Question: Need all only Case Study: Target Costing Aparajitha Limited is a leading Refrigerator Company and sells its products across the World. In the highly competitive



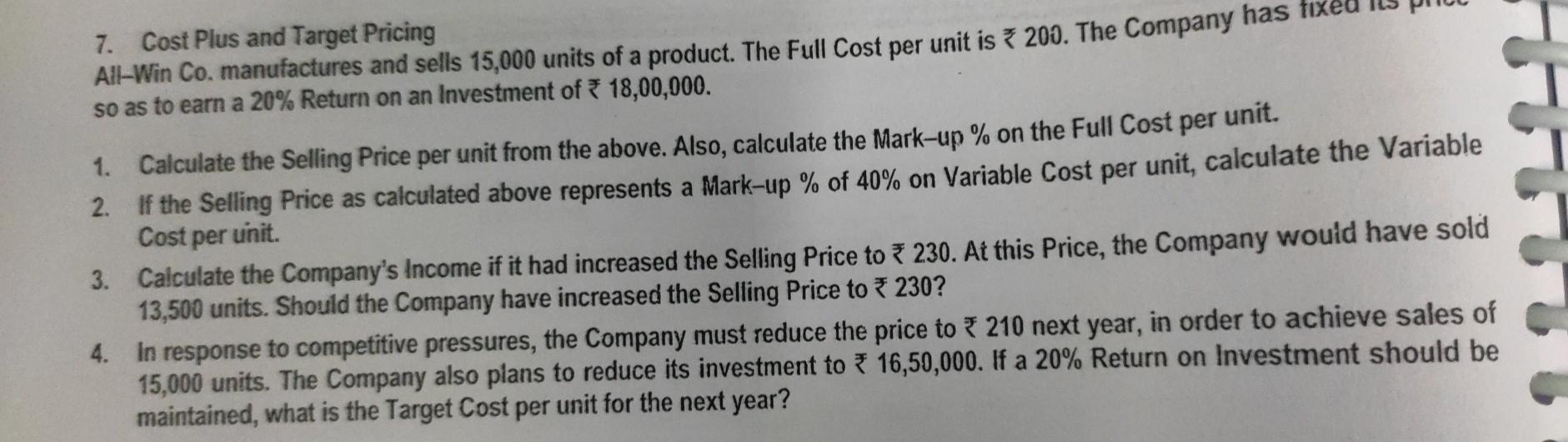
Need all only
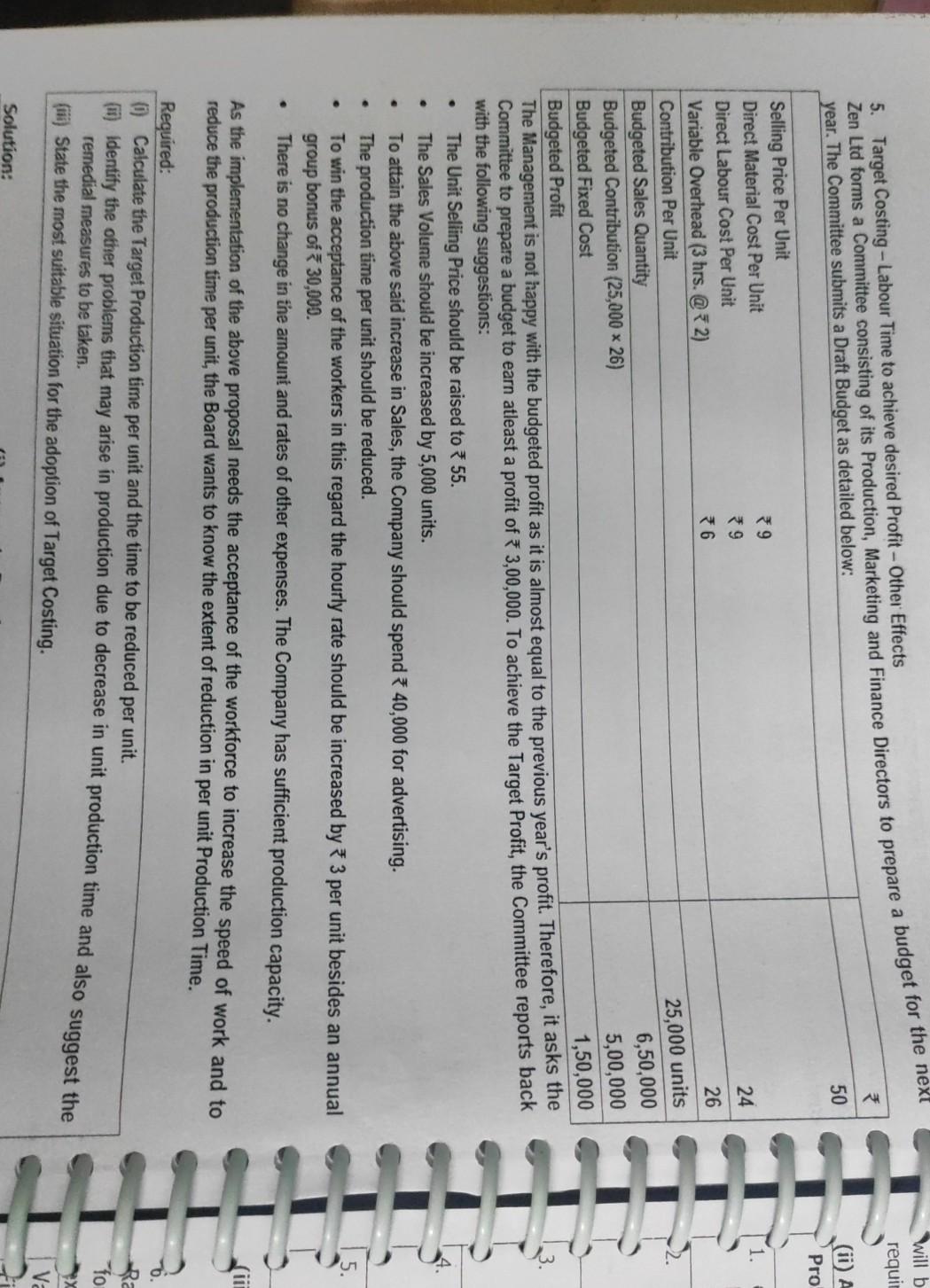
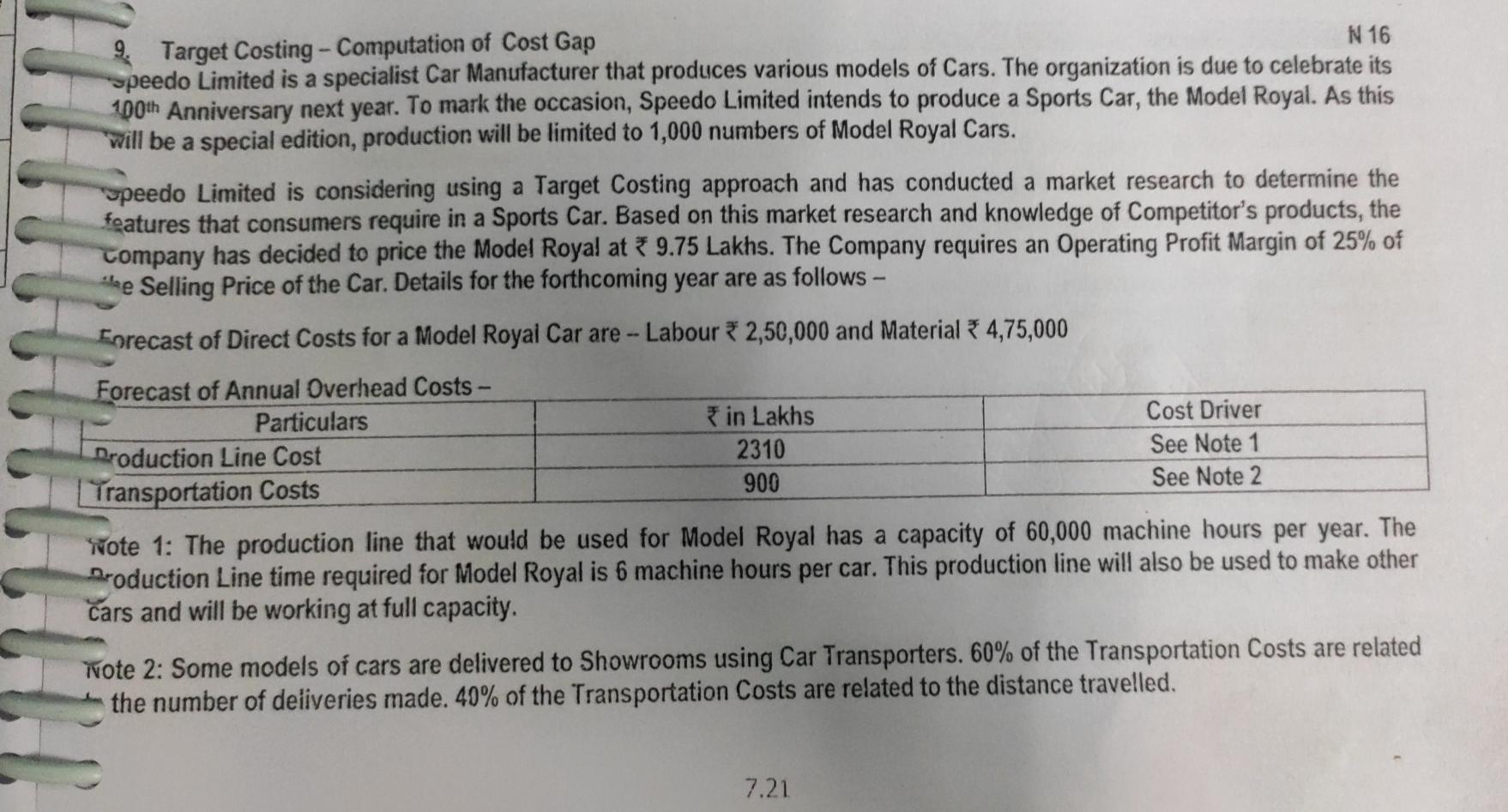
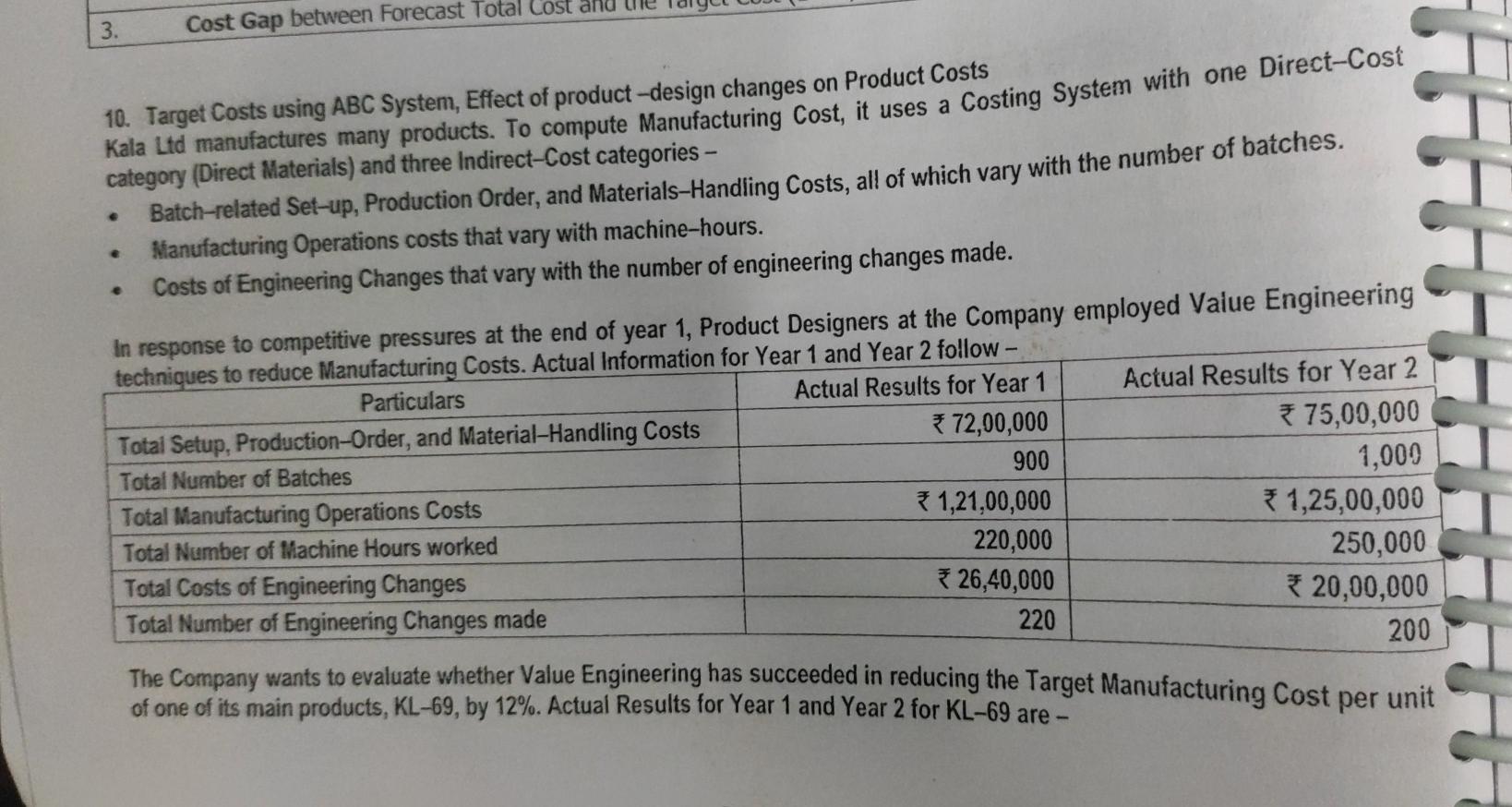
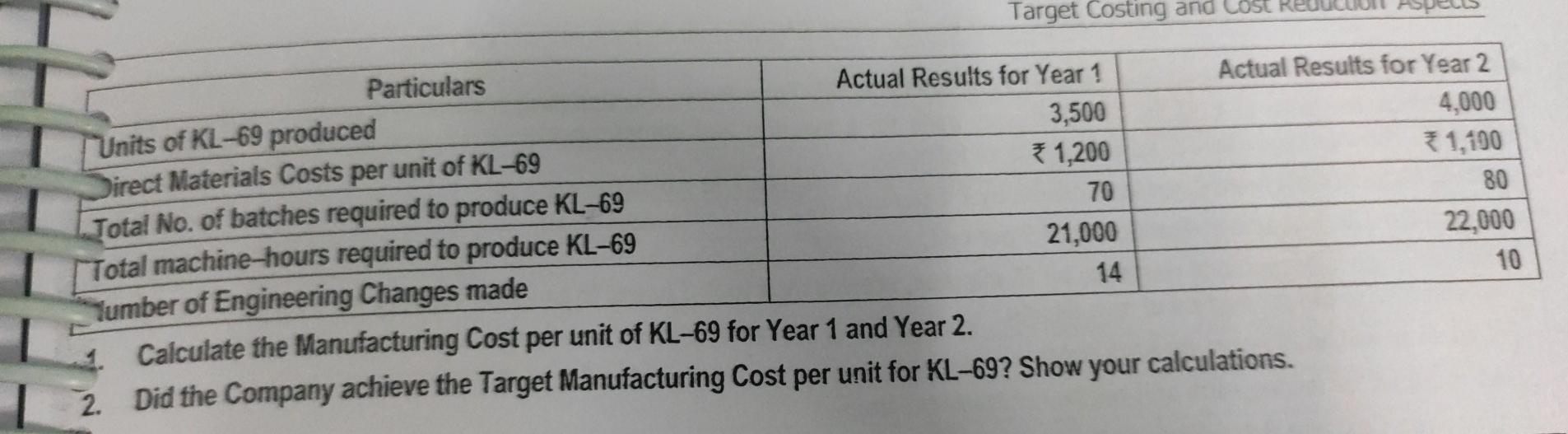
Case Study: Target Costing Aparajitha Limited is a leading Refrigerator Company and sells its products across the World. In the highly competitive environment, the Company has been able to maintain its leadership in its Products for 3rd year in a row now. Though the Revenues have grown year on year, the Costs have increased at a higher rate in the industry as a whole. We have been leaders in Revenue. We must lead in cost reduction front as well. I believe we can achieve this with improvements over time, however minor they might be! For this purpose, we should be open for any type of improvement - right from product design to delivery aspect re-modelling- This is what the CEO of the Company has told its Directors in a recently concluded Board Meeting. The Net Profit Margins of the Company has fallen from 10% in last year to 8% in current year, owing to rise in Raw Material & Repairs Cost. Another significant rise in the cost was on account of repairs of products which are under Warranty. There was an increase in these Repair Costs by about 1% of the total Turnover of the Company. A review of Warranty Repairs by the Company Design Team suggested that suitable design changes be brought in to address 90% of the issues that arise during the Warranty period. If these changes are brought in the Company may be able to avoid substantial replacement / repair costs during the Warranty period. Product Designers have had many discussions in this regard, and have identified certain modifications and changes in components and processes, to address this issue. Required: You