
Matching:Match the Key terms in Column "A" with the textbook definitions in Column "B" by writing the block letter of your choice undercolumn "A" andmatch column "B" with the meanings in column "C" by writing the lower case letter of your choice under column "B".
PLEASE NOTE: I NEED ONLY EVEN NUMBERS QUESTIONS ANSWERS. THANKS!
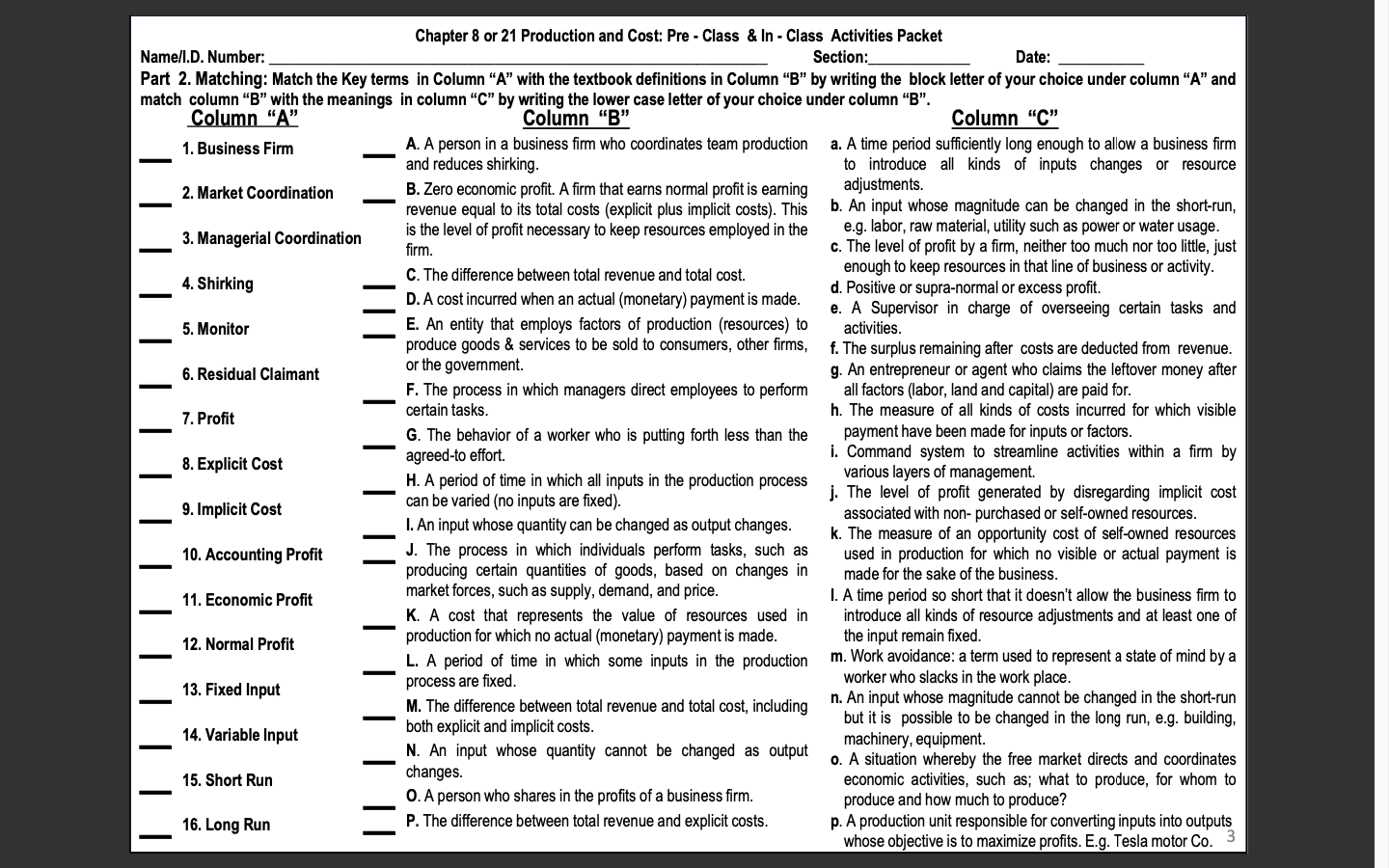
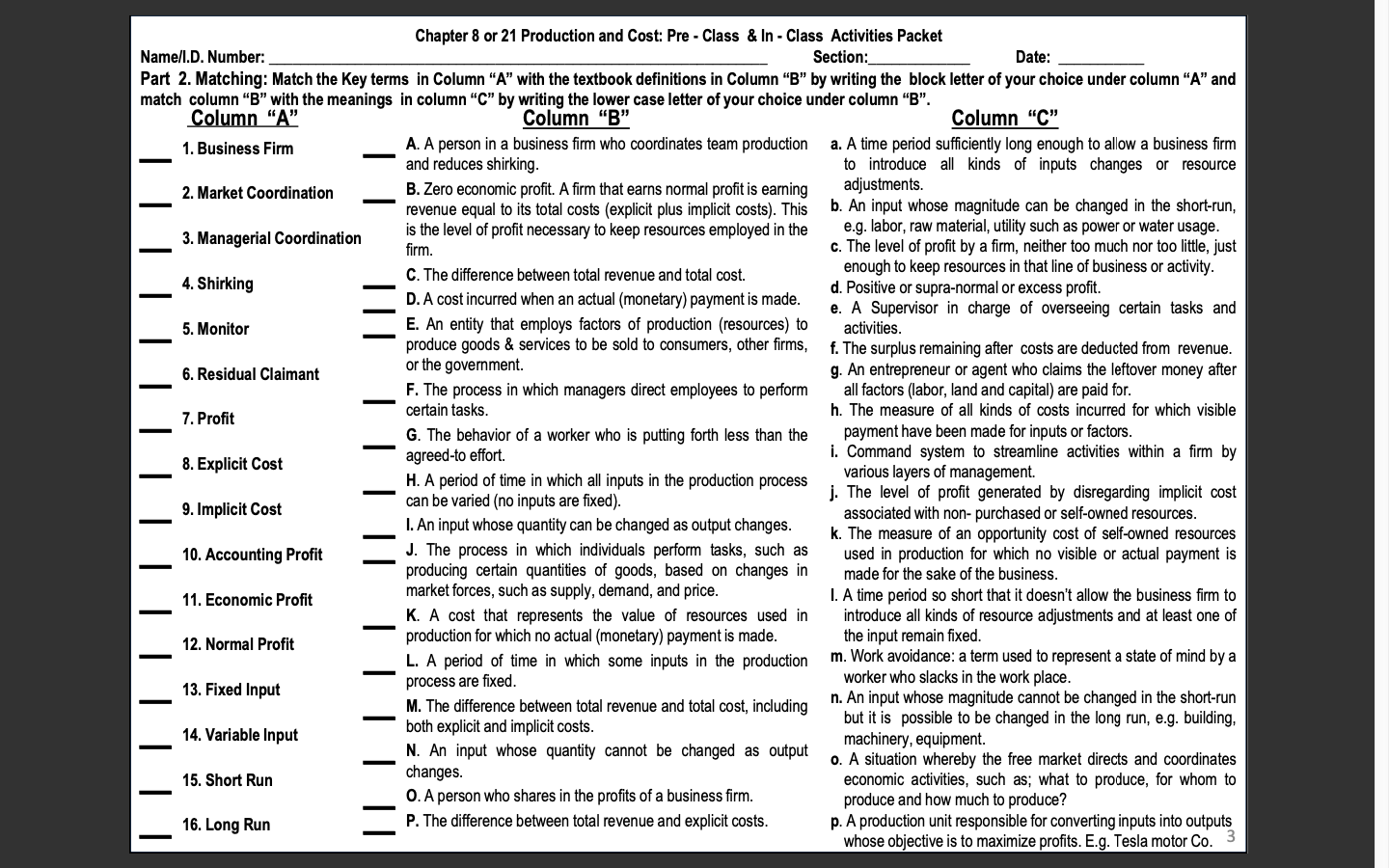
Chapter 8 or 21 Production and Cost: Pre - Class & In - Class Activities Packet Name/I.D. Number: Section: Date: Part 2. Matching: Match the Key terms in Column "A" with the textbook definitions in Column "B" by writing the block letter of your choice under column "A" and match column "B" with the meanings in column "C" by writing the lower case letter of your choice under column "B". Column "A" Column "B" Column "C" 1. Business Firm A. A person in a business firm who coordinates team production a. A time period sufficiently long enough to allow a business firm and reduces shirking. to introduce all kinds of inputs changes or resource 2. Market Coordination B. Zero economic profit. A firm that earns normal profit is earning adjustments. revenue equal to its total costs (explicit plus implicit costs). This b. An input whose magnitude can be changed in the short-run, 3. Managerial Coordination is the level of profit necessary to keep resources employed in the e.g. labor, raw material, utility such as power or water usage irm c. The level of profit by a firm, neither too much nor too little, just enough to keep resources in that line of business or activity. 4. Shirking C. The difference between total revenue and total cost. D. A cost incurred when an actual (monetary) payment is made. d. Positive or supra-normal or excess profit. e. A Supervisor in charge of overseeing certain tasks and 5. Monitor E. An entity that employs factors of production (resources) to activities. produce goods & services to be sold to consumers, other firms, f. The surplus remaining after costs are deducted from revenue. 6. Residual Claimant or the government. g. An entrepreneur or agent who claims the leftover money after F. The process in which managers direct employees to perform all factors (labor, land and capital) are paid for. 7. Profit certain tasks. h. The measure of all kinds of costs incurred for which visible G. The behavior of a worker who is putting forth less than the payment have been made for inputs or factors. 8. Explicit Cost agreed-to effort. i. Command system to streamline activities within a firm by H. A period of time in which all inputs in the production process various layers of management. j. The level of profit generated by disregarding implicit cost 9. Implicit Cost can be varied (no inputs are fixed). I. An input whose quantity can be changed as output changes. associated with non- purchased or self-owned resources. k. The measure of an opportunity cost of self-owned resources 10. Accounting Profit J. The process in which individuals perform tasks, such as used in production for which no visible or actual payment is producing certain quantities of goods, based on changes in made for the sake of the business. 