Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Natural gas is to be liquefied based on the following cascade refrigeration cycle. The natural gas will be stored at a temperature of Tstorage. Provided
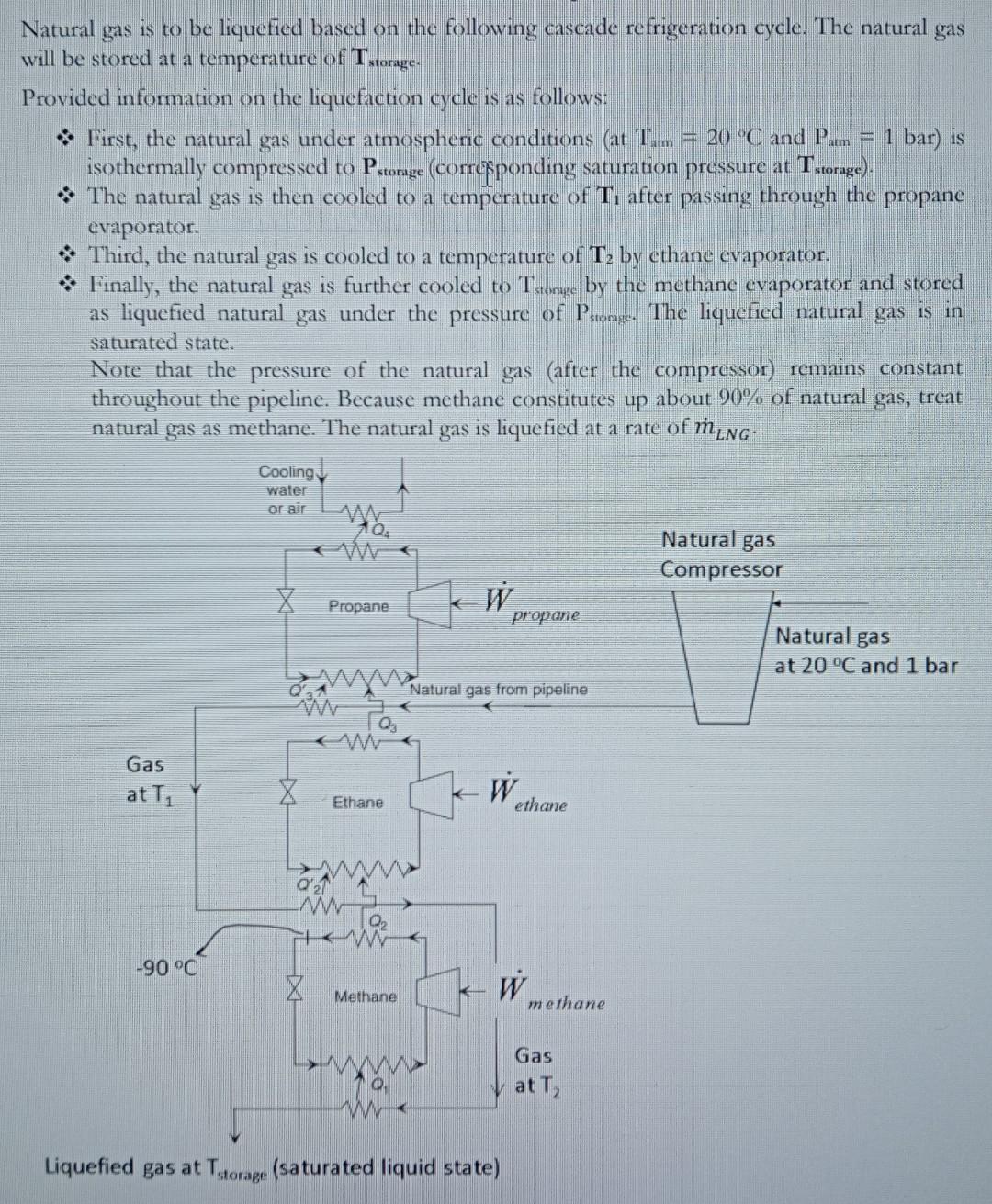

Natural gas is to be liquefied based on the following cascade refrigeration cycle. The natural gas will be stored at a temperature of Tstorage. Provided information on the liquefaction cycle is as follows: * First, the natural gas under atmospheric conditions (at Tarm=20C and Pam=1 bar) is isothermally compressed to Pstorage (corresponding saturation pressure at Tstorage) ). * The natural gas is then cooled to a temperature of T1 after passing through the propane evaporator. \& Third, the natural gas is cooled to a temperature of T2 by ethane evaporator. * Finally, the natural gas is further cooled to Tstoragc by the methane evaporator and stored as liquefied natural gas under the pressure of Pstomge. The liquefied natural gas is in saturated state. Note that the pressure of the natural gas (after the compressor) remains constant throughout the pipeline. Because methane constitutes up about 90% of natural gas, treat natural gas as methane. The natural gas is liquefied at a rate of mLNG. Assuming reasonable evaporation and condensation pressures for the propane, ethane and methane cycles, show the process cycles on the scaled Pb diagrams (for propane, ethane, methane and natural gas lines) using the thermodynamic charts. As shown in the figure, refrigerant temperature at condenser exit of the methane refrigeration cycle is -90 C. * Calculate the compressor powers (Wropane, Wethane and Wmethane). Do not calculate the power of the natural gas compressor. * Report the mass flow rates of the propane, ethane, methane and cooling water. The temperature of the cooling water rises by 5C through the propane condenser. * Determine the COP of the liquefaction plant. Note that all compressors are working based on isentropic compression. Refrigerants are saturated liquid state at condenser exits and saturated vapor state at evaporator cxits. Tstorage (C)=110 T1(C)=20 T2(C)=100 Twater (C)=15 m/NG(kg/s)=1.5
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


