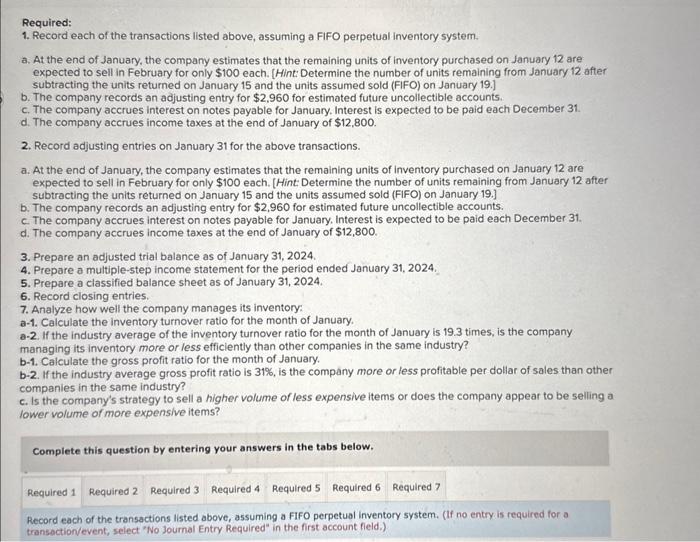
need ALL OF 1-3 conpleted please including the a-d
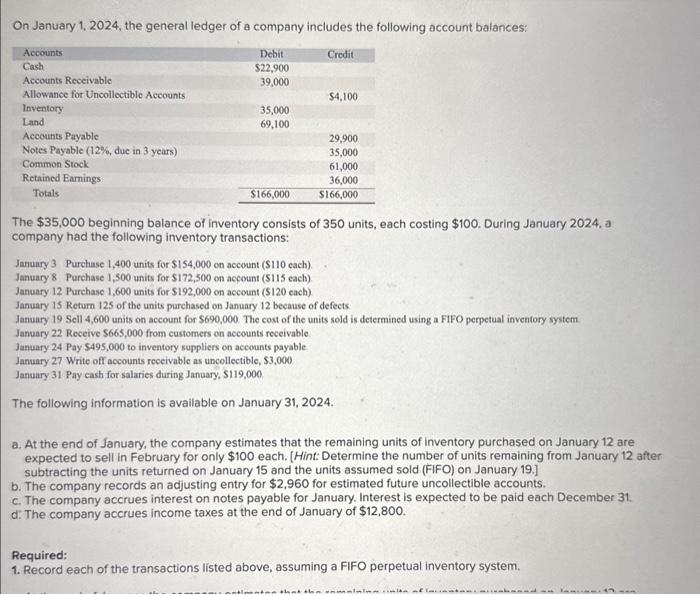
On January 1, 2024, the general ledger of a company includes the following occount balances: The $35,000 beginning balance of inventory consists of 350 units, each costing $100. During January 2024 , a company had the following inventory transactions: January 3 Purchase 1,400 units for $154,000 on account (\$110 each) January 8 Purchase 1,500 units for $172,500 on account (\$115 each). January 12 Purchase 1,600 units for $192,000 on account (\$120 cach) January 15 Return 125 of the units purchased on January 12 because of defects. January 19 Sell 4,600 units on account for $690,000. The cost of the units sold is determined using a FIFO perpetual inventory system. January 22 Receive $665,000 from customers on accounts receivable. January 24 Pay $495,000 to inventory suppliers on accounts payable January 27 Write off accounts receivable as uncollectible, $3,000 January 31 Pay cash for salaries during January, $119,000 The following information is available on January 31,2024. a. At the end of January, the company estimates that the remaining units of inventory purchased on January 12 are expected to sell in February for only $100 each. [Hint: Determine the number of units remaining from January 12 after subtracting the units returned on January 15 and the units assumed sold (FIFO) on January 19.] b. The company records an adjusting entry for $2,960 for estimated future uncollectible accounts. c. The company accrues interest on notes payable for January. Interest is expected to be paid each December 31. d. The company accrues income taxes at the end of January of $12,800. 1. Record each of the transactions listed above, assuming a FIFO perpetual inventory system. a. At the end of January, the company estimates that the remaining units of inventory purchased on January 12 are expected to sell in February for only $100 each. [Hint: Determine the number of units remaining from January 12 after subtracting the units returned on January 15 and the units assumed sold (FIFO) on January 19.] b. The company records an adjusting entry for $2,960 for estimated future uncollectible accounts. c. The company accrues interest on notes payable for January. Interest is expected to be paid each December 31. d. The company accrues income taxes at the end of January of $12,800. 2. Record adjusting entries on January 31 for the above transactions. a. At the end of January, the company estimates that the remaining units of inventory purchased on January 12 are expected to sell in February for only $100 each. [Hint: Determine the number of units remaining from January 12 after subtracting the units returned on January 15 and the units assumed sold (FIFO) on January 19.] b. The company records an adjusting entry for $2,960 for estimated future uncollectible accounts. c. The company accrues interest on notes payable for January. Interest is expected to be paid each December 31. d. The company accrues income taxes at the end of January of $12,800. 3. Prepare an adjusted trial balance as of January 31, 2024. 4. Prepare a multiple-step income statement for the period ended January 31, 2024. 5. Prepare a classified balance sheet as of January 31, 2024. 6. Record closing entries. 7. Analyze how well the company manages its inventory: a-1. Calculate the inventory turnover ratio for the month of January. a-2. If the industry average of the inventory turnover ratio for the month of January is 19.3 times, is the company managing its inventory more or less efficiently than other companies in the same industry? b-1. Calculate the gross profit ratio for the month of January. b-2. If the industry average gross profit ratio is 31%, is the company more or less profitable per dollar of sales than other companies in the same industry? c. Is the company's strategy to sell a higher volume of less expensive items or does the company appear to be selling a lower volume of more expensive items? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Record each of the transactions listed above, assuming a FIFO perpetual inventory system. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.)