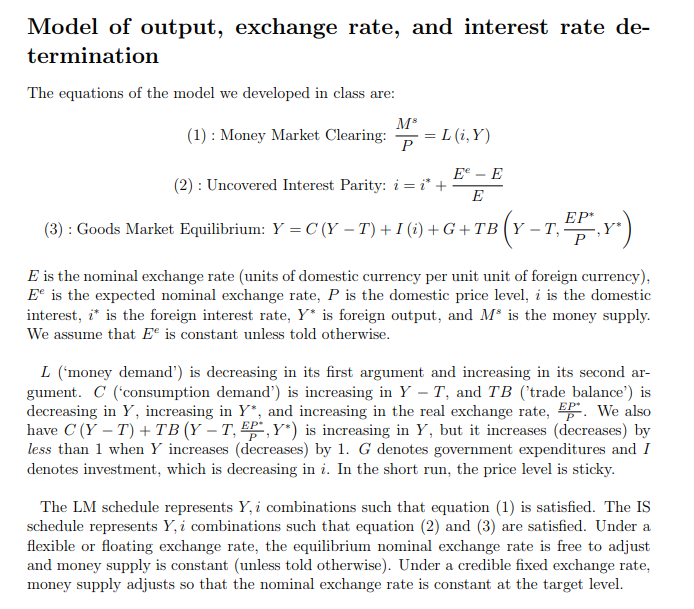
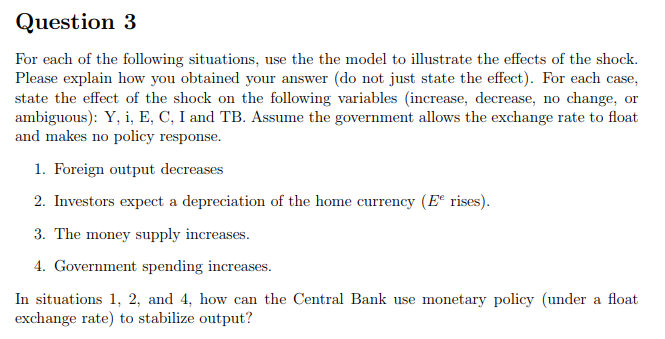
Model of output, exchange rate, and interest rate de- termination The equations of the model we developed in class are: (1) Money Market Clearing: = L (i,Y) _ EC (2) Uncovered Interest Parity: i = i* + E E EP* (3) Goods Market Equilibrium: Y = C (Y - T) + I (i)G+TB (Y -T,' P E is the nominal exchange rate (units of domestic currency per unit unit of foreign currency) Ee is the expected nominal exchange rate, P is the domestic price level, i is the domestic nterest, is the foreign interest rate, Y* is foreign output, and M* is the money supply We assume that Ee is constant unless told otherwise L ('money demand') is decreasing in its first argument and increasing in its second ar gument. C ('consumption demand') is increasing in Y - T, and TB ('trade balance') is decreasing in Y, increasing in Y*, and increasing in the real exchange rate, We also have C (Y T) + TB (Y - T,, Y*) is increasing in Y, but it increases (decreases) by less than 1 when Y increases (decreases) by 1. G denotes government expenditures and I denotes investment, which is decreasing in i. In the short run, the price level is sticky The LM schedule represents Y, i combinations such that equation (1) is satisfied. The IS schedule represents Y, i combinations such that equation (2) and (3) flexible or floating exchange rate, the equilibrium nominal exchange rate is free to adjust and money supply is constant (unless told otherwise). Under a credible fixed exchange rate, money supply adjusts so that the nominal exchange rate is constant at the target level satisfied. Under are a Question 3 use the the model to illustrate the effects of the shock (do not just state the effect). For each case the following variables (increase, decrease, no change ambiguous) Y, i, E, C, I and TB. Assume the government allows the exchange rate to float For each of the following situations Please explain how you obtained your answer state the effect of the shock on or and makes no policy response 1. Foreign output decreases depreciation of the home currency (Ee rises) 2. Investors expect 3. The money supply increases 4. Government spending increases In situations 1, 2, and 4, how can the Central Bank use exchange rate) to stabilize output? monetary policy (under a float Model of output, exchange rate, and interest rate de- termination The equations of the model we developed in class are: (1) Money Market Clearing: = L (i,Y) _ EC (2) Uncovered Interest Parity: i = i* + E E EP* (3) Goods Market Equilibrium: Y = C (Y - T) + I (i)G+TB (Y -T,' P E is the nominal exchange rate (units of domestic currency per unit unit of foreign currency) Ee is the expected nominal exchange rate, P is the domestic price level, i is the domestic nterest, is the foreign interest rate, Y* is foreign output, and M* is the money supply We assume that Ee is constant unless told otherwise L ('money demand') is decreasing in its first argument and increasing in its second ar gument. C ('consumption demand') is increasing in Y - T, and TB ('trade balance') is decreasing in Y, increasing in Y*, and increasing in the real exchange rate, We also have C (Y T) + TB (Y - T,, Y*) is increasing in Y, but it increases (decreases) by less than 1 when Y increases (decreases) by 1. G denotes government expenditures and I denotes investment, which is decreasing in i. In the short run, the price level is sticky The LM schedule represents Y, i combinations such that equation (1) is satisfied. The IS schedule represents Y, i combinations such that equation (2) and (3) flexible or floating exchange rate, the equilibrium nominal exchange rate is free to adjust and money supply is constant (unless told otherwise). Under a credible fixed exchange rate, money supply adjusts so that the nominal exchange rate is constant at the target level satisfied. Under are a Question 3 use the the model to illustrate the effects of the shock (do not just state the effect). For each case the following variables (increase, decrease, no change ambiguous) Y, i, E, C, I and TB. Assume the government allows the exchange rate to float For each of the following situations Please explain how you obtained your answer state the effect of the shock on or and makes no policy response 1. Foreign output decreases depreciation of the home currency (Ee rises) 2. Investors expect 3. The money supply increases 4. Government spending increases In situations 1, 2, and 4, how can the Central Bank use exchange rate) to stabilize output? monetary policy (under a float








