Microecon questions. from 1-4. Plz help me.
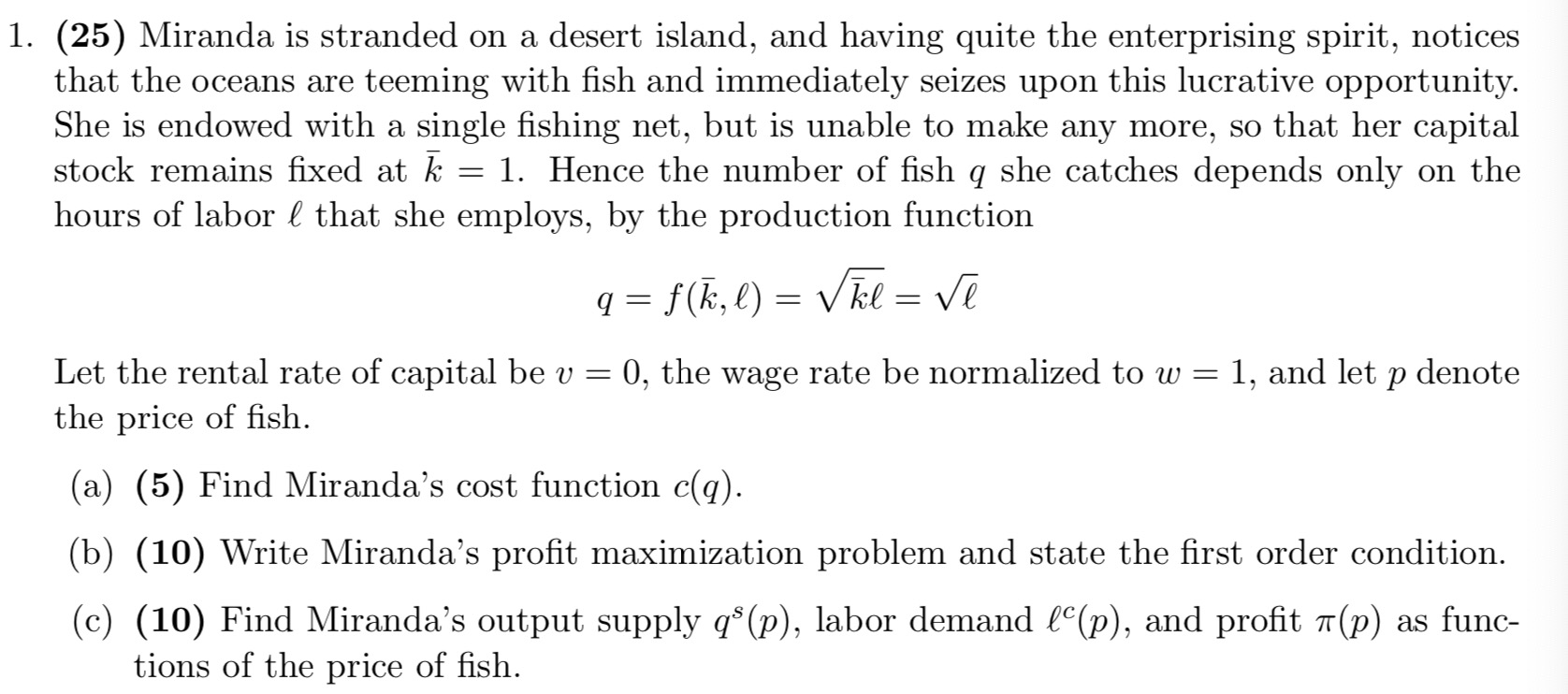
1. (25) Miranda is stranded on a desert island, and having quite the enterprising spirit, notices that the oceans are teeming with sh and immediately seizes upon this lucrative opportunity. She is endowed with a single shing net, but is unable to make any more, so that her capital stock remains xed at E = 1. Hence the number of sh q she catches depends only on the hours of labor E that she employs, by the production function emanate Let the rental rate of capital be 1) = 0, the wage rate be normalized to w = 1, and let p denote the price of sh. (a) (5) Find Miranda's cost function C(q). (b) (10) Write Miranda's prot maXiIniZatiOn problem and state the rst order condition. (0) (10) Find Miranda's output supply (13(1)), labor demand 66(1)), and prot 7r(p) as func- tions of the price of sh. 2. (25) For Miranda, catching sh is not just a protable activity, it is also her only viable source of food. She derives utility from consuming sh q as well as leisure time 1', by the function Man\") = WT?\" Again, let p denote the price of sh and let to = 1 be the hourly wage that Miranda earns from working. She has a total of E = 24 hours per day to divide between labor and leisure, so that 13+ 1' = 24. (a) (5) Suppose that Miranda's expenditure on sh comes entirely from her wages pq = w. Rewrite this condition as a budget constraint. What is the \"price\" of leisure and what is Miranda's \"income\" I? (b) (10) Write Miranda's utility maximization problem and state the rst order conditions. (c) (10) Find Miranda's demand for sh qd(p) and leisure Mp), and her indirect utility v(p). 3. (30) As may have been blatantly obvious to you all along, since Miranda is the only inhabitant of the island, all she's really doing is catching sh for herself and eating them. However, even a single agent economy such as this one has all of the features any economy would, such as supply and demand curves, and equilibrium prices and quantities. Miranda plays many roles in this economy, as all of the prot earned by Miranda the producer is transmitted to Miranda the shareholder, which represents additional income that Miranda the consumer can Spend On sh in addition to the labor income earned by Miranda the worker. (a) (10) Suppose Miranda earns both labor income and prot, so that pg = w}? + (19). Rewrite her utility maximization problem and nd the new demand for sh qd (p) and leisure Np). (b) (10) Find the equilibrium price p* and quantity q* of sh. (c) (10) Find the equilibrium hours of labor E'\" and labor 1"\". 4. (20) Miranda nds this entire exercise to be needlessly tedious. After all, it is rather ludicrous that she should be buying sh from herself from the wages she pays herself for her own labor and the prots she earns selling sh to herself. She gures that she can just ignore the entire market mechanism and prices entirely, and instead simplify her problem by just choosing some Optimal number of hours 4? to Spend gathering sh that would yield the most satisfying balance of food and leisure time. (a) (10) Write Miranda's utility function 11(6) solely in terms of her hours of labor 8 and state the rst order condition to her utility maximization problem. (b) (10) Find the optimal hours of labor 3* and how much sh (1* and leisure r* this would provide Miranda. Is this the same answer you had before