Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following characteristics does NOT pertain to











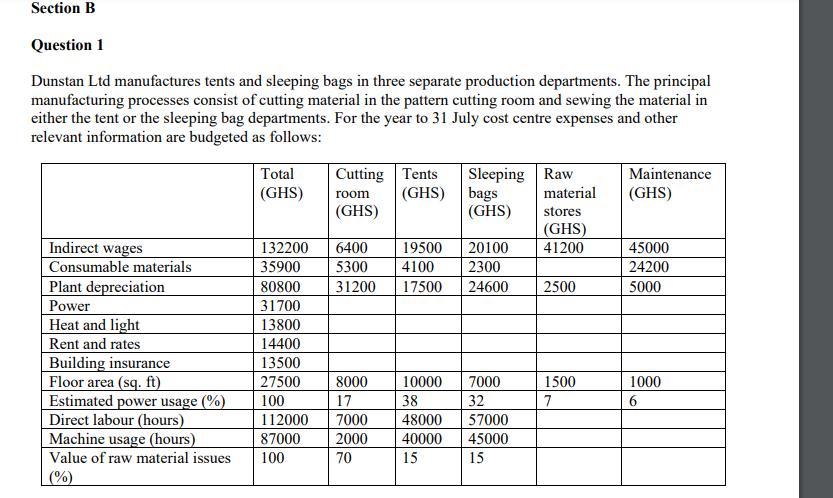


Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following characteristics does NOT pertain to management accounting? a. provides information and estimates about future activity b. generates specific-purpose financial statements and reports c. provides financial and operating data multidisciplinary in scope d. has externally imposed standards 2. Which of the following does NOT describe management accounting? a. evaluation of segments or products within the firm b. emphasis on the future c. externally focused d. detailed information 3. Setting the company's profit targets for the upcoming year is an example of the management function of a. planning. b. control. c. variance analysis. d. internal auditing. 4. Evaluating the performance of a segment of the company is an example of a. planning. b. control. c. internal auditing. d. both a and c. 5. Which one of the following statements about ethical behaviour is true? a. Ethical behaviour is not guided by well-defined rules and is often subjective. b. Ethical behaviour is best described as doing actions that are permitted by law. c. Ethical behaviour always involves choosing between actions that are clearly right or wrong. d. Ethical behaviour is best guided by a policy of placing corporate performance above individual ends. 6. Financial accounting information is least useful in providing: a. information for stating corporate wide goals. b. information for internal decision makers. c. periodic reports for shareholders. d. aggregate information about an organization's assets, obligations and performance. 7. Sunk costs are a. future costs that have no benefit. b. relevant costs that have only short-run benefits. c. target costs. d. cannot be avoided. 8. Which one of the following sentences about step costs is true? a. Step costs increase with each additional unit produced. b. Step costs have no relation to number of units produced. c. Step costs are constant within certain ranges of activity but differ outside those ranges of activity. d. Step costs are variable within narrowly defined ranges of activity, but constant over wider ranges of activity. 9. Which of the following is an example of a possible cost object? a. a product b. a customer c. a department d. All of these could be possible cost objects. 10. Which of the following costs incurred by a furniture manufacturer would be a product cost? a. lumber b. office salaries c. commissions paid to sales staff d. controller's salary 11. Which of the following costs is an indirect product cost? a. property taxes on plant facilities b. wages of assembly workers c. materials used d. president's salary 12. All of Jill Enterprise's operations are housed in one building with the costs of occupying the building accumulated in a separate account. The total costs incurred in May amounted to GHS24,000. The company allocates these costs on the basis of square feet of floor space occupied. Administrative offices, sales offices, and factory operations occupy 9,000, 6,000, and 30,000 square feet, respectively. How much will be classified as a product cost for May? a. GHS4,800 b. GHS3,200 c. GHS16,000 d. GHS24,000 13. Prime product costs include a. only factory overhead. b. only direct labour. c. direct labour and factory overhead. d. direct materials and direct labour. 14. Unit costs are critical for a. valuing inventory. b. determining net income. c. decisions to enter a new product line. d. all of the above. 15. Ordering frequently in small lot sizes minimizes a. ordering cost. b. carrying cost. c. stockout cost. d. all of the above. 16. Economic order quantity refers to the order size that a. minimizes the size of the order. b. minimizes the carrying costs associated with inventory. c. minimizes total inventory costs. d. minimizes the ordering costs associated with inventory. 17. One of the traditional reasons for holding inventory is to minimize total carrying costs and setup costs. The JIT solution is to a. reduce setup costs. b. reduce lead time. c. use total preventive maintenance. d. use total quality control. Figure 2 Hapsburg Manufacturing purchases components produced by Little Company in the manufacture of its main product. For the next year, Hapsburg expects to use a total of 20,000 parts. Hapsburg typically orders 2,000 units at a time. The cost of placing an order is GHS100, and the average annual cost of carrying one unit of inventory is GHS5. 