Need help answering question "i".
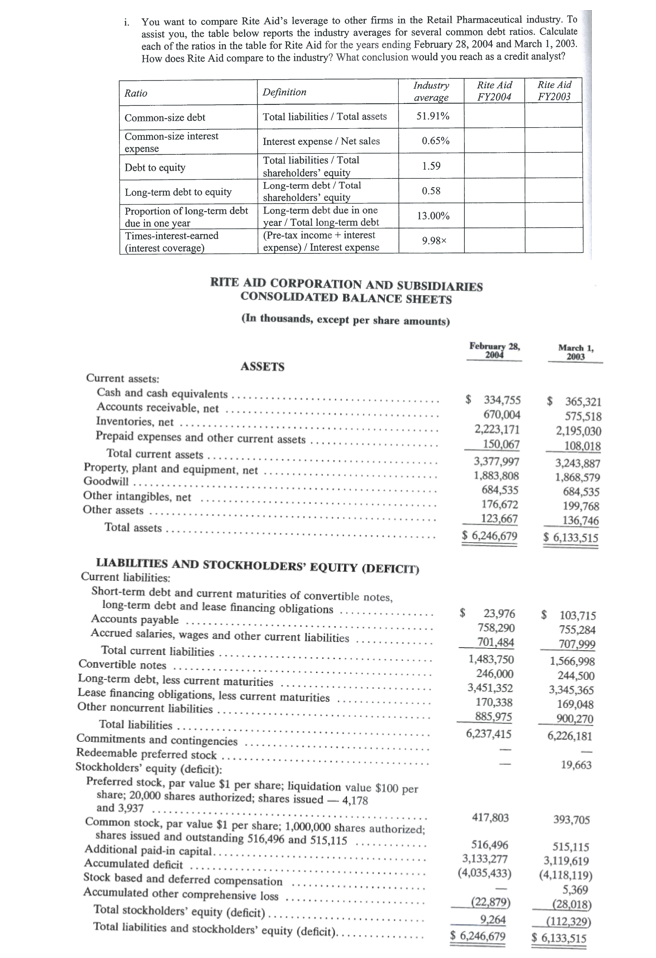
Question: You want to compare Rite Aid's leverage to other firms in the Retail Pharmaceutical industry. To assist you, the table below reports the industry averages for several common debt ratios. Calculate each of the ratios in the table for Rite Aid for the years ending February 28, 2004 and March 1, 2003. How does Rite Aid compare to the industry? What conclusion would you reach as a credit analyst?
 Income statement has been provided
Income statement has been provided
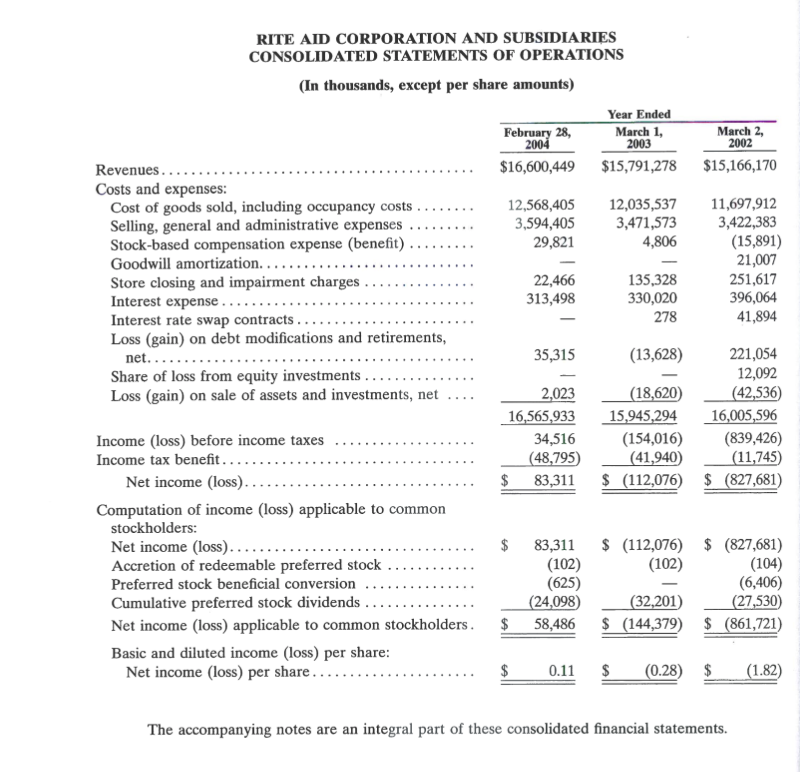
You want to compare Rite Aid's leverage to other firms in the Retail Pharmaceutical industry. To assist you, the table below reports the industry averages for several common debt ratios. Calculate each of the ratios in the table for Rite Aid for the years ending February 28, 2004 and March 1, 2003. How does Rite Aid compare to the industry? What conclusion would you reach as a credit analyst? Ratio Definition Industry average 51.91% Rite Aid FY2004 Rite Aid FY2003 Total liabilities/ Total assets Common-size debt Common-size interest expense 0.65% Debt to equity 1.59 Interest expense / Net sales Total liabilities/Total shareholders' equity Long-term debt / Total shareholders' equity Long-term debt due in one year / Total long-term debt (Pre-tax income + interest expense) / Interest expense Long-term debt to equity Proportion of long-term debt due in one year Times-interest-earned interest coverage) 0.58 13.00% 9.98 RITE AID CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS (In thousands, except per share amounts) February 28, 2001 March 1, 2003 ASSETS Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents ............ Accounts receivable, net ............. Inventories, net ... Prepaid expenses and other current assets .. Total current assets ................ . Property, plant and equipment, net .............. Goodwill.... Other intangibles, net ............ Other assets Total assets ........................ $ 334,755 670,004 2,223,171 150,067 3,377,997 1,883,808 684,535 176,672 123,667 $ 6,246,679 $ 365,321 575,518 2,195,030 108,018 3,243,887 1,868,579 684,535 199,768 136,746 $ 6,133,515 $ 23,976 758,290 701,484 1,483,750 246,000 3,451,352 170,338 885,975 6,237,415 $ 103,715 755,284 707 999 1,566,998 244,500 3,345,365 169,048 900,270 6,226,181 LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY (DEFICIT) Current liabilities: Short-term debt and current maturities of convertible notes, long-term debt and lease financing obligations .... Accounts payable ....... Accrued salaries, wages and other current liabilities .... Total current liabilities .. Convertible notes ...... Long-term debt, less current maturities. Lease financing obligations, less current maturities ... Other noncurrent liabilities. Total liabilities. Commitments and contingencies Redeemable preferred stock ... Stockholders' equity (deficit): Preferred stock, par value $1 per share; liquidation value $100 per share; 20,000 shares authorized; shares issued - 4,178 and 3,937 . Common stock, par value $1 per share; 1,000,000 shares authorized; shares issued and outstanding 516,496 and 515,115 ... Additional paid-in capital..... Accumulated deficit ..... Stock based and deferred compensation ........... Accumulated other comprehensive loss ........... Total stockholders' equity (deficit)............. Total liabilities and stockholders' equity (deficit)............. 