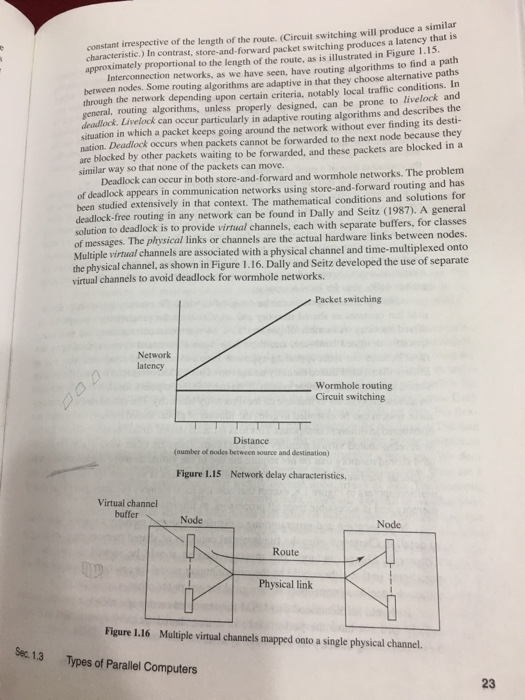
MIN) is a classification covering a multitude of configurations with the common charad- teristic of having a number of levels of switches. Switches in one level are connected to switches in adjacent levels in various symmetrical ways such that a path can made from one side of the network to the other side (and back sometimes). An example of a multistage interconnection network is the Omega network shown in Figure 1.14 (for eight inputs and Mulistage Interconnection Networks. The multistage interconnection netwolk has a very simple routing algorithm using the destination address. Inputs and outputs are given addresses as shown in the figure. Each switching cell requires one control signal to select either the upper output or the lower output (0 specifying the outputs). This network upper output and I specifying the lower). The most significant bit of the destination address is used to control the switch in the first stage: if the most significant bit is 0, the upper output is selected, and if it is 1, the lower output is selected. The next-most significant bit of i destination address is used to select the output of the switch in the next stage, and so on until the final output has been selected. The Omega network is highly blocking, though one path can always be made from any input to any output in a free network. Multistage interconnection networks have a very long history and were originally developed for telephone exchanges, and are still sometimes used for interconnecting computers or groups of computers for really large systems. For example, the ASCI White supercomputer uses an Omega multistage interconnection network. For more information on multistage interconnection networks see Duato, Yalamanchili, and Ni (1997). Communication Methods. The ideal situation in passing a message from a source node to a destination node occurs when there is a direct link between the source node and the destination node. In most systems and computations, it is often necessary to route a message through intermediate nodes from the source node to the destination node. There are two basic ways that messages can be transferred from a source to a destination: circuit switching and packet switching. 2 2 switch elements (straight-through or crossover connections) 001 001 010 011 010 011 Inputs Outputs 100 101 100 101 110 110 Figure 1.14 Omega network 3 Types of Parallel Computers 21