are working as a Finance Manager in the Company. The Finance Director has approached you to understand the significance of the CEO's observations and the impact of the Design Team's activities. You are required to submit a report covering the following aspects: 1. Are the terms "Cost Reduction", "Cost Control" and "Cost Management" synonymous? 2. Can the modifications suggested by the Product Designers be considered as Value Analysis or Value Engineering? 3. What types of issues are covered in a Value Analysis / Engineering Study? 4. Outline the scope of Cost Reduction in Product Design. Solution: 8,00,000 75,000 60,000 50,000 35,000 15,000 55,000 1. Cost Classification - VA, NVA and Grey Area - Evaluation of effect of alternative cost reduction techn The Golmal Repair Shop repairs and services Machine Tools. Annual summary of its costs (by activity) is. 1. Materials and Labour for servicing Machine Tools Item A 2. Re-work Costs Item B 3. Expediting Costs caused by work delays Item C Materials Handling Item D 5. Materials Procurement and Inspection Costs Item E 6. Preventive Maintenance of Equipment Item F 7. Break-down Maintenance of Equipment Item G Required: 1. Classify each cost as Value Added, Non-Value-Added, or in the Grey Area between. 2. For any cost classified in grey-area, assume 65% of it is Value Added and 35% is Non-Value Added. How much of total of all seven costs is Value Added and how much is Non-Value-Added? 3. The Company is considering the following changes at the Shop - (a) introducing Quality Improvement Programs whose net effect will be to reduce re-work and expediting costs by 75% and Materials and Labour Costs for servicing Machine Tools by 5%, (b) working with Suppliers to reduce Materials Procurement and Inspection Costs by 20% and Materials Handling Costs by 25%, and (c) increasing Preventive Maintenance Costs by 50% to reduce Break-down Maintenance Costs by 40%. What is the effect of each of the above programs on Value-Added, Non-Value Added and Total Costs? Comment. 