Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
need help #5-8 Data Table II: Sample Weights Item Weight of Dish/ (grams) Weight of Dish Plus Aspirin Sample (grams) Purified Aspirin Net Weight of
need help #5-8 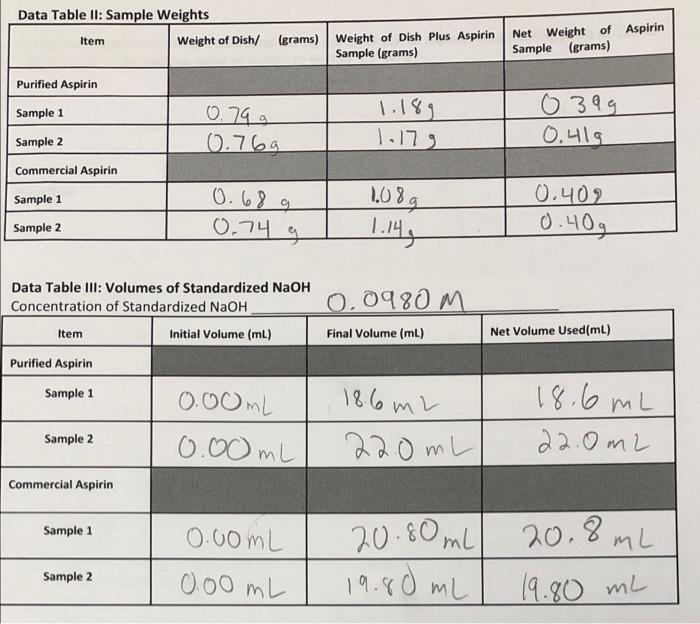

Data Table II: Sample Weights Item Weight of Dish/ (grams) Weight of Dish Plus Aspirin Sample (grams) Purified Aspirin Net Weight of Aspirin Sample (grams) Sample 1 0.79 g 0399 0.41g Sample 2 0.769 1.179 Commercial Aspirin 0.402 Sample 1 Sample 2 0.689 0.74 g 1.089 1.14, 0.40g Data Table III: Volumes of Standardized NaOH Concentration of Standardized NaOH Item Initial Volume (mL) 0.0980 m Final Volume (ml) Net Volume Used(ml) Purified Aspirin Sample 1 186 m2 0.00mL 0.00 mL 18.6 mL 22.0mL Sample 2 22.0mL Commercial Aspirin Sample 1 0.00ML 20.80mL 19.80 mL 20.8mL 19.80 mL Sample 2 0.00 mL 5. . B. Based on the relationship between melting "point" and purity of a compound, describe what you theoretically expect to find for the final melting temperature of purified aspirin or for the melting point range of purified aspirin. A. The final melting temperature should be equal to that for impure aspirin. The final melting temperature should be less than that for impure aspirin. C. The melting point range should be slightly greater than that for impure aspirin. The melting point range should be equal to that for impure aspirin. E. None of the above answers are correct. Based on equation #1, if too much NaOH is added to the reaction flask during the titration of aspirin, will the calculation for % purity be affected, and why? D. 6. A C. No, the amount of NaOH added is not needed for the calculation of % purity. Yes, the numerator of the % purity calculation will be inaccurately large. Yes, the denominator of the % purity calculation will be inaccurately large. Yes, the numerator of the % purity calculation will be inaccurately small Yes, the denominator of the % purity calculation will be inaccurately small. E. 7. What types of testing might be used to distinguish between one type of commercial aspirin and another? A. Titration to determine purity Comparison of final melting temperatures Comparison of melting point ranges All of the above A, B & C are correct None of the above D. E. 8. What would a melting range of 93.5-95.0 C indicate about the purity of recrystallized aspirin if the aspirin showed a melting range of 98.0-106.0 before recrystallization? A. D. The recrystallized aspirin is impure, because the melting range is too broad. The recrystallized aspirin is pure, because the melting point range is relatively narrow. The melting data does not provide you with any indication of the purity of a compound. The melting point is a single temperature, not a range of temperatures. The recrystallized aspirin is impure or it was measured inaccurately because even though the range is narrow, the final melting temperature is lower than that for the original impure sample 

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


