Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Montoure Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following calendar-year purchases and sales transactions Activities Units Acquired at Cost 540 units $40
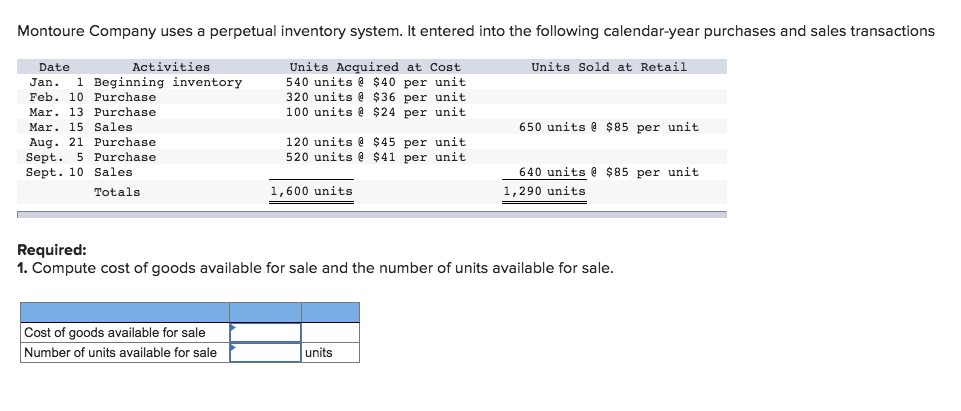

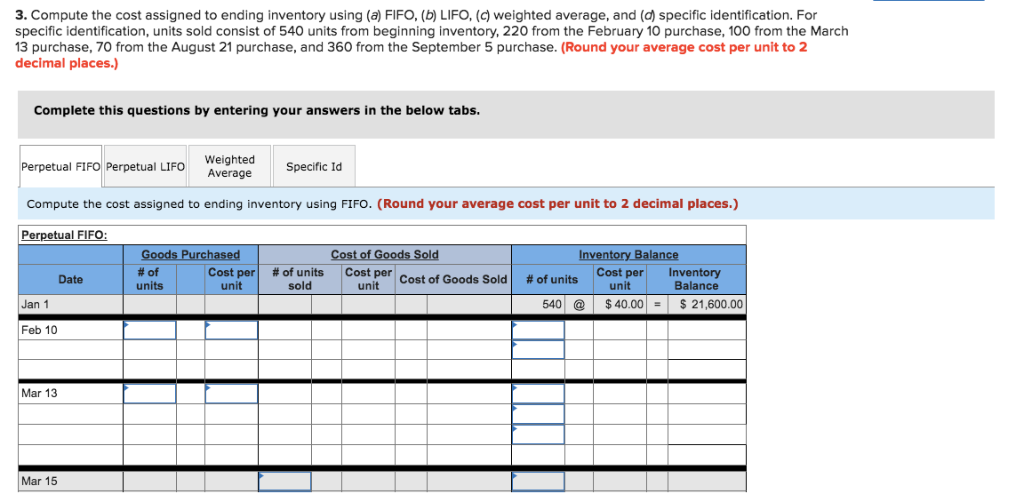
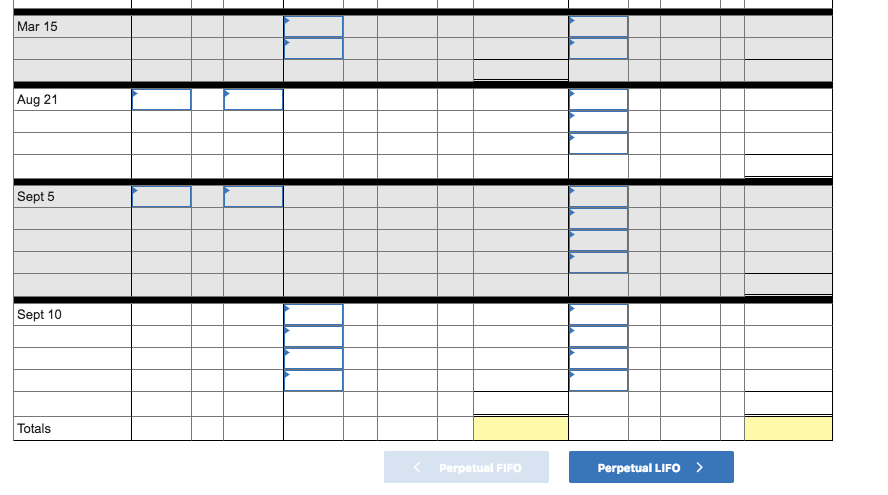
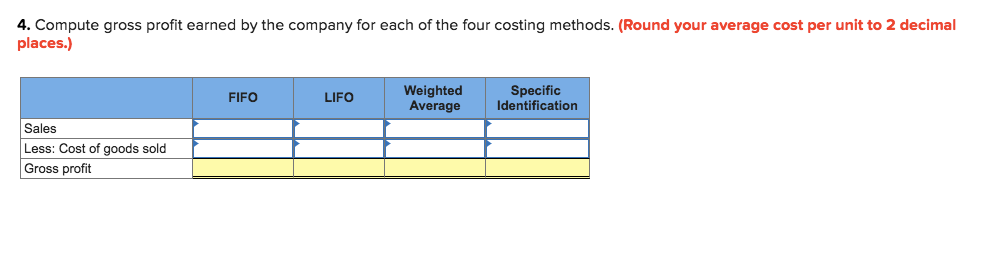
Montoure Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following calendar-year purchases and sales transactions Activities Units Acquired at Cost 540 units $40 per unit 320 units $36 per unit 100 units $24 per unit Units Sold at Retail Date Jan. 1 Beginning inventory Feb. 10 Purchase Mar. 13 Purchase Mar. 15 Sales Aug. 21 Purchase Sept. 5 Purchase Sept. 10 Sales 650 units $85 per unit 120 units $45 per unit 520 units $41 per unit 640 units $85 per unit 1,290 units Totals 1,600 units Required: 1. Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale Cost of goods available for sale Number of units available for sale units 2. Compute the number of units in ending inventory. Ending inventory units 3 Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using a FIFb) LIFO c weighted average and d specific identification. For specific identification, units sold consist of 540 units from beginning inventory, 220 from the February 10 purchase, 100 from the March 13 purchase, 70 from the August 21 purchase, and 360 from the September 5 purchase. (Round your average cost per unit to 2 decimal places.) Complete this questions by entering your answers in the below tabs. Weighted Average Perpetual FIFO Perpetual LIFO Specific Id Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using FIFO. (Round your average cost per unit to 2 decimal places.) Perpetual FIFO Cost of Goods Sold Inventory Balance #of units Cost per unit Cost per Cost of Goods Sold! # of units Cost per Inventory | Date sold unit #Of units unit Balance Jan 1 540$40.0021,600.00 Feb 10 Mar 13 Mar 15 Mar 15 Aug 21 Sept 5 Sept 10 Totals Perpetual FIFO Perpetual LIFO 4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods. (Round your average cost per unit to 2 decimal places.) Weighted Average Identification Specific FIFO LIFO Sales Less: Cost of goods sold Gross profit
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