9,14 Adjt 65,000 35,000 Tota! 8,65,000 2,25,000 10,90,000 8,17,200 97,550 % 79.36% 20.64% 100.00% 89.34% 10.66% Note: Grey Area Costs have been re-allocated to VA and NVA as 65% and 35% respectively. RTP 2. Computation of Target Cost You are the Manager of XYZ Paper Mills and have recently come across a particular type of paper, which is being sold at a substantially lower rate (by another Company ABC Ltd) than the price charged by your own mill. The Value Chain for one use of tonne of such paper for ABC Ltd is: ABC Ltd. Merchant Printer Customer. ABC Ltd sells this particular paper to Merchant at the rate of 1,466 per Tonne. ABC Ltd pays for the Freight which amounts to 30 per Tonne. Average Returns and Allowances amount to 4% of Sales and approximately equals * 60 per Tonne. The Value Chain of your Company, through which the paper reaches the ultimate customer is similar to that of ABC Ltd. However, your Mill does not sell directly to the Merchant, the latter receiving the paper from huge Distribution Centre maintained by your Company at Haryana. Shipment Costs from the Mill to the Distribution Centre is * 11 per Tonne while the Operating costs in the Distribution Center are estimated at 25 per Tonne. The Return on Investment required by the Distribution Centre for the investments made, amount to an estimate 58 per Tonne. Calculate the Mill Manufacturing Target Cost" for this particular paper for XYZ Ltd. Assume that the return on the investment expected by XYZ Ltd is 120 per tonne of paper. 7.16 will b requis Zen Ltd forms a Committee consisting of its Production, Marketing and Finance Directors to prepare a budget for the next () A Pro 25,000 units year. The Committee submits a Draft Budget as detailed below: 50 Selling Price Per Unit Direct Material Cost Per Unit 9 Direct Labour Cost Per Unit 9 24 Variable Overhead (3 hrs. @2) 6 26 Contribution Per Unit Budgeted Sales Quantity Budgeted