need help on adjustment "e" (16), the closing journal entrys, and the analysis
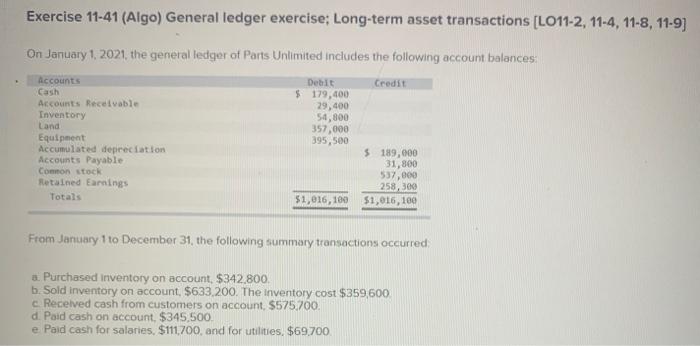
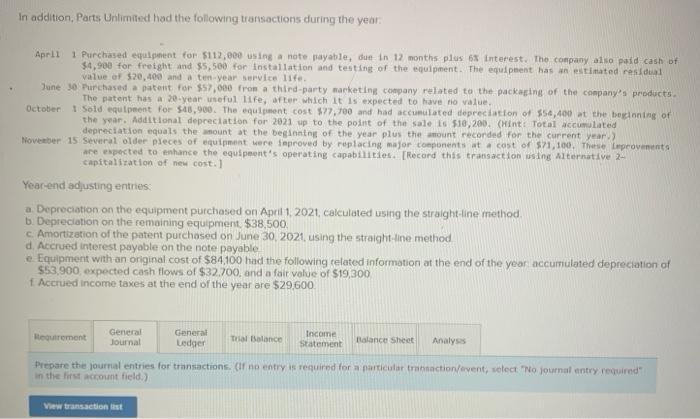
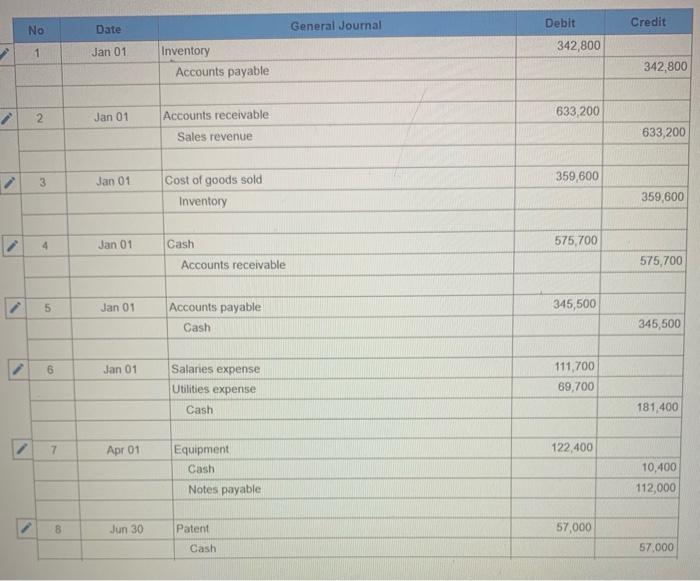
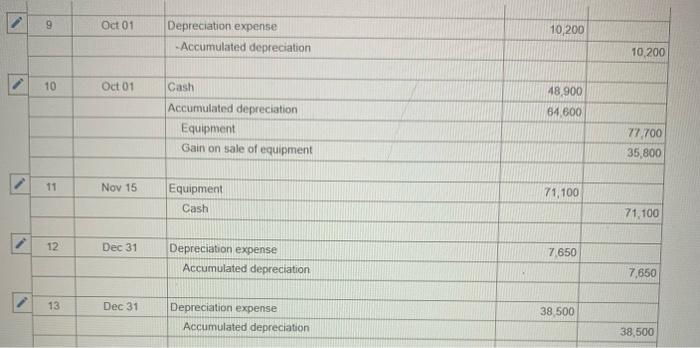
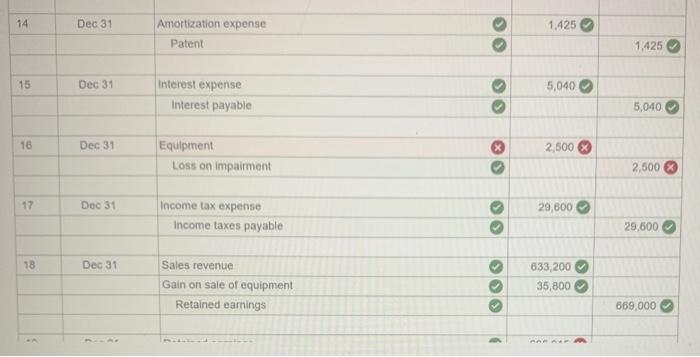
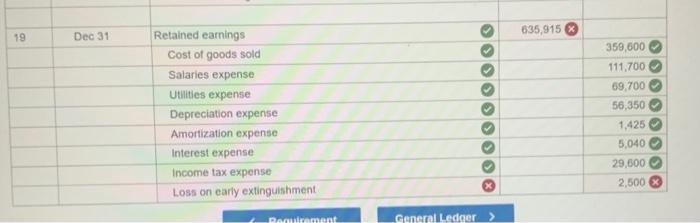
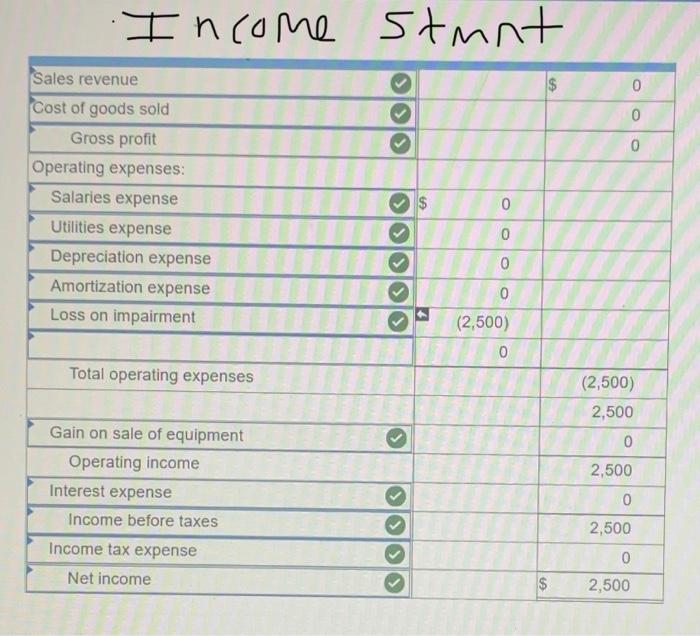
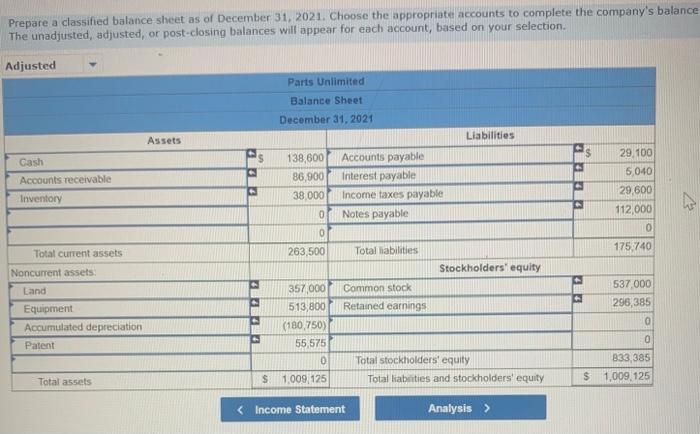
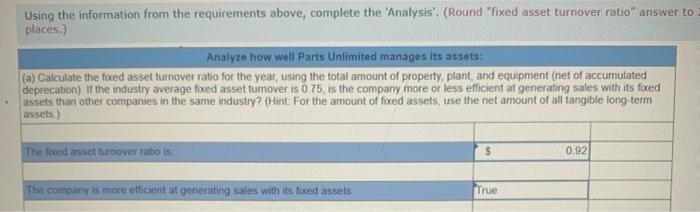
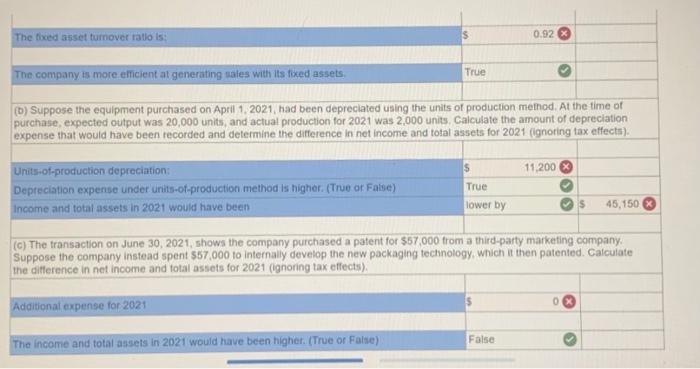
Exercise 11-41 (Algo) General ledger exercise: Long-term asset transactions [LO11-2, 11-4, 11-8, 11-9) On January 1, 2021, the general ledger of Parts Unlimited includes the following account balances: Accounts Debit Credit Cash $ 179,400 Accounts Receivable 29,400 Inventory 54,800 Land 357,000 Equipment 395,500 Accumulated depreciation $ 189,000 Accounts Payable 31,800 Common stock 537,000 Retained Earnings 258,300 Totals $1,016, 100 $1,016, 100 From January 1 to December 31, the following summary transactions occurred a. Purchased Inventory on account, $342.800. b. Sold inventory on account, $633 200. The inventory cost $359,600 c. Received cash from customers on account, $575.700. d. Paid cash on account. $345,500, e Paid cash for salaries, $111,700, and for utilities. $69700 In addition, Parts Unlimited had the following transactions during the year April 1 Purchased equipment for $112,000 using a note payable, due in 12 months plus 6% Interest. The company also paid cash of $4,900 for freight and $5,500 for installation and testing of the equipment. The equipment has an estimated residual value of $20,400 and a ten year service life June 30 Purchased aptent for $57,000 from a third party marketing company related to the packaging of the company's products The patent has a 20-year useful life, after which it is expected to have no value October 1 Sold equipment for 548,900. The equipment cost $27,700 and had accumulated depreciation of $54,400 at the beginning of the year. Additional depreciation for 2021 up to the point of the sale is $10,200. (Hint: Total accumulated depreciation equals the mount at the beginning of the year plus the amount recorded for the current year) November 15 several older pieces of equipment were improved by replacing major components at a cost of $21,100. These aprovemento are expected to enhance the equipment's operating capabilities. Record this transaction using Alternative 24 capitalization of new cost. 1 Year-end adjusting entries a Depreciation on the equipment purchased on April 2021, calculated using the straight line method b. Depreciation on the remaining equipment $38,500, c. Amortization of the patent purchased on June 30, 2021, using the straight-line method d. Accrued interest payable on the note payable e Equipment with an original cost of $84.100 had the following related information at the end of the year accumulated depreciation of $53.900, expected cash flows of $32,700, and a fair value of $19,300 Accrued income taxes at the end of the year are $29,600 Requirement General Journal General Ledger Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Analys Prepare the journal entries for transactions. I no entry is required for a particular traction/event, select "No journal entry required in the first account field.) View transactions No Date Debit Credit General Journal 1 Jan 01 342,800 Inventory Accounts payable 342,800 1 633,200 2 Jan 01 Accounts receivable Sales revenue 633,200 3 Jan 01 359,600 Cost of goods sold Inventory 359,600 4 Jan 01 Cash 575,700 Accounts receivable 575,700 5 Jan 01 345,500 Accounts payable Cash 345,500 6 Jan 01 Salaries expense Utilities expense Cash 111,700 69,700 181,400 2 7 Apr 01 122,400 Equipment Cash Notes payable 10,400 112,000 8 Jun 30 57,000 Patent Cash 57.000 9 Oct 01 10,200 Depreciation expense - Accumulated depreciation 10.200 10 Oct 01 Cash 48.900 64.600 Accumulated