Need help and a better understanding with questions 3, 6, 8, 10, 11, & 12.
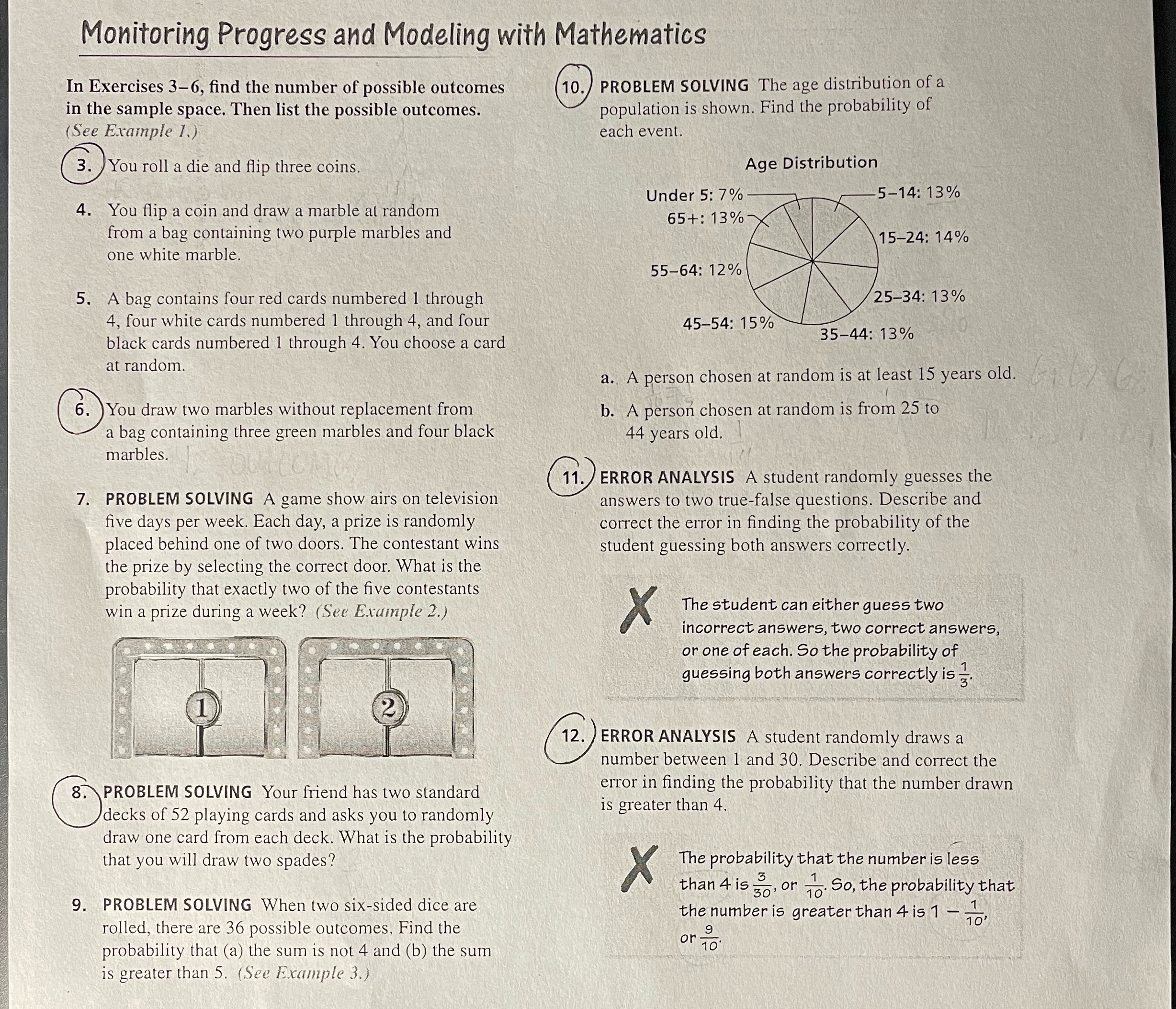
Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics In Exercises 3-6, find the number of possible outcomes 10. PROBLEM SOLVING The age distribution of a in the sample space. Then list the possible outcomes. population is shown. Find the probability of See Example 1.) each event. 3 . You roll a die and flip three coins. Age Distribution Under 5: 7% 5-14: 13% 4. You flip a coin and draw a marble at random 65+: 13% from a bag containing two purple marbles and 15-24: 14% one white marble. 55-64: 12% 5. A bag contains four red cards numbered 1 through 25-34: 13% 4, four white cards numbered 1 through 4, and four 45-54: 15% black cards numbered 1 through 4. You choose a card 35-44: 13% at random. a.. A person chosen at random is at least 15 years old. 6 . You draw two marbles without replacement from b. A person chosen at random is from 25 to a bag containing three green marbles and four black 44 years old. marbles. 11 . ERROR ANALYSIS A student randomly guesses the 7. PROBLEM SOLVING A game show airs on television answers to two true-false questions. Describe and five days per week. Each day, a prize is randomly correct the error in finding the probability of the placed behind one of two doors. The contestant wins student guessing both answers correctly. the prize by selecting the correct door. What is the probability that exactly two of the five contestants win a prize during a week? (See Example 2.) X The student can either guess two incorrect answers, two correct answers, or one of each. So the probability of guessing both answers correctly is 3 12 . ERROR ANALYSIS A student randomly draws a number between 1 and 30. Describe and correct the 8. PROBLEM SOLVING Your friend has two standard error in finding the probability that the number drawn decks of 52 playing cards and asks you to randomly is greater than 4. draw one card from each deck. What is the probability that you will draw two spades? The probability that the number is less X than 4 is 30, or 70. So, the probability that 9. PROBLEM SOLVING When two six-sided dice are the number is greater than 4 is 1 - 7, rolled, there are 36 possible outcomes. Find the or probability that (a) the sum is not 4 and (b) the sum 10' is greater than 5. (See Example 3.)