need help on number 11. and wanted to make sure 1-10 are correct.
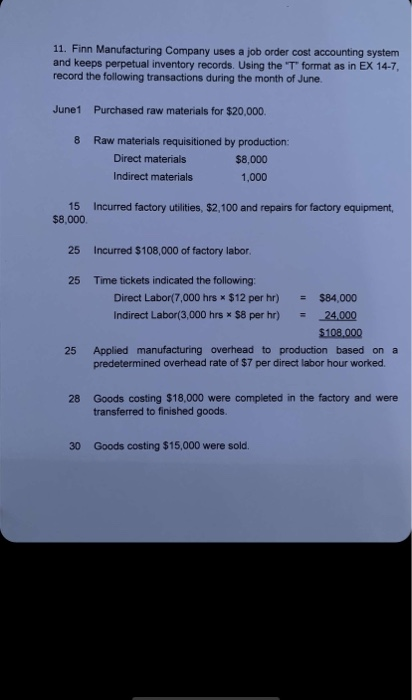
11. Finn Manufacturing Company uses a job order cost accounting system and keeps perpetual inventory records. Using the 'T format as in EX 14-7, record the following transactions during the month of June. June1 Purchased raw materials for $20,000. 8 Raw materials requisitioned by production: Direct materials $8,000 Indirect materials 1,000 15 $8,000 Incurred factory utilities, $2,100 and repairs for factory equipment, 25 incurred $108,000 of factory labor. 25 Time tickets indicated the following: Direct Labor(7,000 hrs * $12 per hr) = $84,000 Indirect Labor(3,000 hrs * $8 per hr) = 24.000 $108.000 Applied manufacturing overhead to production based on a predetermined overhead rate of $7 per direct labor hour worked. 25 28 Goods costing $18,000 were completed in the factory and were transferred to finished goods. 30 Goods costing $15,000 were sold b. Increase Work in Process Inventory and decrease Raw Materials Inventory, Factory Labor, and Manufacturing Overhead. o Increase Raw Materials Inventory and decrease Work in Process Inventory d Increase Finished Goods Inventory and decrease Work in Process Inventory 7. Which of the following is included in factory labor costs? a Gross earnings Employer payroll aces Fringe benefits All of these are included 8. Which one of the following best describes a job cost sheet? It is a form used to record the cost chargeable to a specific and to m e the total and un costs of the completed job b. It is used to track manufacturing overhead to specific jobs c. Et is used by management to understand how direct costs affect proti d. is a daily form that management uses for tracking worker productivity on which employee raises are based 9. Applied factory overhead is 1,650,000 and actual labor costs totaled $1,100,000. How much is the company's predetermined overhead rate to the nearest cent? a $1.45 $131 (C$1.50 10. The labor costs that have been identified as indirect labor should be recorded manufacturing overhead e the indelos worked on d salary expense . 1. A major purpose of cost accounting is to a. classify all costs as operating or nonoperating. b. measure, record, and report period costs. c. provide information to stockholders for investment decisions. d measure, record, and report product costs. 2. The two basic types of cost accounting systems are a job order and job accumulation systems. b. job order and process cost systems. C. process cost and batch systems. d. job order and batch systems. Which of the following would be accounted for using a job order cost system? a. The production of personal computers. b. The production of automobiles The refining of petroleum d.) The construction of a new campus building 4. Process costing is not used when a. similar goods are being produced. b. large volumes are produced. @ jobs have distinguishing characteristics. d. a series of connected manufacturing processes is necessary. The flow of costs in a job order cost system a involves accumulating manufacturing costs incurred and assigning the accumulated costs to work done. b. cannot be measured until all jobs are complete. c. measures product costs for a set time period. d. generally follows a LIFO cost flow assumption 6. When a job is completed and all costs have been accumulated on a job cost sheet, the journal entry that should be made is a. Increase Finished Goods Inventory and decrease Raw Materials Inventory, Factory Labor, and Manufacturing Overhead










