Question
module ALU( input logic [3:0] aluin_a,input logic [3:0] aluin_b, input logic [3:0] opcode, input Cin, output logic [3:0] alu_out, output logic Cout, output logic OF,
module ALU(
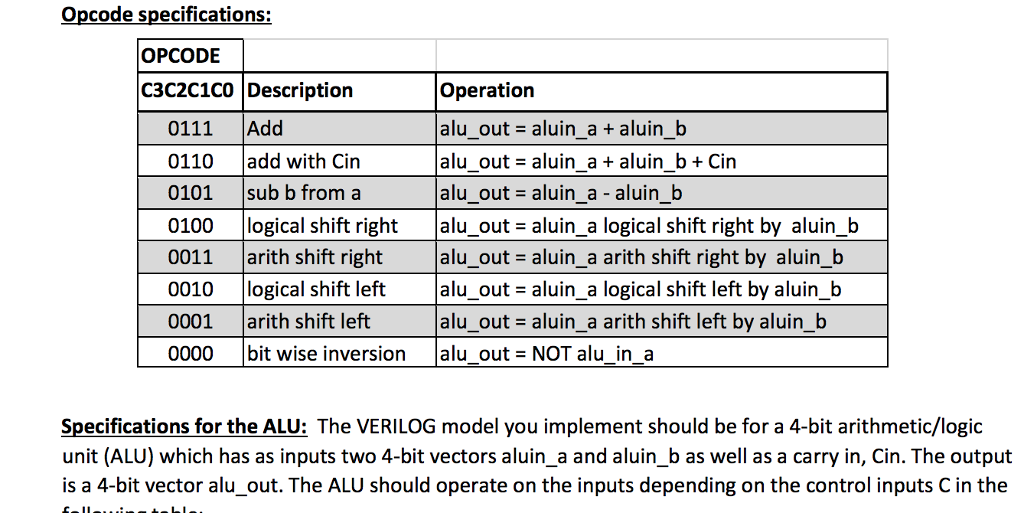
input logic [3:0] aluin_a,input logic [3:0] aluin_b, input logic [3:0] opcode, input Cin, output logic [3:0] alu_out, output logic Cout, output logic OF, output logic zero); // Declare any internal logic signals here //your code. Tip : Please try to indent your code in a proper manner. You will save lot of time while debugging if anything doesnt work the way it should // endmodule 2. Inside the top-level, you may choose to instantiate a 4-bit adder which in turn instantiates 1- bit adder modules. Inputs to the 4-bit adder can be chosen based on OPCODES using a case statement so that you can do shifting. You may also choose to just do an addition operation yourself here and let the compiler / SystemVerilog choose the best adder for you. 3. 4-bit subtraction can be implemented by taking the 2s compliment of aluin_b prior to presenting it as an input to the adder module if you choose to use your own adder module Opcode specifications: Specifications for the ALU: The VERILOG model you implement should be for a 4-bit arithmetic/logic unit (ALU) which has as inputs two 4-bit vectors aluin_a and aluin_b as well as a carry in, Cin. The output is a 4-bit vector alu_out.
write the Verilog code for a 4-bit arithmetic/logic unit (ALU)?
The ALU will be 4bits wide.
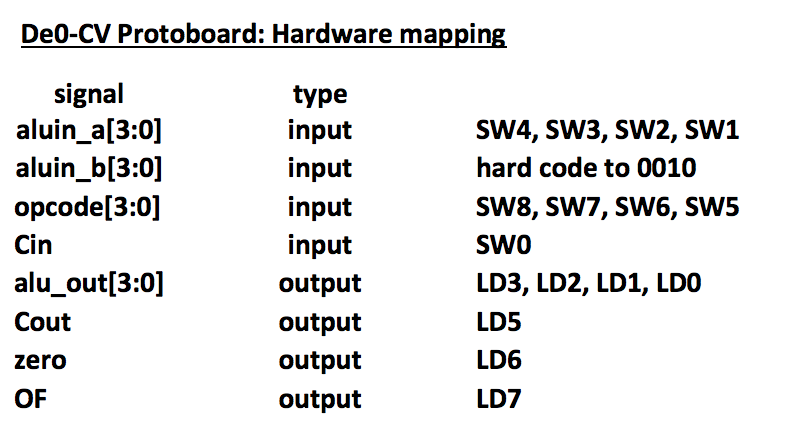
List of Input signals: aluin_a 4 bits : 4 bit primary input 1
aluin_b 4 bits : 4 bit primary input 2
opcode 4 bits : 4 bit input to specify operand on primary inputs 1 and 2
Cin 1 bit : 1 bit input for Carry-in
List of Output signals:
alu_out 4 bits : 4 bit primary output
Cout 1 bit : 1 bit output for Carry Out
OF 1 bit : 1 bit flag to denote Over Flow in alu_out
zero 1bit : 1 bit flag to denote zero result in alu_out
1.a 4-bit adder which in turn instantiates 1- bit adder modules. Inputs to the 4-bit adder can be chosen based on OPCODES using a case statement so that you can do shifting.
2.4-bit subtraction can be implemented by taking the 2s compliment of aluin_b prior to presenting it as an input to the adder module.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


