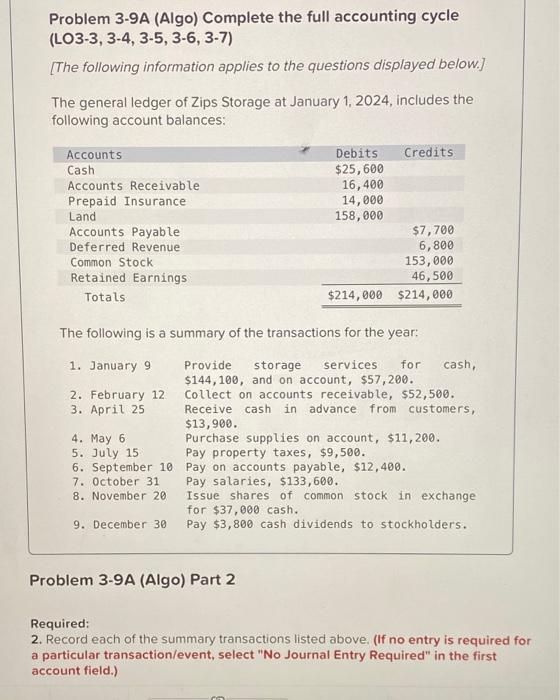
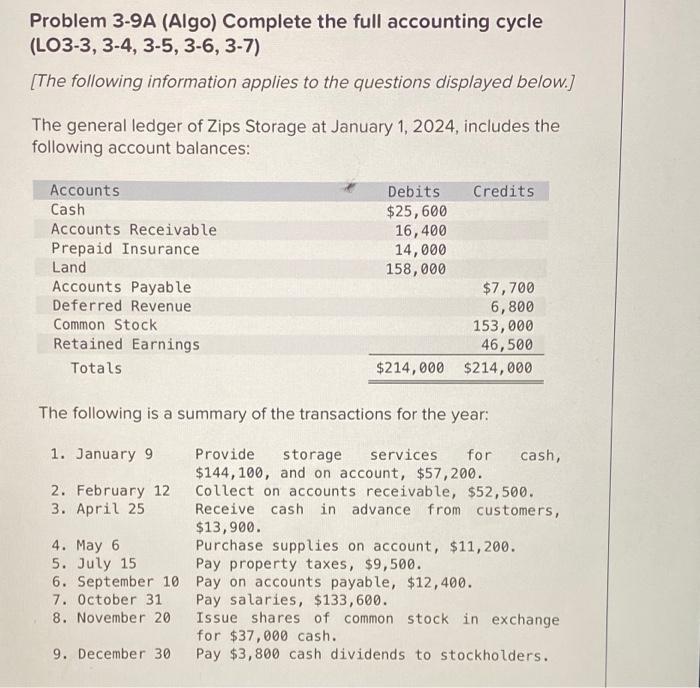
Math Functions Reading Readiness, Inc, has provided you its list of accounts and balances as of January 31. The Controller has asked you to prepare an Income Statement for the month ended January 31. Use the information included in the Excel Simulation and the Excel functions described below to complete the task. - Cell Reference: Allows you to refer to data from another cell in the worksheet. From the Excel Simulation below, if in a blank cell, "=C11" was entered, the formula would output the result from cell C11, or 6,050 in this example. - Basic Math functions: Allows you to use the basic math symbols to perform mathematical functions. You can use the following keys: + (plus sign to add). (minus sign to subtract). " (asterisk sign to multiply), and / (forward slash to divide). From the Excel Simulation below, if in a blank cell "=C11+C12" was entered, the formula would add the values from those cells and output the result, or 10,850 in this example. If using the other math symbols the result would output an appropriate answer for its function. - SUM function: Allows you to refer to multiple cells and adds all the values. You can add individual cell references or ranges to utilize this function. From the Excel Simulation below, if in a blank cell "=SUM(C11,C12,C13)" was entered, the formula would output the result of adding those three separate cells, or 17,732 in this example. Similarly, if in a blank cell "=SUM(C11:C13)" was entered, the formula would output the same result of adding those cells, except they are expressed as a range in the formula, and the result would be 17,732 in this example. - IF function: Allows you to test a condition and return a specific value is the result is true and different value if the result is false. The syntax of the IF function is "=|F(test_condition,value_if_true,value_if_false)" and specific considerations need to be made when using this function. The test_condition argument is an evaluation of the status of a cell, such as if the value of a cell is greater than, less than, or equal to another number or cell. The value_if_true and value_ if false arguments will return any specific result for each option, such as another cell reference, a value, or text. Throughout the entire equation, if text is being used in the test_condition, value_ if true, or value_ if false arguments then the text itself should be entered in quotations so that Excel will recognize the text as a "string of text" instead of another function. From the Excel Simulation below, if in a blank cell "=IF(C6>10000," Cash is great", "Cash is bad") was entered, the formula would output the result of the value_ If true since the test_condition would be result as true, or in this case the text "Cash is great". Excel processes the IF function by separating it out into separate parts. First the test_condition - Excel thinks, find cell C6 and determine if the value is greater than 10000 . Once Excel determines if the result of that test_condition is TRUE or FALSE, it will return the value_ if true or Problem 3-9A (Algo) Complete the full accounting cycle (LO3-3, 3-4, 3-5, 3-6, 3-7) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] The general ledger of Zips Storage at January 1, 2024, includes the following account balances: The following is a summary of the transactions for the year: Problem 3-9A (Algo) Part 2 Required: 2. Record each of the summary transactions listed above. (If no entry is required for a particular transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.) Problem 3-9A (Algo) Complete the full accounting cycle (LO3-3, 3-4, 3-5, 3-6, 3-7) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] The general ledger of Zips Storage at January 1, 2024, includes the following account balances: The following is a summary of the transactions for the year