l.D. Number: Section: Date: Part 2. Matching: Match the Key terms in Column "A" with the definitions in Column "B" by writing the block letter of your choice from Column "B" In the space provided under "A" and match the definitions in column "B" with the meanings or examples or facts in column "C" by writing the lower letter case of your choice in the space provided under column "B". Column "A Column "B" Column "C" 17. Federal Reserve Q. Funds are band and borrowed through a francia 9. Amount of reserves kapt by banks over & above what is Intermediary required by the Fed System (The Fed) R. Anything of value that is owned or that one has claim to A method of financing done by borrowing directly from 18. Reserves S. A financial Intermediary transfers funds from those who creditors without the involvement of banks and other inancial want to lend funds to those who want to borrow them. intermediaries 19. Required Reserve T. Anything that is owed to someone else $. Monetary or non-retary properties owned by baris Ratio (n) U. Relates to an economic agent on one side of a transaction L Debt obligation owed to others. having information that an agent on the other side of the u When debt owed is greater than properties owned 20. Required Reserves transaction does not have V. A method of fnancing that involves banks and other financial 21. Reserve Requirement V. A condition in which one's liabilities are greater than one's companies that go between the two sides assets W. A bark or other financial company that go between the 22. Excess Reserves W. A phenomenon that occurs when the parties on one side of borrower and the lender so as to mobile funds from the the market who have information not known to others, soll savers to the borrower 23. Direct Finance select in a way that adversely affects the parties on the other X. Uneven or unequal access to Information side of the market 24. Indirect Finance y. The union in which individuals with good normation on X. The central bank of the United States take advantage of others who do not have the same 25, Financial Y The sum of bank deposits at the Fed and Vault cash information Z A reserves held beyond the required amount the Z.The situation in which one of the parties to a deal changes Intermediary difference between (total reserves and required reserves his or her behavior unknown to the other party that may have 26. Asymmetric AA Borrowers and lenders come together in a marcat setting negative impact on the other party Information such as in the bond market aa. A financial statement that shows the net worth a bank. BB. A condition that exists when one party to transaction bb. Money kept by banks in their vaults and at the Fed either to 27. Adverse Selection changes his or her behavior in a way that is hidden from and meet their customers need or to meet the requirement of the 28. Moral Hazard costly to the other party Fed. CC. A record of the assets and liabilities of a bank CC. A percentage that is applicable to the Checking Depost hat 29. Balance Sheet DD. The Fed rule that specifies the amount of reserves a bank must be kept by banks to meet reserve requirement. must hold to back up deposits dd. The institution in charge of conducting monetary policy in the 30. Asset EE. A percentage of each dolar deposited that must be held in U.S., is also known as "The Fed (in Economics) 31. Liability reserve form (specifically, as bank deposits at the Fed or vault 02. The policy of the Fed that requires banks to keep a fraction of cash) their checking deposit to meet the needs of their customers 32. Insolvency FF. The minimum dollar amount of reserves that a bank must The amount of money that must be kept by banks to meet hold against its chackable deposits, as mandated by the Fed. reserve requrements mandated by the Fed - - Date: Chapter 12. Money, Banking & The Financial System: Pre-Class & In-Class Activities Packet Name/l.D. Number: Section: Part 2. Matching: Match the Key terms in Column "A" with the definitions in Column "B" by writing the block letter of your choice from Column "B" in the space provided under "A" and match the definitions in column "B" with the meanings or examples or facts in column "C" by writing the lower letter case of your choice in the space provided under column "B". Column. A Column "B" Column "C" 1. Money A. An interest-earning account at a mutual fund company, for which a letter of a. Narrow definition of the money supply that involves cash, your minimum balance is usually required and most of which offer limited travelers checks and checking deposits 2 Barter check writing privileges. Only retail MMMFs are part of M2. b. Fiat or Paper money in circulation 3. Medium of Exchange B. In a barter economy, a requirement, which must be met before a trade can C. United States notes & national banknotes issued by the Fed. be made. It specifies that a trader must find another trader who at the same d. Also known as Demand Deposits' or 'Checking Accounts 4 Unit of Account time is willing to rade what the first trader wants & wants what the first trader has. e. Broader definition of the money supply that includes M1 and 5. Store of Value C. Deposits on which checks can be written. Time, Saving and other deposits A cross between saving and checking deposit that typically 6. Double Coincidence D. Exchanging goods and services for other goods and services without the pays a higher interest rate than a savings account and which use of money of Wants provides the account holder with limited check writing ability E. A banking unangement that allows banks to hold reserves equal to only a 7 M1 fraction of their deposit liabilities g. A type of fixed income fund that invest in debt securities (bonda) characterized by their short maturities & minimal 8. Currency F. Currency held outside banks + checkable deposits + Travelers Checks credit risk G. The ability of an em to hold value over time, a function of money h. a banking