Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Need Detailed Answer of each part Consider the 7-stage pipelined processor with two execution units and pipelined caches, as shown below. Instruction fetch is a
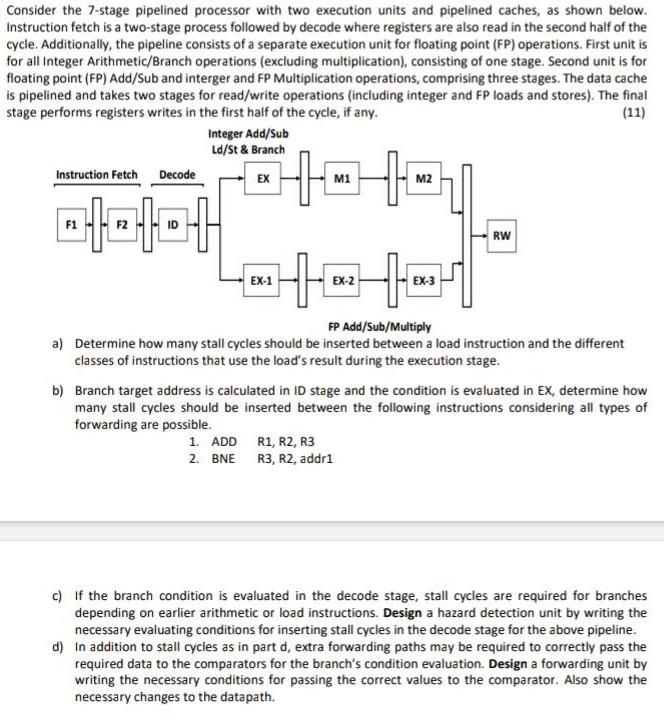
Need Detailed Answer of each part
Consider the 7-stage pipelined processor with two execution units and pipelined caches, as shown below. Instruction fetch is a two-stage process followed by decode where registers are also read in the second half of the cycle. Additionally, the pipeline consists of a separate execution unit for floating point (FP) operations. First unit is for all Integer Arithmetic/Branch operations (excluding multiplication), consisting of one stage. Second unit is for floating point (FP) Add/Sub and interger and FP Multiplication operations, comprising three stages. The data cache is pipelined and takes two stages for read/write operations (including integer and FP loads and stores). The final stage performs registers writes in the first half of the cycle, if any. Integer Add/Sub Ld/St & Branch Instruction Fetch Decode EX M1 M2 -1-101 -- Help RW EX-1 EX-2 EX-3 FP Add/Sub/Multiply a) Determine how many stall cycles should be inserted between a load instruction and the different classes of instructions that use the load's result during the execution stage. b) Branch target address is calculated in D stage and the condition is evaluated in EX, determine how many stall cycles should be inserted between the following instructions considering all types of forwarding are possible. 1. ADD R1, R2, R3 2. BNE R3, R2, addri c) If the branch condition is evaluated in the decode stage, stall cycles are required for branches depending on earlier arithmetic or load instructions. Design a hazard detection unit by writing the necessary evaluating conditions for inserting stall cycles in the decode stage for the above pipeline. d) In addition to stall cycles as in part d, extra forwarding paths may be required to correctly pass the required data to the comparators for the branch's condition evaluation. Design a forwarding unit by writing the necessary conditions for passing the correct values to the comparator. Also show the necessary changes to the datapath. Consider the 7-stage pipelined processor with two execution units and pipelined caches, as shown below. Instruction fetch is a two-stage process followed by decode where registers are also read in the second half of the cycle. Additionally, the pipeline consists of a separate execution unit for floating point (FP) operations. First unit is for all Integer Arithmetic/Branch operations (excluding multiplication), consisting of one stage. Second unit is for floating point (FP) Add/Sub and interger and FP Multiplication operations, comprising three stages. The data cache is pipelined and takes two stages for read/write operations (including integer and FP loads and stores). The final stage performs registers writes in the first half of the cycle, if any. Integer Add/Sub Ld/St & Branch Instruction Fetch Decode EX M1 M2 -1-101 -- Help RW EX-1 EX-2 EX-3 FP Add/Sub/Multiply a) Determine how many stall cycles should be inserted between a load instruction and the different classes of instructions that use the load's result during the execution stage. b) Branch target address is calculated in D stage and the condition is evaluated in EX, determine how many stall cycles should be inserted between the following instructions considering all types of forwarding are possible. 1. ADD R1, R2, R3 2. BNE R3, R2, addri c) If the branch condition is evaluated in the decode stage, stall cycles are required for branches depending on earlier arithmetic or load instructions. Design a hazard detection unit by writing the necessary evaluating conditions for inserting stall cycles in the decode stage for the above pipeline. d) In addition to stall cycles as in part d, extra forwarding paths may be required to correctly pass the required data to the comparators for the branch's condition evaluation. Design a forwarding unit by writing the necessary conditions for passing the correct values to the comparator. Also show the necessary changes to the datapathStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


