Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
matlab Part 2: Implement a uniform quantization algorithm (without generating an LUT) to convert from 24bit color images (i.e., *_color.jpg in HW1_sample_images.zip) to 8bit 256
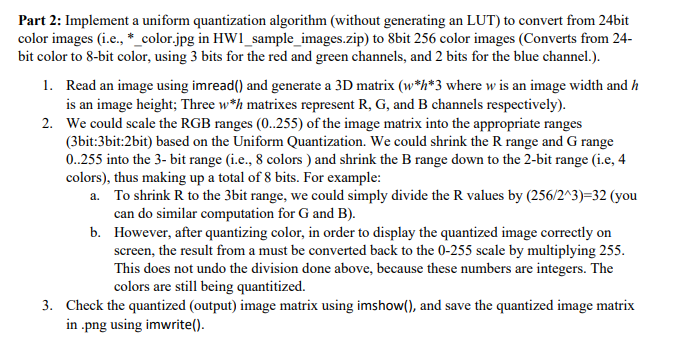
matlab
Part 2: Implement a uniform quantization algorithm (without generating an LUT) to convert from 24bit color images (i.e., *_color.jpg in HW1_sample_images.zip) to 8bit 256 color images (Converts from 24- bit color to 8-bit color, using 3 bits for the red and green channels, and 2 bits for the blue channel.). 1. Read an image using imread() and generate a 3D matrix (w*h*3 where w is an image width and h is an image height; Three w*h matrixes represent R, G, and B channels respectively). 2. We could scale the RGB ranges (0..255) of the image matrix into the appropriate ranges (3bit:3bit:2bit) based on the Uniform Quantization. We could shrink the range and Grange 0.255 into the 3- bit range (i.e., 8 colors ) and shrink the B range down to the 2-bit range (i.e, 4 colors), thus making up a total of 8 bits. For example: a. To shrink R to the 3bit range, we could simply divide the values by (256/243)=32 (you can do similar computation for G and B). b. However, after quantizing color, in order to display the quantized image correctly on screen, the result from a must be converted back to the 0-255 scale by multiplying 255. This does not undo the division done above, because these numbers are integers. The colors are still being quantitized. 3. Check the quantized (output) image matrix using imshow(), and save the quantized image matrix in.png using imwrite(). Part 2: Implement a uniform quantization algorithm (without generating an LUT) to convert from 24bit color images (i.e., *_color.jpg in HW1_sample_images.zip) to 8bit 256 color images (Converts from 24- bit color to 8-bit color, using 3 bits for the red and green channels, and 2 bits for the blue channel.). 1. Read an image using imread() and generate a 3D matrix (w*h*3 where w is an image width and h is an image height; Three w*h matrixes represent R, G, and B channels respectively). 2. We could scale the RGB ranges (0..255) of the image matrix into the appropriate ranges (3bit:3bit:2bit) based on the Uniform Quantization. We could shrink the range and Grange 0.255 into the 3- bit range (i.e., 8 colors ) and shrink the B range down to the 2-bit range (i.e, 4 colors), thus making up a total of 8 bits. For example: a. To shrink R to the 3bit range, we could simply divide the values by (256/243)=32 (you can do similar computation for G and B). b. However, after quantizing color, in order to display the quantized image correctly on screen, the result from a must be converted back to the 0-255 scale by multiplying 255. This does not undo the division done above, because these numbers are integers. The colors are still being quantitized. 3. Check the quantized (output) image matrix using imshow(), and save the quantized image matrix in.png using imwrite()Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


