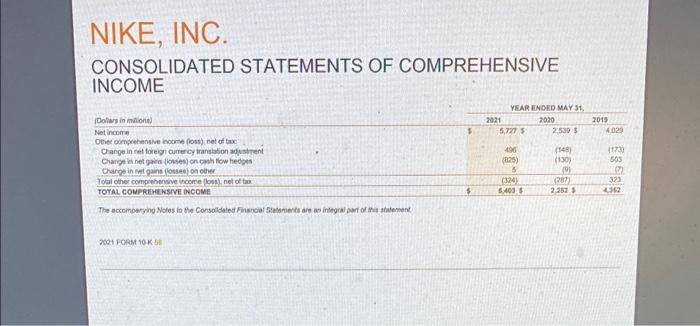
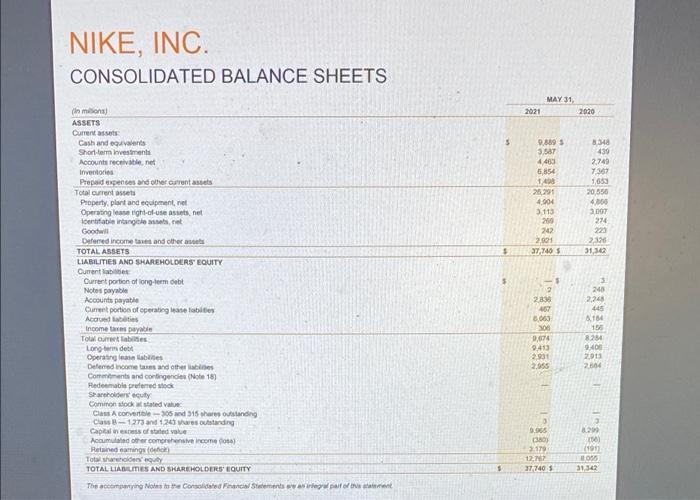
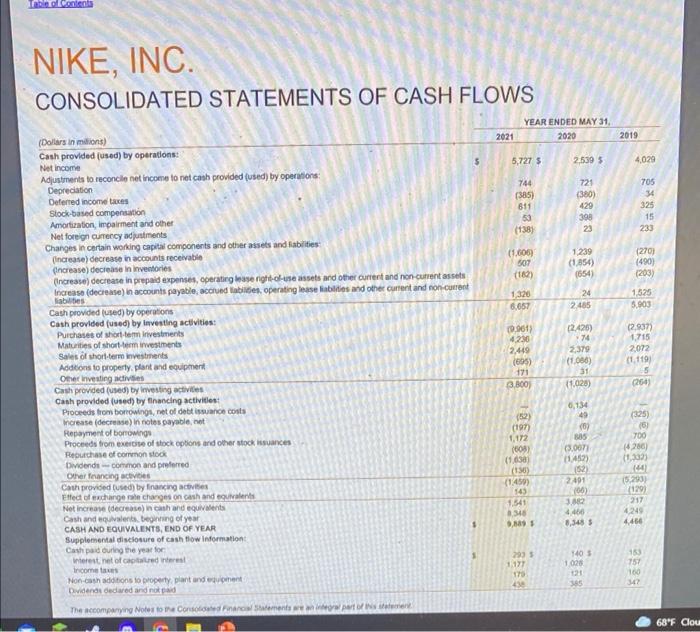
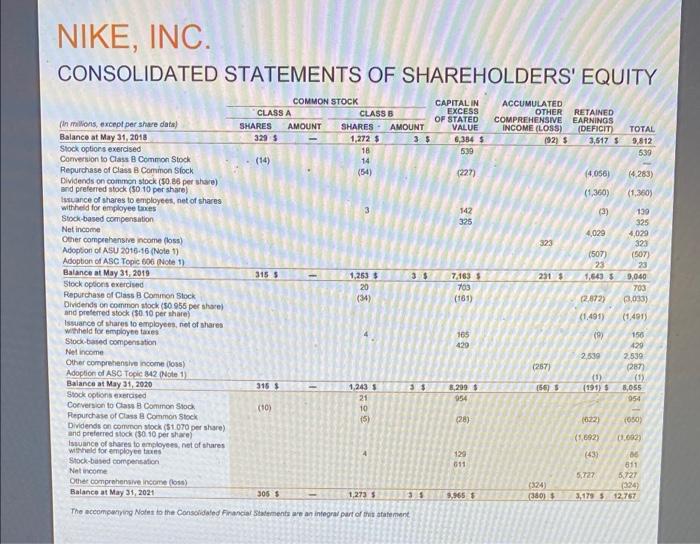
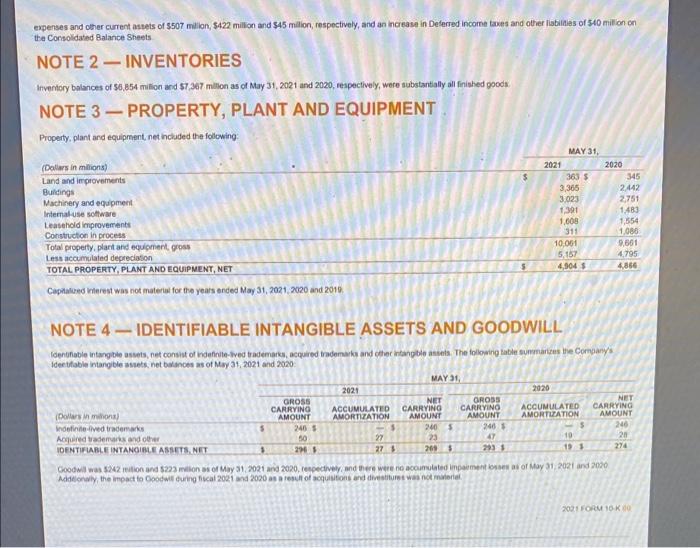
Moving to another question will save this response. Question 31 Use the following formula to calculate Nike's accounts receivable turnover ratio at the last two balance sheet dates: Account receivable turnover ratio = Revenues/Accounts receivable, net Select the correct answer below O a. The company collected accounts receivable faster in the most recent reporting period than the prior reporting period Ob. The company collected accounts receivable slower in the most recent reporting period than the prior reporting period Oc. The company collected accounts receivable at the same rate as in the prior reporting period. NIKE, INC. CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME (in milions except per share data) 2021 Revenues 5 Cost of sales Gross prof Demand creation expense Operating overhead expense Total setting and administrative expense Interest expense (income), net Other (income) expense, net Income before income taxes Income tax expense NET INCOME Earnings per common share Basic Diluted Weighted average common shares outstanding Basic Diluted The accompanying Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements are an integral part of this statement $ YEAR ENDED MAY 31, 2020 37403 S 21,162 16,241 3.592 9.534 13,120 69 139 2,887 348 2,639 44,538 24,576 19.902 3,114 9.911 13.025 262 14 6,061 004 6.727 3.64 356 1,5730 1,5004 1.63 5 1.60 $ 2019 4801 772 4,029 2.56 2.49 15797 1018.4 2021 FORM 10-K 57 1,5568 1.501.6 39,117 21,643 17474 3.753 8,940 12,702 40 (78) NIKE, INC. CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME YEAR ENDED MAY 31, (Dollars in millions) 2021 2020 Net income 2,539 $ Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax Change in net foreign currency translation adjustment (148) (130) Change in net gains (losses) on cash flow hedges Change in net gains (losses) on other (9) Total other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax (287) TOTAL COMPREHENSIVE INCOME 2,282 $ The accompanying Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements are an integral part of this statement 2021 FORM 10-K 58 $ 5,727 496 (825) 5 (324) 5,403 2019 4,029 (173) 503 3 323 4,362 NIKE, INC. CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS (in millions) ASSETS Current assets Cash and equivalents Short-term investments Accounts receivable, net Inventories Prepaid expenses and other current assets Total current assets Property, plant and equipment, net Operating lease right-of-use assets, net Identifiable intangible assets, net Goodwill Defemed income taxes and other assets TOTAL ASSETS LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY Current abilities Current portion of long-term debt Notes payable Accounts payable Cument portion of operating lease labities Accrued lablities Income taxes payable Total current labiies Long-term dett Operating lease liables Deferred income taxes and other liables Commitments and contingencies (Note 18) Redeemable preferred stock Shareholders' equity Common stock at stated value Class A convertible-305 and 315 shares outstanding Class B-1,273 and 1,243 shares outstanding Capital in excess of stated value Accumulated other comprehensive income (os) Retained earnings (de) Total shareholders' equity TOTAL LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY The accompanying Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements are an integral part of this statement S S 2021 MAY 31, 9,889 3,587 4,463 6,854 1,498 26,291 4,904 3,113 269 242 2,921 37,740 2,836 467 8,063 306 9,674 9,413 2,931 2.965 0 9.965 (380) 3:179 12,767 37.740 1 2020 8,348 439 2,749 7,367 1,653 20,556 4,000 3,097 274 223 2,326 31,342 3 248 2,248 445 A104 156 8.284 9,400 2.913 2604 8.299 (06) (191) 055 31,342 Table of Contents NIKE, INC. CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS (Dollars in millions) 2021 Cash provided (used) by operations: Net income Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided (used) by operations: Depreciation Deferred income taxes Stock-based compensation Amortization, impairment and other Net foreign currency adjustments Changes in certain working capital components and other assets and abilities: (Increase) decrease in accounts receivable (ncrease) decrease in inventories (Increase) decrease in prepaid expenses, operating lease right-of-use assets and other current and non-current assets Increase (decrease) in accounts payable, accrued abilities, operating lease liabilities and other current and non-current liabilities Cash provided (used) by operations Cash provided (used) by Investing activities: Purchases of short-term investments Maturities of short-term investments Sales of short-term investments Additions to property, plant and equipment Other investing activities Cash provided (used) by investing activities Cash provided (used) by financing activities: Proceeds from borrowings, net of debt issuance costs Increase (decrease) in notes payable, net Repayment of bonowings Proceeds from exercise of stock options and other stock issuances Repurchase of common stock Dividends common and preferred Other financing activities Cash provided (used) by financing activites Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and equivalents Net increase (decrease) in cash and equivalents Cash and equivalents, beginning of year CASH AND EQUIVALENTS, END OF YEAR Supplemental disclosure of cash flow Information: Cash paid during the year for Interest, net of capitalred interest Income taxes Non-cash additions to property, plant and equipment Dividends declared and not paid The accompanying Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements are an integral part of this statement YEAR ENDED MAY 31, 2020 2,539 $ 721 (380) 429 398 23 1,239 (1,854) (654) 24 2,485 (2426) 74 2,379 (1,066) 31 (1.028) 6,134 49 (6) 5,727 S 744 (385) 611 53 (138) (1,006) 507 (182) 1,326 6,657 (9.961) 4,230 2,449 (605) 171 (3,800) (52) (197) 1,172 (608) (1,038) (136) (1459) 143 1.541 8,346 9,809 293 1,177 179 438 885 (3.007) (1452) (52) 2491 (06) 3882 4,466 8,348 S 140 S 1,026 121 385 2019 4,029 705 34 325 15 233 (270) (490) (203) 1,525 5,903 (2,937) 1,715 2,072 (1,119) (264) (325) (6) 700 (4,266) (1,332) (44) (5,293) (129) 217 4,249 4,466 153 757 160 347 68F Clou NIKE, INC. CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY COMMON STOCK CLASS A CLASS B CAPITAL IN EXCESS OF STATED VALUE ACCUMULATED OTHER RETAINED COMPREHENSIVE EARNINGS INCOME (LOSS) (DEFICIT) TOTAL (in millions, except per share data) Balance at May 31, 2018 Stock options exercised SHARES AMOUNT 329 S SHARES AMOUNT 1,272 $ 3 $ (92) $ 3,517 $ 9,812 18 539 Conversion to Class B Common Stock (14) 14 (54) (4.056) (4,283) Repurchase of Class B Common Stock Dividends on common stock ($0.86 per share) and preferred stock (50 10 per share) (1,360) (1,360) Issuance of shares to employees, net of shares withheld for employee taxes (3) 139 325 Stock-based compensation Net income Other comprehensive income (loss) Adoption of ASU 2016-16 (Note 1) Adoption of ASC Topic 606 (Note 1) Balance at May 31, 2019 1,253 $ Stock options exercised 20 (34) Repurchase of Class B Common Stock Dividends on common stock (50 955 per share) and preferred stock ($0.10 per share) Issuance of shares to employees, net of shares withheld for employee taxes Stock-based compensation Net income Other comprehensive income (loss) Adoption of ASC Topic 842 (Note 1) Balance at May 31, 2020 315 $ Stock options exercised Conversion to Class B Common Stock (10) Repurchase of Class B Common Stock (5) Dividends on common stock ($1.070 per share) and preferred stock (30. 