Question: //============================================================================ // Name : VectorSorting.cpp // Author : Your name // Version : 1.0 // Copyright : Copyright 2017 SNHU COCE // Description : Vector
//============================================================================ // Name : VectorSorting.cpp // Author : Your name // Version : 1.0 // Copyright : Copyright 2017 SNHU COCE // Description : Vector Sorting Algorithms //============================================================================
#include
#include "CSVparser.hpp"
using namespace std;
//============================================================================ // Global definitions visible to all methods and classes //============================================================================
// forward declarations double strToDouble(string str, char ch);
// define a structure to hold bid information struct Bid { string bidId; // unique identifier string title; string fund; double amount; Bid() { amount = 0.0; } };
//============================================================================ // Static methods used for testing //============================================================================
/** * Display the bid information to the console (std::out) * * @param bid struct containing the bid info */ void displayBid(Bid bid) { cout
/** * Prompt user for bid information using console (std::in) * * @return Bid struct containing the bid info */ Bid getBid() { Bid bid;
cout
cout
cout > bid.fund;
cout
return bid; }
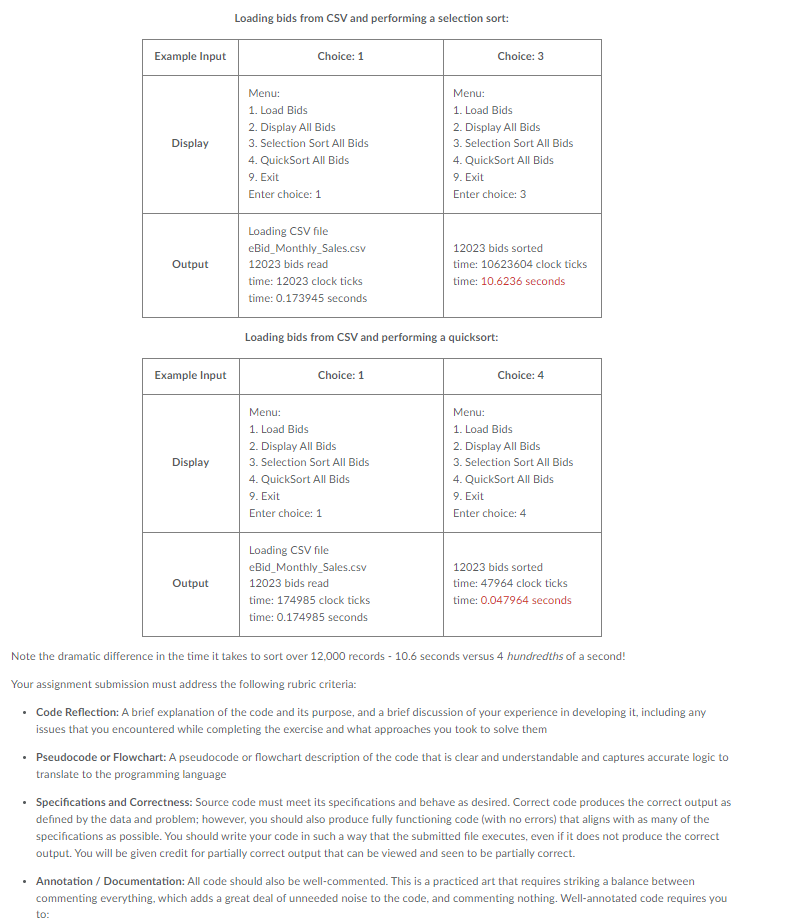
/** * Load a CSV file containing bids into a container * * @param csvPath the path to the CSV file to load * @return a container holding all the bids read */ vector // Define a vector data structure to hold a collection of bids. vector // initialize the CSV Parser using the given path csv::Parser file = csv::Parser(csvPath); try { // loop to read rows of a CSV file for (int i = 0; i // Create a data structure and add to the collection of bids Bid bid; bid.bidId = file[i][1]; bid.title = file[i][0]; bid.fund = file[i][8]; bid.amount = strToDouble(file[i][4], '$'); //cout // push this bid to the end bids.push_back(bid); } } catch (csv::Error &e) { std::cerr // FIXME (2a): Implement the quick sort logic over bid.title /** * Partition the vector of bids into two parts, low and high * * @param bids Address of the vector // pick the middle element as pivot point // while not done // keep incrementing low index while bids[low] /* If there are zero or one elements remaining, all bids are partitioned. Return high */ // else swap the low and high bids (built in vector method) // move low and high closer ++low, --high //return high; } /** * Perform a quick sort on bid title * Average performance: O(n log(n)) * Worst case performance O(n^2)) * * @param bids address of the vector /* Base case: If there are 1 or zero bids to sort, partition is already sorted otherwise if begin is greater than or equal to end then return*/ /* Partition bids into low and high such that midpoint is location of last element in low */ // recursively sort low partition (begin to mid) // recursively sort high partition (mid+1 to end) } // FIXME (1a): Implement the selection sort logic over bid.title /** * Perform a selection sort on bid title * Average performance: O(n^2)) * Worst case performance O(n^2)) * * @param bid address of the vector // check size of bids vector // set size_t platform-neutral result equal to bid.size() // pos is the position within bids that divides sorted/unsorted // for size_t pos = 0 and less than size -1 // set min = pos // loop over remaining elements to the right of position // if this element's title is less than minimum title // this element becomes the minimum // swap the current minimum with smaller one found // swap is a built in vector method } /** * Simple C function to convert a string to a double * after stripping out unwanted char * * credit: http://stackoverflow.com/a/24875936 * * @param ch The character to strip out */ double strToDouble(string str, char ch) { str.erase(remove(str.begin(), str.end(), ch), str.end()); return atof(str.c_str()); } /** * The one and only main() method */ int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { // process command line arguments string csvPath; switch (argc) { case 2: csvPath = argv[1]; break; default: csvPath = "eBid_Monthly_Sales_Dec_2016.csv"; } // Define a vector to hold all the bids vector // Define a timer variable clock_t ticks; int choice = 0; while (choice != 9) { cout > choice; switch (choice) { case 1: // Initialize a timer variable before loading bids ticks = clock(); // Complete the method call to load the bids bids = loadBids(csvPath); cout // Calculate elapsed time and display result ticks = clock() - ticks; // current clock ticks minus starting clock ticks cout break; case 2: // Loop and display the bids read for (int i = 0; i break; // FIXME (1b): Invoke the selection sort and report timing results // FIXME (2b): Invoke the quick sort and report timing results } } cout return 0; } 

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


