Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
MYSQL GRANT Statement The CREATE USER statement creates one or more user accounts with no privileges. It means that the user accounts can log


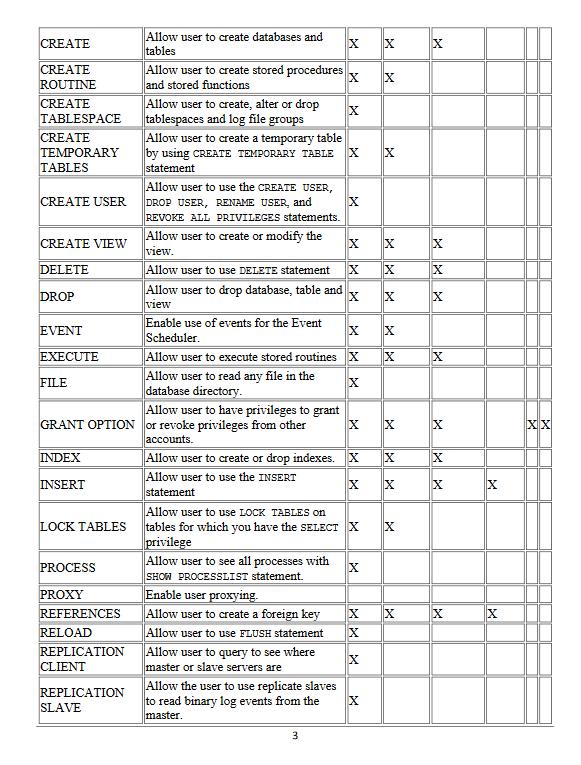
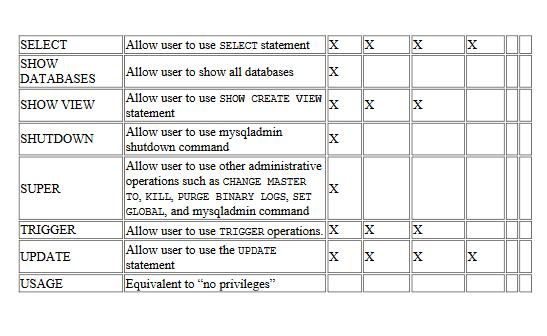
MYSQL GRANT Statement The CREATE USER statement creates one or more user accounts with no privileges. It means that the user accounts can log in to the MySQL, but cannot do anything such as selecting a database and querying data from tables. To allow user accounts to work with database objects, you need to grant the user accounts privileges. And the GRANT statement grants a user account one or more privileges. You must specify the privilege _level that determines the level to which the privileges apply. MySQL supports the following main privilege levels: Global privileges apply to all databases in a MySQL Server. To assign global privileges, you use the syntax, for example: GRANT SLECT ON TO bob@localhost; The account user bob@localhost can query data from all tables in all database of the current MySQL Server. Database privileges apply to all objects in a database. To assign database-level privileges, you use the ON database_name.* syntax, for example: GRANT INSERT ON classicmodels.* TO bob@localhost; In this example, bob@localhost can insert data into all tables in the classicmodels database. Table privileges apply to all columns in a table. To assign table-level privileges, you use the ON database_name.table_name syntax, for example: GRANT DELETE ON classicmodels.employees TO bob@localhost; In this example, bob@localhost can delete rows from the table employees in the database classicmodels. If you skip the database name, MySQL uses the default database or issues an error if there is no default database. Column privileges apply to single columns in a table. You must specify the column or columns for each privilege, for example: GRANT SELECT (employeeNumner, lastName, firstName, email), UPDATE (lastName) ON employees TO bob@localhost; In this example, bob@localhost can select data from four columns employeeNumber, lastName, firstName, and email and update only the lastName column in the employees table. Stored routine privileges apply to stored procedures and stored functions, for example: GRANT EXECUTE ON PROCEDURE CheckCredit TO bob@localhost; In this example, bob@localhost can execute the stored procedure CheckCredit in the current database. Proxy user privileges allow one user to be a proxy for another. The proxy user gets all privileges of the proxied user. For example: GRANT PROXY ON root To alice@localhost; In this example, alice@localhost assumes all privileges of root. Finally, specify the account name of the user that you want to grant privileges after the TO keyword. Notice that in order to use the GRANT statement, you must have the GRANT OPTION privilege and the privileges that you are granting. If the read only system variable is enabled, you need to have the SUPER privilege to execute the GRANT statement. MYSQL GRANT statement examples Typically, you use the CREATE USER statement to create a new user account first and then use the GRANT statement to grant privileges to the user. First, create a new user called super@localhost by using the following CREATE USER statement: CREATE USER super@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'Securel Pass! '; Second, show the privileges assigned to super@localhost user by using the SHOW GRANTS statement. SHOW GRANTS FOR super@localhost; Grants for super @localhost GRANT USAGE ON **TO 'super'@'localhost' The USAGE means that the super@localhost can log in the database but has no privilege. Third, grant all privileges in all databases in the current database server to super@localhost: GRANT ALL ON classicmodels.* TO super@localhost; Fourth, use the SHOW GRANTS statement again: SHOW GRANTS FOR super@localhost; Grants for super @localhost GRANT USAGE ON **TO super @'localhost GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON "dassicmodels. *TO super @ "localhost Permissible privileges for GRANT statement The following table illustrates all permissible privileges that you can use for the GRANT and REVOKE statement: Privilege Global ALL [PRIVILEGES] ALTER ALTER ROUTINE Meaning Database Grant all privileges at specified access level except GRANT OPTION Allow user to use of ALTER TABLEstatement Allow user to alter and drop stored procedures or stored functions. Level Table Column X Stored Routine X Proxy X CREATE CREATE ROUTINE CREATE TABLESPACE CREATE TEMPORARY TABLES CREATE USER CREATE VIEW DELETE DROP EVENT EXECUTE FILE INDEX INSERT LOCK TABLES PROCESS PROXY REFERENCES RELOAD REPLICATION CLIENT Allow user to create databases and tables REPLICATION SLAVE Allow user to create stored procedures and stored functions Allow user to create, alter or drop X tablespaces and log file groups Allow user to use the CREATE USER, DROP USER, RENAME USER, and REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES statements. Allow user to create a temporary table by using CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE X statement GRANT OPTION or revoke privileges from other accounts. Enable use of events for the Event Scheduler. Allow user to create or modify the view. Allow user to use DELETE statement Allow user to drop database, table and view X Allow user to have privileges to grant X X Allow user to execute stored routines X Allow user to read any file in the X database directory. X Allow user to see all processes with SHOW PROCESSLIST statement. Enable user proxying. Allow user to create a foreign key Allow user to use FLUSH statement Allow user to query to see where master or slave servers are X Allow the user to use replicate slaves to read binary log events from the master. Allow user to create or drop indexes. X Allow user to use the INSERT statement 3 X X Allow user to use LOCK TABLES on tables for which you have the SELECT X privilege X XX X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X XX SELECT SHOW DATABASES SHOW VIEW SHUTDOWN SUPER TRIGGER UPDATE USAGE Allow user to use SELECT statement X x Allow user to show all databases X Allow user to use SHOW CREATE VIEW X statement Allow user to use mysqladmin shutdown command Allow user to use other administrative operations such as CHANGE MASTER TO, KILL, PURGE BINARY LOGS, SET GLOBAL, and mysqladmin command Allow user to use TRIGGER operations. X Allow user to use the UPDATE X statement Equivalent to "no privileges" X X X X X X X x X
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


