Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
my answer was wrong Croyden is a calendar year, accrual basis corporation. Mr. and Mrs. Croyden (cash basis taxpayers) are the sole corporate shareholders. Mr.
my answer was wrong 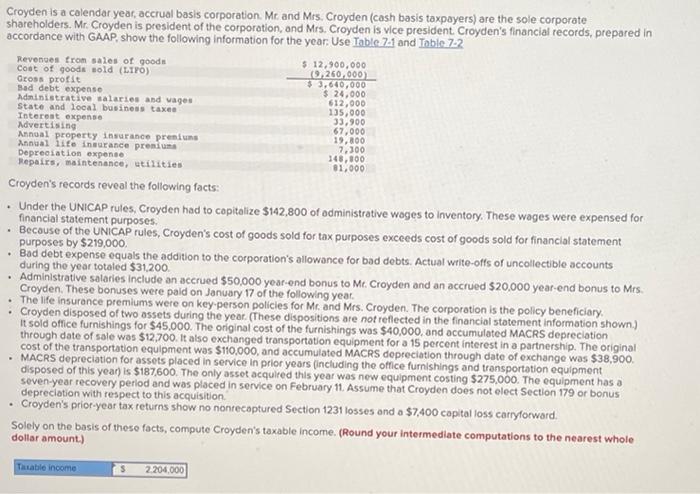
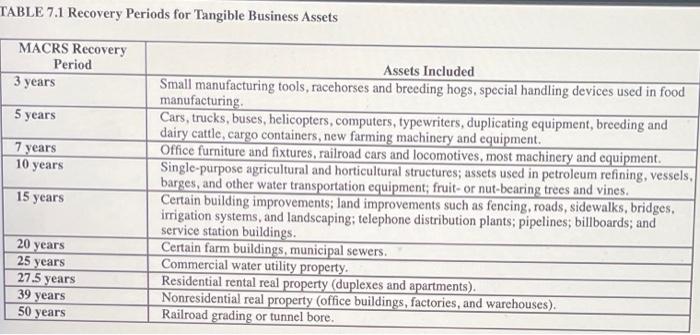
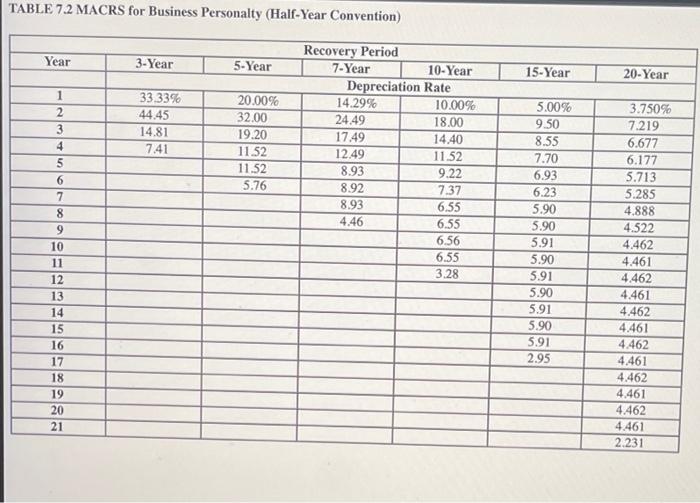
Croyden is a calendar year, accrual basis corporation. Mr. and Mrs. Croyden (cash basis taxpayers) are the sole corporate shareholders. Mr. Croyden is president of the corporation, and Mrs. Croyden is vice president Croyden's financial records, prepared in accordance with GAAP, show the following information for the year. Use Table 74 and Table 72 Revenues from sales of goods $ 12,900,000 Cost of goods sold (LIPO) (9.260.000) Gross profit $3,640,000 Bad debt expense $ 24,000 Administrative salaries and wages 612,000 State and local business taxes 135,000 Interest expenso 33,900 Advertising 67,000 Annual property insurance presiune 19,800 Annual life insurance premium 7.300 Depreciation expense 148,000 Hepairs, maintenance, utilities 81,000 Croyden's records reveal the following facts: Under the UNICAP rules, Croyden had to capitalize $142,800 of administrative wages to inventory. These wages were expensed for financial statement purposes. Because of the UNICAP rules, Croyden's cost of goods sold for tax purposes exceeds cost of goods sold for financial statement purposes by $219,000 Bad debt expense equals the addition to the corporation's allowance for bad debts. Actual write-offs of uncollectible accounts during the year totaled $31.200. Administrative salaries include an accrued $50,000 year-end bonus to Me, Croyden and an accrued $20,000 year-end bonus to Mrs. Croyden. These bonuses were pald on January 17 of the following year. The life insurance premiums were on key person policies for Me and Mrs. Croyden. The corporation is the policy beneficiary Croyden disposed of two assets during the year. (These dispositions are not reflected in the financial statement information shown) It sold office furnishings for $45,000. The original cost of the furnishings was $40,000, and accumulated MACRS depreciation through date of sale was $12,700. It also exchanged transportation equipment for a 15 percent interest in a partnership. The original cost of the transportation equipment was $110,000, and accumulated MACRS depreciation through date of exchange was $38,900. MACRS depreciation for assets placed in service in prior years (including the office furnishings and transportation equipment disposed of this year) is $187,600. The only asset acquired this year was new equipment costing $275,000. The equipment has a seven-year recovery period and was placed in service on February 11. Assume that Croyden does not elect Section 179 or bonus depreciation with respect to this acquisition Croyden's prior-year tax returns show no nonrecaptured Section 1231 losses and a $7,400 capital loss carryforward. Solely on the basis of these facts, compute Croyden's taxable income. (Round your intermediate computations to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Titable income $ 2204,000 TABLE 7.1 Recovery Periods for Tangible Business Assets MACRS Recovery Period 3 years 5 years 7 years 10 years 15 years Assets Included Small manufacturing tools, racehorses and breeding hogs, special handling devices used in food manufacturing Cars, trucks, buses, helicopters, computers, typewriters, duplicating equipment, breeding and dairy cattle, cargo containers, new farming machinery and equipment Office furniture and fixtures, railroad cars and locomotives, most machinery and equipment. Single-purpose agricultural and horticultural structures; assets used in petroleum refining, vessels, barges, and other water transportation equipment, fruit-or nut-bearing trees and vines. Certain building improvements; land improvements such as fencing, roads, sidewalks, bridges. irrigation systems, and landscaping, telephone distribution plants; pipelines, billboards; and service station buildings. Certain farm buildings, municipal sewers. Commercial water utility property. Residential rental real property (duplexes and apartments). Nonresidential real property office buildings, factories, and warehouses). Railroad grading or tunnel bore. 20 years 25 years 27.5 years 39 years 50 years TABLE 7.2 MACRS for Business Personalty (Half-Year Convention) Year 3-Year 5-Year 15-Year 20-Year 33.33% 44.45 14.81 7.41 20.00% 32.00 19.20 11.52 11.52 5.76 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Recovery Period 7-Year 10-Year Depreciation Rate 14.29% 10.00% 24.49 18.00 17.49 14.40 12.49 11.52 8.93 9.22 8.92 7.37 8.93 6.55 4.46 6.55 6.56 6.55 3.28 5.00% 9.50 8.55 7.70 6.93 6.23 5.90 5.90 5.91 5.90 5.91 5.90 5.91 5.90 5.91 2.95 3.750% 7.219 6.677 6.177 5.713 5.285 4.888 4.522 4.462 4.461 4.462 4.461 4.462 4.461 4.462 4.461 4.462 4.461 4.462 4.461 2.231 


Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