depreciation Equipment Gain on sale of equipment 77.700 35,800 11 Nov 15 Equipment Cash 71,100 71,100 12 Dec 31 Depreciation expense Accumulated depreciation 7.650 7,650 13 Dec 31 Depreciation expense Accumulated depreciation 38,500 38,500 14 Dec 31 Amortization expense 1,425 Patent 1.425 15 Dec 31 5,040 Interest expense Interest payable 5,040 18 Dec 31 2,500 > Equipment Loss on impairment XS 2,500 17 Dec 31 29,600 Income tax expense Income taxes payable 29,600 18 Dec 31 Sales revenue Gain on sale of equipment Retained earnings 633,200 35,800 O 669,000 19 Dec 31 635,915 00 Retained earnings Cost of goods sold Salaries expense Utilities expense Depreciation expense Amortization expense Interest expense Income tax expense Loss on early extinguishment 359,600 111.700 69,700 56,350 1.425 5,040 SS 29,600 2,500 inment General Ledger Income stunt $ 0 OIOIO 0 0 Sales revenue Cost of goods sold Gross profit Operating expenses: Salaries expense Utilities expense Depreciation expense Amortization expense Loss on impairment $ 0 0 OOOOO 0 0 (2,500) 0 Total operating expenses (2,500) 2,500 > 0 2,500 Gain on sale of equipment Operating income Interest expense Income before taxes Income tax expense Net income 0 2,500 OOO 0 $ $ 2,500 Prepare a classified balance sheet as of December 31, 2021. Choose the appropriate accounts to complete the company's balance The unadjusted, adjusted, or post-closing balances will appear for each account, based on your selection. Adjusted Parts Unlimited Balance Sheet December 31, 2021 Assets Liabilities S Cash Accounts receivable Inventory 138,600 86.900 38,000 01 Accounts payable Interest payable Income taxes payable Notes payable 29.100 6,040 29,600 112,000 0 0 263,500 Total liabilities 175,740 Total current assets Noncurrent assets Land Stockholders' equity Common stock Retained earnings 537.000 296,385 Equipment Accumulated depreciation Patent 357,000 513,800 (180750) 55,575 D 0 Total stockholders' equity