18. Refer to Figure 2. Hapsburg's total ordering cost is a. GHS1,000. b. GHS5,000. c. GHS10,000. d. GHS500. Figure 3 Cozy Stoves produces wood-burning stoves. In order to produce the frames for the stoves, special equipment must be set up. The setup cost per frame is GHS40. The cost of carrying frames in inventory is GHS5 per frame per year. The company produces 100,000 stoves per year. 19. Refer to Figure 3. Cozy Stoves' total carrying costs associated with the economic order quantity are a. GHS3,612. b. GHS3,162. c. GHS506. d. GHS316. Figure 1 Mrs. Brown's Bagel Company manufactures specialty bagels. The company buys flour in 50-pound bags that cost GHS25 each. The company uses 10,000 bags per year, and usage occurs evenly throughout the year. The average cost to carry a 50-pound bag in inventory per year is GHS4, and the cost to place an order is GHS10. The company works 250 days per year. 20. Refer to Figure 1. If Brown's lead time is four working days, the average rate of usage is 40 bags per day, and the company carries a safety stock of 20 bags, the reorder point would be a. 180 bags. b. 140 bags. c. 160 bags. d. 100 bags. Figure 4 Steele Ltd. has the following information for January, February, and March 2011: January 10,000 7,000 Production costs per unit (based on 10,000 units) are as follows: Units produced Units sold February 10,000 8,500 Direct materials Direct labour Variable factory overhead Fixed factory overhead Variable selling and admin. expenses Fixed selling and admin. expenses March 10,000 10,500 GHS12 8 6 4 10 4 There were no beginning inventories for January 2011, and all units were sold for GHS50. Costs are stable over the three months. 21. Refer to Figure 4. What is the January ending inventory for Steele Ltd. Using the variable costing method? a. GHS260,000 b. GHS78,000 c. GHS108,000 d. GHS90,000 Which document(s) you would expect to find in the records of Chocolate Ltd as evidence of each of the following transactions or events which took place during the month of June? 22. Evidence that the buying department of Chocolate Ltd had authority to order new supplies of cocoa beans from a supplier_ 23. Evidence that the cocoa beans arrived at the stores of Chocolate Ltd in good condition and in the quantities expected_ 24. Evidence that the amount payable to the supplier is correct in quantities and prices_ 25. Evidence that the storekeeper of Chocolate Ltd had the authority to release cocoa beans to the production unit, for conversion to chocolate_ Section B Question 1 Dunstan Ltd manufactures tents and sleeping bags in three separate production departments. The principal manufacturing processes consist of cutting material in the pattern cutting room and sewing the material in either the tent or the sleeping bag departments. For the year to 31 July cost centre expenses and other relevant information are budgeted as follows: Indirect wages Consumable materials Plant depreciation Power Heat and light Rent and rates Building insurance Floor area (sq. ft) Estimated power usage (%) Direct labour (hours) Machine usage (hours) Value of raw material issues (%) Total (GHS) 13800 14400 13500 27500 100 Cutting Tents (GHS) 132200 6400 35900 80800 31700 112000 87000 100 room (GHS) 19500 20100 5300 4100 2300 31200 17500 24600 8000 17 Sleeping Raw bags (GHS) 7000 2000 70 10000 7000 38 32 48000 40000 15 57000 45000 15 material stores (GHS) 41200 2500 1500 7 Maintenance (GHS) 45000 24200 5000 1000 6 a) Prepare in columnar form a statement calculating the overhead absorption rates for each direct labour hour for each of the three production units. You should use bases of apportionment and absorption which you consider most appropriate and the bases should be clearly indicated in your statement. b) Determine the price to be quoted for a customer order using the information below: Direct material 2500 Direct labour Cutting Tents 5 hours @ 10GHS per hour 10 hours @ 10GHS per hour Sleeping bags 12 hours @ 10GHS per hour The company wants to make a profit of 30% on the total product cost. c) At the end of the period, actual labour hours worked are as follows: Cutting room 7000hours 50000hours Tents Sleeping bags 60000hours The total actual overhead cost incurred was 360,000GHS. Determine the amount of over/ under absorption of overheads. How will this amount be treated in the statement of profit or loss of Dunstan ltd? Question 2 Compare and contrast absorption and marginal costing.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.40 Rating (162 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 Answer d has externally imposed standard Explanation Management Accounting is meant for internal users Management Accounting is not bound by the externally imposed rules of financial reporting 2 Ans...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


