Question
Multilayer films are utilized to improve the barrier properties of packaging for food products during storage by tailoring to the specific needs of the product.
Multilayer films are utilized to improve the barrier properties of packaging for food products during storage by tailoring to the specific needs of the product. Incorporating reactive scavenging agents also improves barrier properties. A model was created using a 1D reaction-diffusion mass transfer model to predict and optimize the barrier-to-oxygen performance and the physical configurations of the co-extruded multilayer active films, which results in partial differential equations. However, by assuming that the mass transfer of oxygen occurs under steady-state conditions and the number of scavenging moles does not change over time, the model can be simplified to an ordinary differential equation.
A) Create a graph to represent the concentration of oxygen in each layer of the package.
B) Examine how the thickness of the layers affects the concentration of oxygen by creating graphs for different thicknesses.
Provide a diagram of the packaging design.
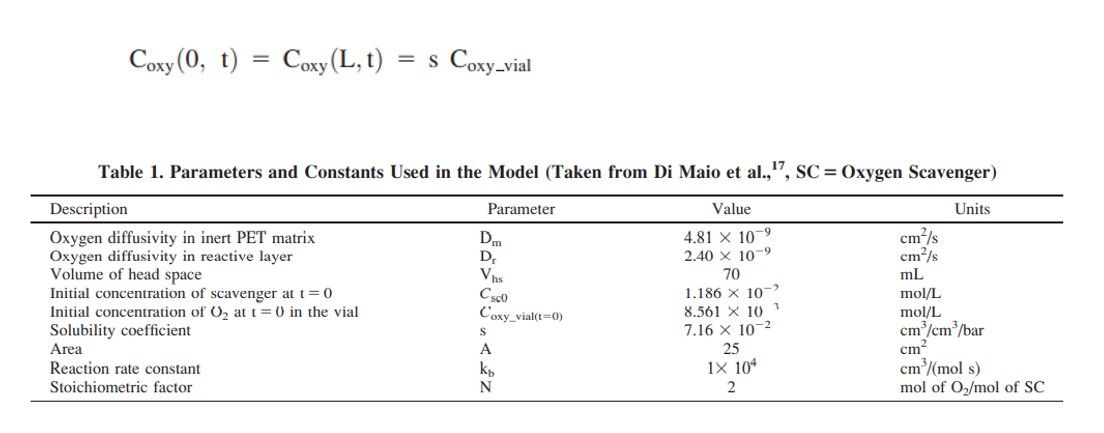
Include all the information used in the calculations in the report.
Include a detailed explanation of how the model equation was solved, including the boundary conditions used.
Examine how the thickness of each layer impacts the movement of oxygen through the package. Please consider using this packaging to protect fresh food from the atmospheric environment. Assume that oxygen partial pressure on the food side of the packaging should not exceed 0.1 atm. The other side of the film is in contact with air.
The oxygen concentrations at the film/film interface can be assumed the same.
Use equations and values in pictures.
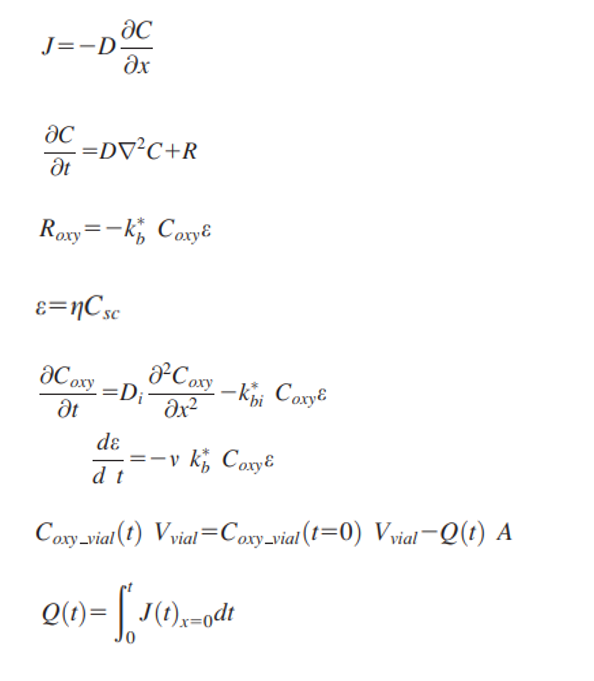
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


