Question
Matrix.h: #include #include using namespace std; #ifndef MATRIX_H #define MATRIX_H class Matrix { friend ostream& operator public: Matrix(); // initialize Matrix class object with rowN=1,
Matrix.h:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#ifndef MATRIX_H
#define MATRIX_H
class Matrix
{
friend ostream& operator
public:
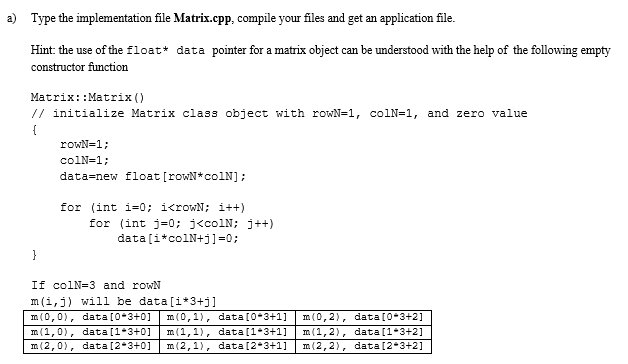
Matrix();
// initialize Matrix class object with rowN=1, colN=1, and zero value
Matrix(const int rN,const int cN );
// initialize Matrix class object with row number rN, col number cN and zero values
Matrix(const Matrix &srcMatrix );
// initialize Matrix class object with another Matrix class object
Matrix(const int rN, const int cN, const float *srcPtr);
// initialize Matrix class object with row number rN, col number cN and a pointer to an array
const float * getData()const;
// create a temp pointer and copy the array values which data pointer points,
// then returns temp.
int getRowN()const; // returns rowN
int getColN()const; // returns colN
void print()const; // prints the Matrix object in rowNxcolN form
Matrix transpose(); // takes the transpose of the matrix
Matrix operator+(const Matrix &rhsMatrix)const;
//+ operator which allows m1+m2 and returns a temp Matrix object
Matrix operator-(const Matrix &rhsMatrix)const;
//- operator which allows m1-m2 and returns a temp Matrix object
Matrix operator*(const Matrix &rhsMatrix)const;
//* operator which allows product of m1*m2
//(element-wise) and returns a temp Matrix object
float operator()(const int r,const int c)const;
//() operator which allows returning m1(r,c),
//m1(0,0) is on the first row, first col
Matrix& operator=(const Matrix &rhsMatrix);
//= operator which allows m1=m2 and returns this pointer of m1
Matrix& operator+=(const Matrix &rhsMatrix);
//+= operator which allows m1+=m2 and returns this pointer of m1
Matrix& operator-=(const Matrix &rhsMatrix);
//-= operator which allows m1-=m2 and returns this pointer of m1
Matrix& operator*=(const Matrix &rhsMatrix);
//*= operator which allows m1*=m2 (element-wise) and returns this pointer of m1
int operator==(const Matrix &rhsMatrix)const;
//== operator which returns 1 if (m1==m2)
int operator!=(const Matrix &rhsMatrix)const;
//== operator which returns 1 if (m1!=m2)
private:
//() operator which allows returning m1(r,c),
//m1(0,0) is on the first row,first col
int rowN, colN;
float* data;
// e.g: if pointer data points an array of [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] and the rowN=3 and coln=2
// matrix is actually
// 1 2 3
// 4 5 6
};
#endif
testMatrix.cpp:
#include "Matrix.h"
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float arr1[]={1,2,3,4,5, 11,12,13,14,15, 21,22,23,24,25};
float arr2[]={9,8,7,6,5, 19,18,17,16,15, 29,28,27,26,25};
Matrix m1(3,5);
Matrix m2(m1);
Matrix m3(3,5,arr1);
Matrix m4(3,5,arr2);
//-------------------
cout
m1.print();
cout
m2.print();
cout
m3.print();
cout
m3.transpose().print();
cout
m4.print();
//------------------
cout
const float* const elements=m3.getData();
const int rN=m3.getRowN();
const int cN=m3.getColN();
for (int i=0; i { for (int j=0; j cout cout } //------------------- cout (m3+=m4).print(); cout (m3-=m4).print(); cout (m3+m4).print(); cout m3.print(); cout (m3=m3+m4).print(); cout m3.print(); cout //--------------- (m1==m2)?cout (m3!=m4)?cout cout (m4*m4).print(); //--------------- cout cout return 0; }
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