Contribution (25,000 * 26) 6,50,000 Budgeted Fixed Cost 5,00,000 Budgeted Profit 1,50,000 The Management is not happy with the budgeted profit as it is almost equal to the previous year's profit. Therefore, it asks the Committee to prepare a budget to earn atleast a profit of 3,00,000. To achieve the Target Profit, the Committee reports back with the following suggestions: The Unit Selling Price should be raised to 55. The Sales Volume should be increased by 5,000 units. To attain the above said increase in Sales, the Company should spend 40,000 for advertising. The production time per unit should be reduced. . To win the acceptance of the workers in this regard the hourly rate should be increased by * 3 per unit besides an annual group bonus of 30,000. There is no change in the amount and rates of other expenses. The Company has sufficient production capacity. . As the implementation of the above proposal needs the acceptance of the workforce to increase the speed of work and to reduce the production time per unit, the Board wants to know the extent of reduction in per unit Production Time. Required: Calculate the Target Production time per unit and the time to be reduced per unit. m) identify the other problems that may arise in production due to decrease in unit production time and also suggest the remedial measures to be taken. (1) State the most suitable situation for the adoption of Target Costing. fo X va Solution: 7. Cost Plus and Target Pricing All-Win Co. manufactures and sells 15,000 units of a product. The Full Cost per unit is 3 200. The Company has to so as to earn a 20% Return on an investment of 18,00,000. 1. Calculate the Selling Price per unit from the above. Also, calculate the Mark-up % on the Full Cost per unit. 2. If the Selling Price as calculated above represents a Mark-up % of 40% on Variable Cost per unit, calculate the Variable Cost per unit. 3. Calculate the Company's Income if it had increased the Selling Price to 230. At this Price, the Company would have sold 13,500 units. Should the Company have increased the Selling Price to *230? 