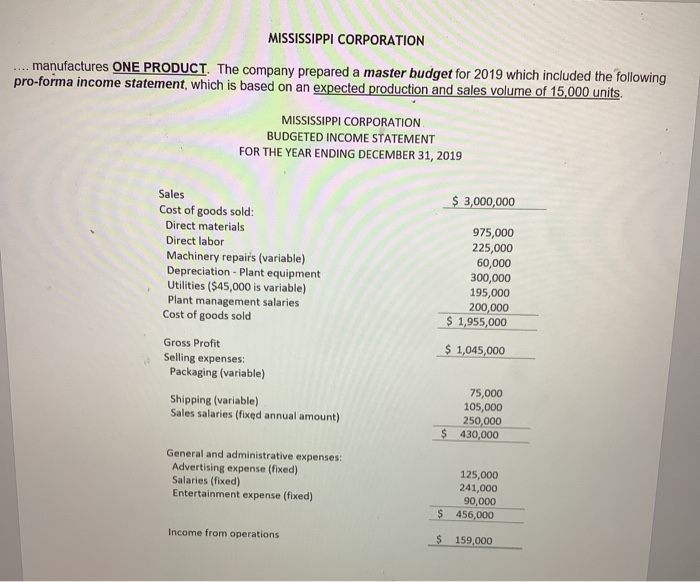
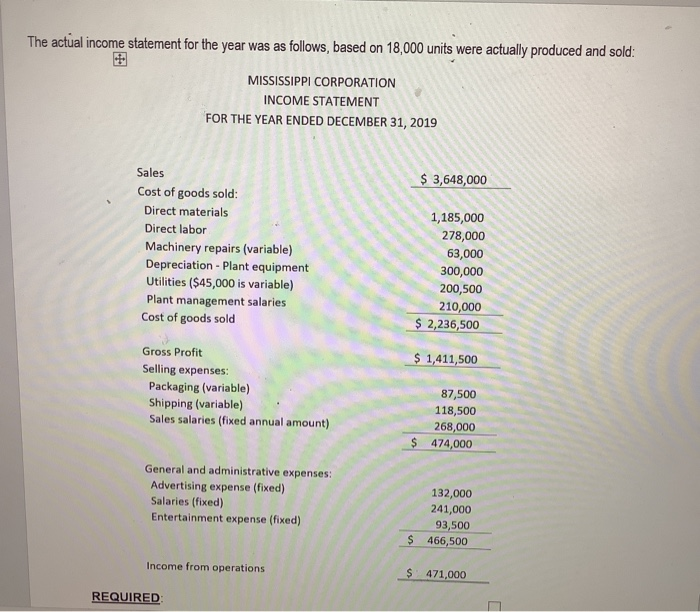
MISSISSIPPI CORPORATION manufactures ONE PRODUCT. The company prepared a master budget for 2019 which included the following pro-forma income statement, which is based on an expected production and sales volume of 15,000 units. MISSISSIPPI CORPORATION BUDGETED INCOME STATEMENT FOR THE YEAR ENDING DECEMBER 31, 2019 $ 3,000,000 Sales Cost of goods sold: Direct materials Direct labor Machinery repairs (variable) Depreciation - Plant equipment Utilities ($45,000 is variable) Plant management salaries Cost of goods sold 975,000 225,000 60,000 300,000 195,000 200,000 $ 1,955,000 $ 1,045,000 Gross Profit Selling expenses Packaging (variable) Shipping (variable) Sales salaries (fixed annual amount) 75,000 105,000 250,000 $ 430,000 General and administrative expenses: Advertising expense (fixed) Salaries (fixed) Entertainment expense (fixed) 125,000 241,000 90,000 $ 456,000 Income from operations $ 159,000 The actual income statement for the year was as follows, based on 18,000 units were actually produced and sold: MISSISSIPPI CORPORATION INCOME STATEMENT FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2019 $ 3,648,000 Sales Cost of goods sold: Direct materials Direct labor Machinery repairs (variable) Depreciation - Plant equipment Utilities ($45,000 is variable) Plant management salaries Cost of goods sold 1,185,000 278,000 63,000 300,000 200,500 210,000 $ 2,236,500 6 1,411,500 Gross Profit Selling expenses: Packaging (variable) Shipping (variable) Sales salaries (fixed annual amount) 87,500 118,500 268,000 $ 474,000 General and administrative expenses: Advertising expense (fixed) Salaries (fixed) Entertainment expense (fixed) 132,000 241,000 93,500 $ 466,500 Income from operations $ 471,000 REQUIRED 4. If, instead, the company manufactured MULTIPLE PRODUCTS, what might have accounted for the variances noted in #3 above? NOW ASSUME that the following standards have been established for the production of one unit: Direct materials 5 lbs @ $13 per lb. Direct Labor 1 hour @ $15 per hr. The actual results shown above reflect actual materials usage of 118,500 pounds and actual labor of 22,240 hours 5. What is meant by a standard, as used above? WHY are these important? 6. Further break down the Flexible Budget Variance (Standard Cost Variance) by computing and analyzing the direct materials price and usage (quantity) variances AND the direct labor rate and efficiency variances Explain TWO possible causes for each. Use the picture method as shown in the book 7. NOW ASSUME that the company uses a standard costing system for recording product costs. The company recognizes direct materials variances at the time of usage. Journalize the following, assuming that the company uses normal costing AND standard costing a) Direct materials purchases, on account b) Direct materials payments to vendors c) Direct materials usage in production d) Direct materials variances e) Direct labor incurrence in production