10 per share) Issuance of shares to employees, net of shares withheld for employee taxes Stock-based compensation Net income Other comprehensive income (loss) Balance at May 31, 2021 306 S - 1,273 S 35 The accompanying Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements are an integral part of this statement 315 1,243 21 10 3.5 3$ 6,384 $ 539 (227) 142 325 7,163 $ 703 (161) 165 429 8,299 $ 954 (28) 129 611 9,965 323 231 $ (267) (54) (324) (360) 4,029 (507) 23 1,643 (2.872) (1.491) (9) 2,539 (1) 4,029 323 (507) 23 9,040 703 (3,033) (1,491) 156 429 2,539 (287) (1) (191) 8,055 954 (622) (050) (1,692) (1.002) (43) 86 611 5,727 5,727 (324) 3,179 $ 12,767 Cash and equivalents represent cash and short-term, highly liquid investments, that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash, and so near their matunity they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates, including commercial paper, U.S. Treasury, U.S. Agency, money market funds, time deposits and corporate debt securities with maturities of 90 days or less at the date of purchase SHORT-TERM INVESTMENTS Short-term investments consist of highly liquid investments, including commercial paper, U.S. Treasury, U.S. Agency time deposits and corporate debt securities with maturities over 90 days at the date of purchase At May 31, 2021 and 2020, Short-term investments consisted of available-for-sale debt securities, which are recorded at fair value with unrealized gains and losses reported, net of tax, in Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), unless unrealized losses are determined to be unrecoverable. Realized gains and losses on the sale of securities are determined by specific identification. The Company considers all available-for-sale debt securities, including those with maturity dates beyond 12 months, as available to support current operational liquidity needs and, therefore, classifies all securities with maturity dates beyond 90 days at the date of purchase as current assets within Short-term investments on the Consolidated Balance Sheets Refer to Note 6-Fair Value Measurements for more information on the Company's Short-term investments. ALLOWANCE FOR UNCOLLECTIBLE ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE Accounts receivable, net consist primarily of amounts due from customers. The Company makes ongoing estimates relating to the collectability of its accounts receivable and maintains an allowance for expected losses resulting from the inability of its customers to make required payments. In addition to judgments about the creditworthiness of significant customers based on ongoing credit evaluations, the Company considers historical levels of credit losses, as well as macroeconomic and industry trends, such as the impacts of COVID-19, to determine the amount of the allowance. Accounts receivable with anticipated collection dates greater than 12 months from the balance sheet date and related allowances are considered non-current and recorded in Deferred income taxes and other assets. The allowance for uncollectible accounts receivable was $93 million and $214 million as of May 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively INVENTORY VALUATION Inventories are stated at lower of cost and net realizable value, and valued on either an average or a specific identification cost basis. In some instances, the Company ships products directly from its suppliers to the customer, with the related inventory and cost of sales recognized on a specific identification basis. Inventory costs primarily consist of product cost from the Company's suppliers, as well as inbound freight, import duties, taxes, insurance, logistics and other handling fees PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT AND DEPRECIATION Property, plant and equipment are recorded at cost. Depreciation is determined on a straight-aine basis for land improvements, buildings and leasehold improvements over 2 to 40 years and for machinery and equipment over 2 to 15 years Depreciation and amortization of assets used in manufacturing, warehousing and product distribution are recorded in Cost of sales. Depreciation and amortization of all other assets are recorded in Operating overhead expense SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT COSTS Expenditures for major software purchases and software developed for internal use are capitalized and amortized over a 2- to 12-year period on a straight-line