4. In response to competitive pressures, the Company must reduce the price to 210 next year, in order to achieve sales of 15,000 units. The Company also plans to reduce its investment to 16,50,000. If a 20% Return on Investment should be maintained, what is the Target Cost per unit for the next year? % Target Costing - Computation of Cost Gap N 16 speedo Limited is a specialist Car Manufacturer that produces various models of Cars. The organization is due to celebrate its 100th Anniversary next year. To mark the occasion, Speedo Limited intends to produce a Sports Car, the Model Royal. As this will be a special edition, production will be limited to 1,000 numbers of Model Royal Cars. speedo Limited is considering using a Target Costing approach and has conducted a market research to determine the features that consumers require in a Sports Car. Based on this market research and knowledge of Competitor's products, the Company has decided to price the Model Royal at * 9.75 Lakhs. The Company requires an Operating Profit Margin of 25% of ee Selling Price of the Car. Details for the forthcoming year are as follows - Forecast of Direct Costs for a Model Royal Car are - Labour *2,50,000 and Material 4,75,000 Forecast of Annual Overhead Costs - Particulars in Lakhs Cost Driver Droduction Line Cost 2310 See Note 1 Transportation Costs 900 See Note 2 Note 1: The production line that would be used for Model Royal has a capacity of 60,000 machine hours per year. The Production Line time required for Model Royal is 6 machine hours per car. This production line will also be used to make other Cars and will be working at full capacity. Wote 2: Some models of cars are delivered to Showrooms using Car Transporters. 60% of the Transportation Costs are related the number of deliveries made. 40% of the Transportation Costs are related to the distance travelled. 