f) Payments to direct labor employees MISSISSIPPI CORPORATION manufactures ONE PRODUCT. The company prepared a master budget for 2019 which included the following pro-forma income statement, which is based on an expected production and sales volume of 15,000 units. MISSISSIPPI CORPORATION BUDGETED INCOME STATEMENT FOR THE YEAR ENDING DECEMBER 31, 2019 $ 3,000,000 Sales Cost of goods sold: Direct materials Direct labor Machinery repairs (variable) Depreciation - Plant equipment Utilities ($45,000 is variable) Plant management salaries Cost of goods sold 975,000 225,000 60,000 300,000 195,000 200,000 $ 1,955,000 $ 1,045,000 Gross Profit Selling expenses Packaging (variable) Shipping (variable) Sales salaries (fixed annual amount) 75,000 105,000 250,000 $ 430,000 General and administrative expenses: Advertising expense (fixed) Salaries (fixed) Entertainment expense (fixed) 125,000 241,000 90,000 $ 456,000 Income from operations $ 159,000 The actual income statement for the year was as follows, based on 18,000 units were actually produced and sold: MISSISSIPPI CORPORATION INCOME STATEMENT FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2019 $ 3,648,000 Sales Cost of goods sold: Direct materials Direct labor Machinery repairs (variable) Depreciation - Plant equipment Utilities ($45,000 is variable) Plant management salaries Cost of goods sold 1,185,000 278,000 63,000 300,000 200,500 210,000 $ 2,236,500 6 1,411,500 Gross Profit Selling expenses: Packaging (variable) Shipping (variable) Sales salaries (fixed annual amount) 87,500 118,500 268,000 $ 474,000 General and administrative expenses: Advertising expense (fixed) Salaries (fixed) Entertainment expense (fixed) 132,000 241,000 93,500 $ 466,500 Income from operations $ 471,000 REQUIRED 4. If, instead, the company manufactured MULTIPLE PRODUCTS, what might have accounted for the variances noted in #3 above? NOW ASSUME that the following standards have been established for the production of one unit: Direct materials 5 lbs @ $13 per lb. Direct Labor 1 hour @ $15 per hr. The actual results shown above reflect actual materials usage of 118,500 pounds and actual labor of 22,240 hours 5. What is meant by a standard, as used above? WHY are these important? 6. Further break down the Flexible Budget Variance (Standard Cost Variance) by computing and analyzing the direct materials price and usage (quantity) variances AND the direct labor rate and efficiency variances Explain TWO possible causes for each. Use the picture method as shown in the book 7. NOW ASSUME that the company uses a standard costing system for recording product costs. The company recognizes direct materials variances at the time of usage. Journalize the following, assuming that the company uses normal costing AND standard costing a) Direct materials purchases, on account b) Direct materials payments to vendors c) Direct materials usage in production d) Direct materials variances e) Direct labor incurrence in production f) Payments to direct labor employees