need assistance with question 5-1A
Can whomever assists please follow the examples i added for the 3rd and 4th part of the question

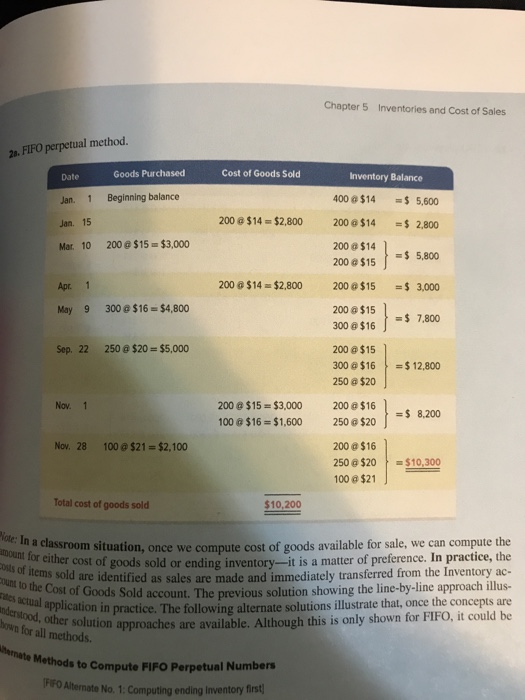
Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March. (For specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 80 units from be- ginning inventory and 340 units from the March 5 purchase; the March 29 sale consisted of 40 units from the March 18 purchase and 120 units from the March 25 purchase.) PROBLEM SET A Problem 5-1A Perpetual: Alternative cost flows Date Activities Units Acquired at Cost Units Sold at Retail P1 400 units@ $55.00 per unit Mar. 9 Sales 420 units @ $85.00 per unit 160 units@ $95.00 per unit 580 units Required 1. Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale. 2. Compute the number of units in ending inventory 3. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using (o) FIFO,() LIFO, ) weighted average, an$1 Check (3) Enaing inve FIFO, $14,800 LIFCo S13,680: WA, $14.352 45 d) specific identification. (Round all amounts to cents.) 4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods in part 3. (4) LIFO gross $17.980 Chapter 5 Inventories and Cost of Sales 2a. FIFO perpetual method. Goods Purchased Cost of Goods Sold Inventory Balance Date Jan. 1 Beginning balance Jan. 15 Mar 10 200@ $15- $3,000 400 $14 5,600 200 @ $14-$2.800 200 0 $14 2,800 200$14 200 @$15 5,800 Apr. 1 200$14 $2,800 200@$15 3,000 May 9 300@$16 $4,800 200@ $15 300 0$16 7,800 200@$15 300@$1612,800 250@ $20 Sep. 22 250@ $20-$5,000 Nov. 1 200@$15 $3,000 200$16 00@ $16 $1,600 250 e $20 J $8,200 Nov. 28 100@$21-$2,100 200@$16 50 @$20-$10.300 00 $21 Total cost of goods sold $10,200 In a classroom situation, once we compute cost of goods available for sale, we can compute the amount for either ots hrcost of goods sold or ending inventory-it is a matter of preference. In practice, the of items sold are identified as ount to the Cost of Goods as sales are made and immediately transferred from the Inventory ac- Sold account. The previous solution showing the line-by-line approach illus- account. actual nderstood, other solution hown for all methods. pplication in practice. The following alternate solutions illustrate that, once the concepts are pproaches are available. Although this is only shown for FIFO.it could be are Methods to Compute FIFO Perpetual Numbers IFFO Alternate No. 1: Computing ending Inventory firs Chapter !5 2b. LIFO perpetual method. Inventory Balance of Goods Sold Cent 00514 5,600 Goeds Purdhased 200 0 514-32.800 2002.800 200 314 200 0$155,800 Jan. 15 Mar. 10 200 0 $15-$3.000 00$15-$3,000 20042800 2000$14 -s 7,000 00$16 200 0 $14 300 0 $16$12,600 250 0 $20 May 9 300 @$16-$4,800 3. Sep 22 250 0 $20 $5,000 50 $20-$5,000 200 $14 00516-3 800 250 0 $16 68 Nov 200 0 $14 Nov. 28 100 0 $21-$2,100 00 0 $21 Total cost of goods sold 4. M 2c. Weighted average perpetual method. Date Goods Punchased Cost of Goods Sold Inventory Balance 5. A Jan. 1 Beginning balance 400 @ $14.005,600 ($5.600400 units = $1400 evg. cost Jan 15 200 @ $14.002.000 os14.00 $ 2.900 Mat. 10 200 $15.00-$3,000 200 $14.00 200$15.005,800 $5,800/400 units $1450 avg. cost Apr. 1 200 8 514.50-$ 2.900 200 9 51450 2.900 May 9 $16.00 = $4.800 200 $14.50 300 @ $16.007,700 $7,700/500 units $15,40 avg. cost) 5000 154012.700 250$20.00 $12,700/750 units $16.93 avg. cost) 30801410 Sep. 22 250 $20.00 $5,000 Nov. 1 300 e $16.93 5,079 450$16.937,618.50 Nov. 28 100 $21.00 $2,100 50 $16.93 9,718.50/550 units $17.67 avg. cost Total cost of goods sold Cost of goods wold (514 79) plas ending bvesury (59,718 50) is $2.50 les than the cost of goods available for sale 510 179 Chapter 5 Inventories and Cost of Sale Specific identification method. Cost of goods available for sale (from part 1)............. Ending inventory $20,500 May 9 Purchase (300@$16) Sep. 22 Purchase (150@$20) Nov. 28 Purchase (100@$21) $4,800 3,000 2,100 9,900 $10,600 Cost of goods sold The additional tracking data provided are used to identify the items in ending inventory