7.21 3. Cost Gap between Forecast Total cost and 10. Target Costs using ABC System, Effect of product-design changes on Product Costs Kala Ltd manufactures many products . To compute Manufacturing Cost, it uses a Costing System with one Direct-Cost category (Direct Materials) and three Indirect-Cost categories - Batch-related Set-up, Production Order, and Materials-Handling Costs, all of which vary with the number of batches. Manufacturing Operations costs that vary with machine-hours. Costs of Engineering Changes that vary with the number of engineering changes made. In response to competitive pressures at the end of year 1, Product Designers at the Company employed Value Engineering techniques to reduce Manufacturing Costs. Actual Information for Year 1 and Year 2 follow- Actual Results for Year 1 Actual Results for Year 2 Particulars Total Setup, Production-Order, and Material Handling Costs *72,00,000 *75,00,000 Total Number of Batches 900 1,000 Total Manufacturing Operations Costs 1,21,00,000 1,25,00,000 Total Number of Machine Hours worked 220,000 250,000 Total Costs of Engineering Changes *26,40,000 * 20,00,000 Total Number of Engineering Changes made 220 200 The Company wants to evaluate whether Value Engineering has succeeded in reducing the Target Manufacturing Cost of one of its main products, KL-69, by 12%. Actual Results for Year 1 and Year 2 for KL-69 are - per unit Target Costing and cost Particulars Actual Results for Year 1 Actual Results for Year 2 Units of KL-69 produced 3,500 4,000 Direct Materials Costs per unit of KL-69 1,200 1,100 Total No. of batches required to produce KL-69 70 80 Total machine-hours required to produce KL-69 21,000 22,000 Tumber of Engineering Changes made 14 10 1. Calculate the Manufacturing Cost per unit of KL-69 for Year 1 and Year 2. 2. Did the Company achieve the Target Manufacturing Cost per unit for KL-69? Show your calculations
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