11. Economic Profit market forces, such as supply, demand, and price. I. A time period so short that it doesn't allow the business firm to K. A cost that represents the value of resources used in introduce all kinds of resource adjustments and at least one of 12. Normal Profit production for which no actual (monetary) payment is made. he input remain fixed. L. A period of time in which some inputs in the production m. Work avoidance: a term used to represent a state of mind by a worker who slacks in the work place. 13. Fixed Input process are fixed M. The difference between total revenue and total cost, including n. An input whose magnitude cannot be changed in the short-run but it is possible to be changed in the long run, e.g. building, 14. Variable Input both explicit and implicit costs. N. An input whose quantity cannot be changed as output machinery, equipment. o. A situation whereby the free market directs and coordinates 15. Short Run changes. economic activities, such as; what to produce, for whom to O. A person who shares in the profits of a business firm. produce and how much to produce? 16. Long Run P. The difference between total revenue and explicit costs. p. A production unit responsible for converting inputs into outputs whose objective is to maximize profits. E.g. Tesla motor Co. 3Chapter 8 or 21 Production and Cost: Pre - Class & In - Class Activities Packet Name/I.D. Number: Section: Date: Part 2. Matching: Match the Key terms in Column "A" with the textbook definitions in Column "B" by writing the block letter of your choice under column "A" and match column "B" with the meanings in column "C" by writing the lower case letter of your choice under column "B". Column "A" Column "B" Column "C" Q. Total cost divided by quantity of output: ATC = TC/Q. q. Costs that cannot be recovered once they are incurred 17. Marginal Physical Product R. Costs that do not vary with output; the costs associated with fixed (bygones are bygones). 18. Law of Diminishing inputs. r. A situation whereby output increases, say by 10% as a Marginal Returns (LDMR) S. Costs that vary with output; the costs associated with variable result of increase in inputs, say by 5%. 19. Fixed Costs inputs. S. Costs that are incurred to buy variable inputs. T. As ever larger amounts of a variable input are combined with fixed t. As more and more variable inputs are added to be used 20. Variable Costs inputs, eventually the marginal physical product of the variable input with a fixed input, the corresponding output obtainable will decline. from these additional inputs decline. 