19,663 417,803 393,705 516,496 3,133,277 (4,035,433) 515,115 3,119,619 (4,118,119) 5,369 (28,018) (112,329) $ 6,133,515 (22,879) 9,264 $ 6,246,679 RITE AID CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS (In thousands, except per share amounts) Year Ended March 1, 2003 $15,791,278 February 28, 2004 $16,600,449 March 2, 2002 $15,166,170 12,568,405 3,594,405 29,821 12,035,537 3,471,573 4,806 Revenues................ Costs and expenses: Cost of goods sold, including occupancy costs. Selling, general and administrative expenses ......... Stock-based compensation expense (benefit) ...... Goodwill amortization........... Store closing and impairment charges .......... Interest expense ........ Interest rate swap contracts ..... Loss (gain) on debt modifications and retirements, 11,697,912 3,422,383 (15,891) 21,007 251,617 396,064 41,894 22,466 313,498 135,328 330,020 278 n e t .... ................................. 35,315 (13,628) Share of loss from equity investments ....... Loss (gain) on sale of assets and investments, net .... 2,023 16,565,933 34,516 (48,795) $ 83,311 (18,620 15,945,294 (154,016) (41,940) $ (112,076) 221,054 12,092 (42,536) 16,005,596 (839,426) (11,745) $ (827,681) $ Income (loss) before income taxes ..... Income tax benefit.......... Net income (loss)...... .............. Computation of income (loss) applicable to common stockholders: Net income (loss)................ ... Accretion of redeemable preferred stock ....... Preferred stock beneficial conversion ............... Cumulative preferred stock dividends Net income (loss) applicable to common stockholders. Basic and diluted income (loss) per share: Net income (loss) per share...... $ (112,076) (102) 83,311 (102) (625) (24,098) 58,486 $ (827,681) (104) (6,406) (27,530 $ (861,721) (32,201) $ (144,379) $ $ 0.11 $ (0.28) $ (1.82) The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements. You want to compare Rite Aid's leverage to other firms in the Retail Pharmaceutical industry. To assist you, the table below reports the industry averages for several common debt ratios. Calculate each of the ratios in the table for Rite Aid for the years ending February 28, 2004 and March 1, 2003. How does Rite Aid compare to the industry? What conclusion would you reach as a credit analyst? Ratio Definition Industry average 51.91% Rite Aid FY2004 Rite Aid FY2003 Total liabilities/ Total assets Common-size debt Common-size interest expense 0.65% Debt to equity 1.59 Interest expense / Net sales Total liabilities/Total shareholders' equity Long-term debt / Total shareholders' equity Long-term debt due in one year / Total long-term debt (Pre-tax income + interest expense) / Interest expense Long-term debt to equity Proportion of long-term debt due in one year Times-interest-earned interest coverage) 0.58 13.00% 9.98 RITE AID CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS (In thousands, except per share amounts) February 28, 2001 March 1, 2003 ASSETS Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents ............ Accounts receivable, net ............. Inventories, net ... Prepaid expenses and other current assets .. Total current assets ................ . Property, plant and equipment, net .............. Goodwill.... Other intangibles, net ............ Other assets Total assets ........................ $ 334,755 670,004 2,223,171 150,067 3,377,997 1,883,808 684,535 176,672 123,667 $ 6,246,679 $ 365,321 575,518 2,195,030 108,018 3,243,887 1,868,579 684,535 199,768 136,746 $ 6,133,515 $ 23,976 758,290 701,484 1,483,750 246,000 3,451,352 170,338 885,975 6,237,415 $ 103,715 755,284 707 999 1,566,998 244,500 3,345,365 169,048 900,270 6,226,181 LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY (DEFICIT) Current liabilities: Short-term debt and current maturities of convertible notes, long-term debt and lease financing obligations .... Accounts payable ....... Accrued salaries, wages and other current liabilities .... Total current liabilities .. Convertible notes ...... Long-term debt, less current maturities. Lease financing obligations, less current maturities ... Other noncurrent liabilities. Total liabilities. Commitments and contingencies Redeemable preferred stock ... Stockholders' equity (deficit): Preferred stock, par value $1 per share; liquidation value $100 per share; 20,000 shares authorized; shares issued - 4,178 and 3,937 . Common stock, par value $1 per share; 1,000,000 shares authorized; shares issued and outstanding 516,496 and 515,115 ... Additional paid-in capital..... Accumulated deficit ..... Stock based and deferred compensation ........... Accumulated other comprehensive loss ........... Total stockholders' equity (deficit)............. Total liabilities and stockholders' equity (deficit)............. 19,663 417,803 393,705 516,496 3,133,277 (4,035,433) 515,115 3,119,619 (4,118,119) 5,369 (28,018) (112,329) $ 6,133,515 (22,879) 9,264 $ 6,246,679 RITE AID CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS (In thousands, except per share amounts) Year Ended March 1, 2003 $15,791,278 February 28, 2004 $16,600,449 March 2, 2002 $15,166,170 12,568,405 3,594,405 29,821 12,035,537 3,471,573 4,806 Revenues................ Costs and expenses: Cost of goods sold, including occupancy costs. Selling, general and administrative expenses ......... Stock-based compensation expense (benefit) ...... Goodwill amortization........... Store closing and impairment charges .......... Interest expense ........ Interest rate swap contracts ..... Loss (gain) on debt modifications and retirements, 11,697,912 3,422,383 (15,891) 21,007 251,617 396,064 41,894 22,466 313,498 135,328 330,020 278 n e t .... ................................. 35,315 (13,628) Share of loss from equity investments ....... Loss (gain) on sale of assets and investments, net .... 2,023 16,565,933 34,516 (48,795) $ 83,311 (18,620 15,945,294 (154,016) (41,940) $ (112,076) 221,054 12,092 (42,536) 16,005,596 (839,426) (11,745) $ (827,681) $ Income (loss) before income taxes ..... Income tax benefit.......... Net income (loss)...... .............. Computation of income (loss) applicable to common stockholders: Net income (loss)................ ... Accretion of redeemable preferred stock ....... Preferred stock beneficial conversion ............... Cumulative preferred stock dividends Net income (loss) applicable to common stockholders. Basic and diluted income (loss) per share: Net income (loss) per share...... $ (112,076) (102) 83,311 (102) (625) (24,098) 58,486 $ (827,681) (104) (6,406) (27,530 $ (861,721) (32,201) $ (144,379) $ $ 0.11 $ (0.28) $ (1.82) The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements

 Income statement has been provided
Income statement has been provided