basis. The Company's policy provides for the capitalization of external direct costs associated with developing or obtaining internal use computer software. The Company also capitalize certain payroll and payroll-related costs for employees who are directly associated with internal use computer software projects. The amount of capitalizable payroll costs with respect to these employees is limited to the time directly spent on such projects. Costs associated with preliminary project stage activities, training, maintenance and all other post-implementation stage activities are expensed as incurred. Development costs of computer software to be sold, leased or otherwise marketed as an integral part of a product are subject to capitalization beginning when a products technological feasibility has been established and ending when a product is available for general release to customers in most instances, the Company's products are released soon after technological feasibility has been established: therefore, software development costs incurred subsequent to achievement of technological feasibility are usually not significant, and generally, most software development costs have been expensed as incurred payments, which are based on a percent of retail sales over specified levels or adjust periodically for inflation as a result of changes in a published index, primarily the Consumer Price Index, and are expensed as incurred FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS The Company measures certain financial assets and liabilities at fair value on a recurring basis, including derivatives, equity securities and available-for-sale debt securities. Fair value is the price the Company would receive to sell an asset or pay to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction with a market participant at the measurement date. The Company uses a three-level hierarchy established by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) that prioritizes fair value measurements based on the types of inputs used for the various valuation techniques (market approach, income approach and cost approach) The levels of the tair value hierarchy are described below: Level 1: Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilites. Level 2 Inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, these include quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets and quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active. Level 3: Unobservable inputs with little or no market data available, which require the reporting ensity to develop its own assumptions The Company's assessment of the significance of a particular input to the fair value measurement in its entirety requires judgment and considers factors specific to the asset or lability. Financial assets and liabilities are classified in their entirety based on the most conservative level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement Pricing vendors are utilized for a majority of Level 1 and Level 2 investments. These vendors either provide a quoted market price in an active market or use observable inputs without applying significant adjustments in their pricing Observable inputs include broker quotes, interest rates and yield curves observable at commonly quoted intervals, volatilities and credit risks. The fair value of derivative contracts is determined using observable market inputs such as the daily market foreign cumency rates, forward pricing curves, currency volatities, currency correlations and interest rates and considers nonperformance risk of the Company and its counterparties The Company's fair value measurement process includes comparing fair values to another independent pricing vendor to ensure appropriate fair values are recorded. Refer to Note 6-Fair Value Measurements for additional information FOREIGN CURRENCY TRANSLATION AND FOREIGN CURRENCY TRANSACTIONS Adjustments resulting from translating foreign functional cumency financial statements into U.S. Dollars are included in the foreign currency translation adjustment, a component of Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in Total shareholders' equity The Company's global subsidiaries have various monetary assets and liabilities, primarily receivables and payables, which are denominated in currencies other than their functional currency. These balance sheet items are subject to remeasurement, the impact of which is recorded in Other (income) expense, net, within the Consolidated Statements of income. ACCOUNTING FOR DERIVATIVES AND HEDGING ACTIVITIES The Company uses derivative financial instruments to reduce ts exposure to changes in foreign currency exchange rates and interest rates All derivatives are recorded at fair value on the Consolidated Balance Sheets and changes in the fair value of derivative financial instruments are either recognized in Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) (a component of Total shareholders' equity), Long-term debt or Net income depending on the nature of the underlying exposure, whether the derivative is formally designated as a hedge and, if designated, the extent to which the hedge is effective. The Company classifies the cash flows at settement from derivatives in the same category as the cash flows from the related hedged items. For undesignated hedges and designated cash flow hedges, this is primarity within the Cash provided by operations component of the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows For designated net investment hedges, this is within the Cash used by investing activities component of the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows. For the Company's fair value hedges, which are interest rate swaps used to mitigate the change in fair value of its fixed-rate debl attributable to changes in interest rates, the related cash flows from periodic interest payments are refled within the Cash provided by operations component of the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows Refer to Note 14-Risk Management and Derivatives for addeional information on the Company's risk management program and derivatives 2021 FORM 10-KIT expenses and other current assets of $507 million, $422 million and $45 million, respectively, and an increase in Deferred income taxes and other liabilities of 540 million on the Consolidated Balance Sheets NOTE 2-INVENTORIES Inventory balances of $6,854 million and $7,367 million as of May 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively, were substantially all finished goods NOTE 3 PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT Property, plant and equipment, net included the following: MAY 31, (Dollars in millions) 363 $ 345 Land and improvements Buildings 3,365 2,442 Machinery and equipment 3,023 2,751 Internal-use software 1,391 1,483 1,008 Leasehold improvements 1,554 311 1,086 Construction in process Total property, plant and equipment, gross 10,001 9,661 5,157 Less accumulated depreciation 4,795 4,904 $ TOTAL PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT, NET 4,866 Capitalized interest was not material for the years ended May 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019. NOTE 4-IDENTIFIABLE INTANGIBLE ASSETS AND GOODWILL Identifiable intangible assets, net consist of indefinite-lived trademarks, acquired trademarks and other intangible assets. The following table summarizes the Company's Identifiable intangible assets, net balances as of May 31, 2021 and 2020 MAY 31, 2021 2020 NET NET GROSS CARRYING AMOUNT ACCUMULATED CARRYING AMOUNT AMORTIZATION (Dollars in miliona) GROSS ACCUMULATED CARRYING CARRYING AMORTIZATION AMOUNT AMOUNT S $ 240 246 $ 47 27 27 1 293 5 209 1 indefinite-lived trademarks 246 19 Acquired trademarks and other 28 246 $ 50 2945 1 19 1 274 IDENTIFIABLE INTANGIBLE ASSETS, NET Goodwill was $242 rition and $223 million as of May 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively, and there were no accumulated impairment losses as of May 31, 2021 and 2020 Additionally, the impact to Goodwill during fiscal 2021 and 2020 as a result of acquisitions and divestitures was not materiel. 2021 FORM 10-K00 2021 2020