Microeconomic questions are asked below, provide solutions for these
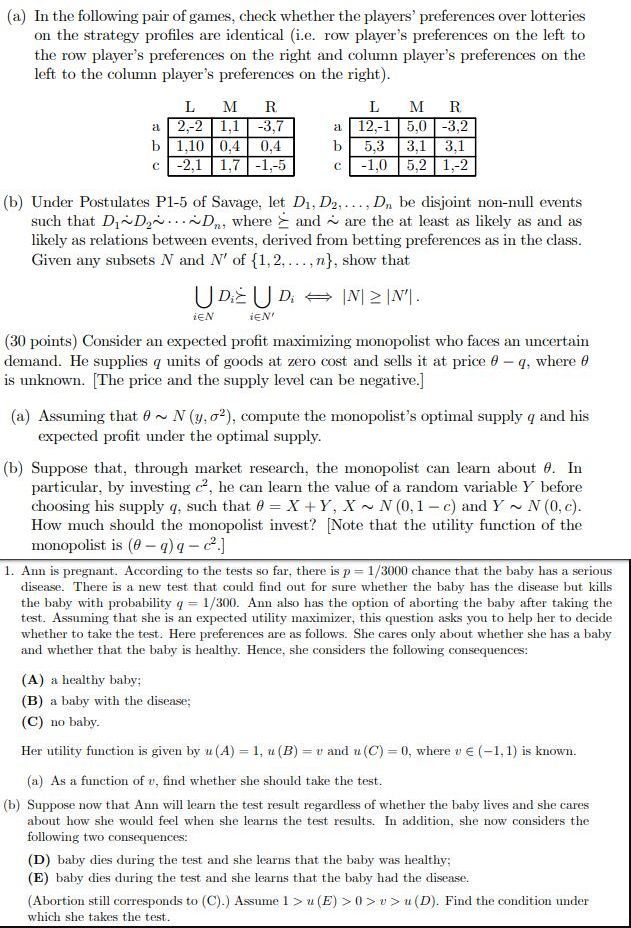
(a) In the following pair of games, check whether the players' preferences over lotteries on the strategy profiles are identical (i.e. row player's preferences on the left to the row player's preferences on the right and column player's preferences on the left to the column player's preferences on the right). L M R. L M R 2.-2 -3,7 12,-1 5,0 -3,2 1,10 0,4 0.4 b 5.3 3,1 3.1 -2,1 1,7 -1,-5 -1,0 5,2 1,-2 (b) Under Postulates P1-5 of Savage, let D1, D2, ...; D, be disjoint non-null events such that Di~Dy. ..~Dn, where > and ~ are the at least as likely as and as likely as relations between events, derived from betting preferences as in the class. Given any subsets N and N' of {1, 2. .... n}, show that UD UD; - IN12 IN'I. iEN iEN' (30 points) Consider an expected profit maximizing monopolist who faces an uncertain demand. He supplies q units of goods at zero cost and sells it at price 0 - q, where of is unknown. [The price and the supply level can be negative.] (a) Assuming that 8 ~ N (y, o'), compute the monopolist's optimal supply q and his expected profit under the optimal supply. (b) Suppose that, through market research, the monopolist can learn about 0. In particular, by investing c', he can learn the value of a random variable Y before choosing his supply q, such that 0 = X + Y, X ~ N (0, 1 - c) and Y ~ N (0, c). How much should the monopolist invest? [Note that the utility function of the monopolist is (0 - q) q - c2.] 1. Ann is pregnant. According to the tests so far, there is p = 1/3000 chance that the baby has a serious disease. There is a new test that could find out for sure whether the baby has the disease but kills the baby with probability q = 1/300. Ann also has the option of aborting the baby after taking the test. Assuming that she is an expected utility maximizer, this question asks you to help her to decide whether to take the test. Here preferences are as follows. She cares only about whether she has a baby and whether that the baby is healthy. Hence, she considers the following consequences: (A) a healthy baby; (B) a baby with the disease; (C) no baby. Her utility function is given by u (A) = 1, u (B) = v and u (C) =0, where v e (-1, 1) is known. (a) As a function of v, find whether she should take the test. (b) Suppose now that Ann will learn the test result regardless of whether the baby lives and she cares about how she would feel when she learns the test results. In addition, she now considers the following two consequences: (D) baby dies during the test and she learns that the baby was healthy; (E) baby dies during the test and she learns that the baby had the disease. (Abortion still corresponds to (C).) Assume 1> " (E) > 0 > > > u (D). Find the condition under which she takes the test.There are three periods, t = 0, 1,2. In t = 1 Mary maximizes her utility over leisure and consumption given the following function: UI(M, CI) = NICE subject to the following budget constraint: Ci + wiN = 24w1 where wi = 10. Note the price of the consumption good is assumed to be one in all periods. After she has made this decision, in t = 2 she maximizes this utility function: U2(N2, C2) = Nici subject to the following budget constraint: C2 + w2 N2 = 24w2 where w2 = 20. (a) (6 points) For t = 1, 2 calculate Mary's choice of leisure and consumption in each period. (b) (6 points ) For t = 1, provide economic intuition for the income and substitution effects of a wage increase on leisure. Can you say anything about the relative magnitudes of these income and substitution effects? (c) (7 points) Go back to your solution in part (a). If the interest rate is 10% per period, what is the present value of her consumption in t = 0? Please use 0.9 and 0.8 as approximations for 1/(1.1) and 1/(1.1) respectively. (d) (7 points) Mary now has the option of obtaining additional job training in t = 0 at an investment cost of $200. As a result, her wage rate increases in t = 1 to wj = 20 and in t = 2 to w2 = 30. Calculate the net present value of this investment on consumption. Consider only the value of consumption (and not the value of leisure). (e) (7 points ) For more general utility functions, when will the net present value of the investment on consumption from part (d) likely be negative? Use income and substi tution effects in your explanation. (f) (7 points) Does Mary have a Laffer curve for income taxes (as opposed to consumption taxes)