Total liabilities and stockholders' equity 833,385 $ 1,009, 125 Total assets $ 1,009, 125 Using the information from the requirements above, complete the 'Analysis'. (Round "fixed asset turnover ratio answer to places.) Analyze how well Parts Unlimited manages its assets: (a) Calculate the tuxed asset turnover ratio for the year, using the total amount of property, plant, and equipment (net of accumulated deprecation) If the industry average fixed asset tumover is 0.75, is the company more or less efficient at generating sales with its foxed assets than other companies in the same industry? (Hint For the amount of fixed assets, use the net amount of all tangible long-term assets) The fixed asset turnover ratio is $ 0.92 The company is more efficient at generating sales with its fixed assets True The fixed asset turnover ratio is: 0.92 The company is more efficient at generating sales with its fixed assets, True (b) Suppose the equipment purchased on April 1.2021, had been depreciated using the units of production method. At the time of purchase, expected output was 20,000 units and actual production for 2021 was 2,000 units. Calculate the amount of depreciation expense that would have been recorded and determine the difference in net income and total assets for 2021 (ignoring tax effects). $ 11.200 True Units-of-production depreciation: Depreciation expense under units-of-production method is higher (True or False) Income and total assets in 2021 would have been lower by 45,150 (c) The transaction on June 30, 2021, shows the company purchased a patent for $57.000 from a third-party marketing company Suppose the company instead spent $57,000 to Internally develop the new packaging technology, which it then patented. Calculate the difference in net income and total assets for 2021 (ignoring tax effects), Additional expense for 2021 False The income and total assets in 2021 would have been higher. (True or False)