21. Total Cost (TC) U. Total fixed cost divided by quantity of output: AFC=TFC/Q. u. Per unit fixed cost incurred to produce a unit output. V. The sum of fixed costs and variable costs. 22. Marginal Cost (MC) V. The lowest scale necessary to achieve production at the W. A cost incurred in the past that cannot be changed by current lowest per unit cost in a competitive industry decisions and therefore cannot be recovered. 23. Average Fixed Cost (AFC) X. A curve that shows the lowest (unit) cost at which the firm can w. The sum of all costs incurred to produce a given product. produce any given level of output. 24. Average Variable Cost (AVC) Y. Economies that exist when inputs are increased by some X. Costs that are incurred to buy the so called "fixed percentage & output increases by a greater percentage, causing unit inputs" 25. Average Total Cost (ATC) costs to fall. y. A situation whereby output increases, say by 10% as a Z. The condition when inputs are increased by some percentage & result of increase in inputs, say by 10% 26. Average-Marginal Rule output increases by an equal percentage, causing unit costs to z. The inverse or negative relationship between the remain constant. average product and the marginal product associated 27. Sunk Cost AA. Total variable cost divided by quantity of output: AVC = TVC/Q. with the variable input such as labor. BB. When the marginal magnitude is above the average magnitude, aa. The additional product produced because of the use of the average magnitude rises; when the marginal magnitude is below the additional variable input. 28. Long-Run Average the average magnitude, the average magnitude falls. bb. Per unit variable cost incurred to produce a unit of Total Cost Curve(LRATC) CC. The change in total cost that results from a change in output. 29. Economies of Scale output: MC = ATC/AQ cc. The additional cost that the firm incurs as a result of DD. The condition when inputs are increased by some percentage producing one more unit of output 30. Constant Returns to Scale and output increases by a smaller percentage, causing unit costs to dd. A curve that sows the minimum or lowest average rise. total cost at which a firm can produce any given level of 31. Diseconomies of Scale EE. The change in output that results from changing the variable input output in the long run (when all inputs are variable). by one unit, holding all other inputs fixed. ee. A situation whereby output increases, say by 5% as a 32. Minimum Efficient Scale FF. The lowest output level at which average total costs are result of increase in inputs, say by 10%. minimized. ff. Per unit total cost incurred to produce a unit of output.. 4