system in which only a fraction of bank 9. Federal Reserve H. An Interesteaming account at a commercial bank or thrilt Institution deposits are backed by actual cash on hand as determined Notes Normaly checks cannot be written on savings deposits, and the funds in a by the Fed 10. Checkable Deposits savings deposit can be withdrawn at any time without a penalty payment An account at a bank that helps to save & yields interest I. Anything that is generally acceptable in exchange for goods and services a payment to depositors 11. M2 function of money An account at a bank to keep the money for a specified period J. An Interest-earning deposit with a specified maturity date. Time deposits of time in exchange for higher deposit rate payment 12. Savings Deposit are subject to penales for early withdrawal, that is withdrawal before the Example: Certificate of Deposits (CD) maturity date Small-denomination time deposits are less than $100,000, k. Exchanging good for the goods before the emergence 13. Time Deposit K. Coins and Paper Money 14. Money Market Deposit LA Interesteaming account at a bank of thrination for which a One of the function of money # means to conduct minimum balance is usually required most of which offer limited check transaction Account(MMDA) witing privileges m. One of the functions of money as a means to compare and M. Paper Money issued by the Federal Reserve contrast the value of different commodities 15. Money Market Mutual N. Any good is widely accepted for purpose of exchange and the n. One of the functions of money as a means to preserve Fund (MMMF) repayment of debt purchasing power for the future 0 Anything used as medium of exchange O MI + savings deposits including money market deposit accounts) 16. Fractional Reserve mall.denomination time deposits + money market mutlindreta). D. A conditions for barter to happen a reciprooly or multaneous roul for the goods that the two partes have P. A common measure in which relative values are pressed a function of Banking low money of money - - TI Chapter 12. Money, Banking & The Financial System: Pre-Class & In-Class Activities Packet Name/l.D. Number: Section: Date: Part 2. Matching: Match the Key terms in Column "A" with the definitions in Column "B" by writing the block letter of your choice from Column "B" In the space provided under "A" and match the definitions in column "B" with the meanings or examples or facts in column "C" by writing the lower letter case of your choice in the space provided under column "B". Column "A Column "B" Column "C" 17. Federal Reserve Q. Funds are band and borrowed through a francia 9. Amount of reserves kapt by banks over & above what is Intermediary required by the Fed System (The Fed) R. Anything of value that is owned or that one has claim to A method of financing done by borrowing directly from 18. Reserves S. A financial Intermediary transfers funds from those who creditors without the involvement of banks and other inancial want to lend funds to those who want to borrow them. intermediaries 19. Required Reserve T. Anything that is owed to someone else $. Monetary or non-retary properties owned by baris Ratio (n) U. Relates to an economic agent on one side of a transaction L Debt obligation owed to others. having information that an agent on the other side of the u When debt owed is greater than properties owned 20. Required Reserves transaction does not have V. A method of fnancing that involves banks and other financial 21. Reserve Requirement V. A condition in which one's liabilities are greater than one's companies that go between the two sides assets W. A bark or other financial company that go between the 22. Excess Reserves W. A phenomenon that occurs when the parties on one side of borrower and the lender so as to mobile funds from the the market who have information not known to others, soll savers to the borrower 23. Direct Finance select in a way that adversely affects the parties on the other X. Uneven or unequal access to Information side of the market 24. Indirect Finance y. The union in which individuals with good normation on X. The central bank of the United States take advantage of others who do not have the same 25, Financial Y The sum of bank deposits at the Fed and Vault cash information Z A reserves held beyond the required amount the Z.The situation in which one of the parties to a deal changes Intermediary difference between (total reserves and required reserves his or her behavior unknown to the other party that may have 26. Asymmetric AA Borrowers and lenders come together in a marcat setting negative impact on the other party Information such as in the bond market aa. A financial statement that shows the net worth a bank. BB. A condition that exists when one party to transaction bb. Money kept by banks in their vaults and at the Fed either to 27. Adverse Selection changes his or her behavior in a way that is hidden from and meet their customers need or to meet the requirement of the 28. Moral Hazard costly to the other party Fed. CC. A record of the assets and liabilities of a bank CC. A percentage that is applicable to the Checking Depost hat 29. Balance Sheet DD. The Fed rule that specifies the amount of reserves a bank must be kept by banks to meet reserve requirement. must hold to back up deposits dd. The institution in charge of conducting monetary policy in the 30. Asset EE. A percentage of each dolar deposited that must be held in U.S., is also known as "The Fed (in Economics) 31. Liability reserve form (specifically, as bank deposits at the Fed or vault 02. The policy of the Fed that requires banks to keep a fraction of cash) their checking deposit to meet the needs of their customers 32. Insolvency FF. The minimum dollar amount of reserves that a bank must The amount of money that must be kept by banks to meet hold against its chackable deposits, as mandated by the Fed. reserve requrements mandated by the Fed









