Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Revenue variances Lowell Manufacturing Inc. has a normal selling price of $20 per unit and has been selling 125,000 units per month. In November,

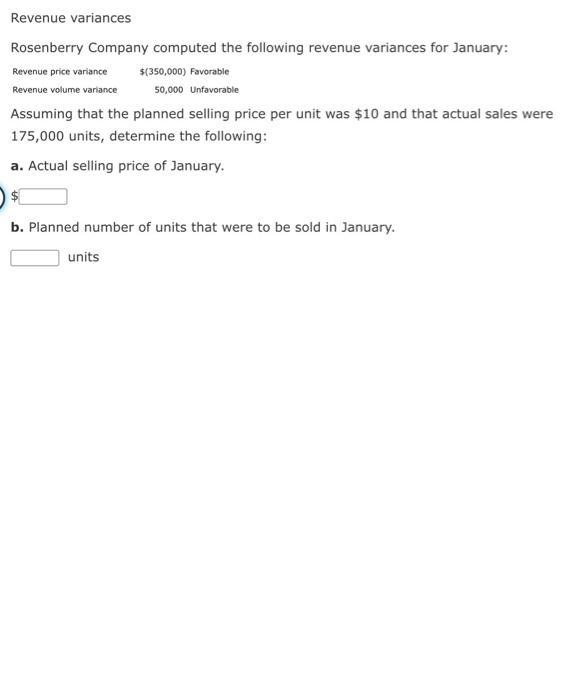
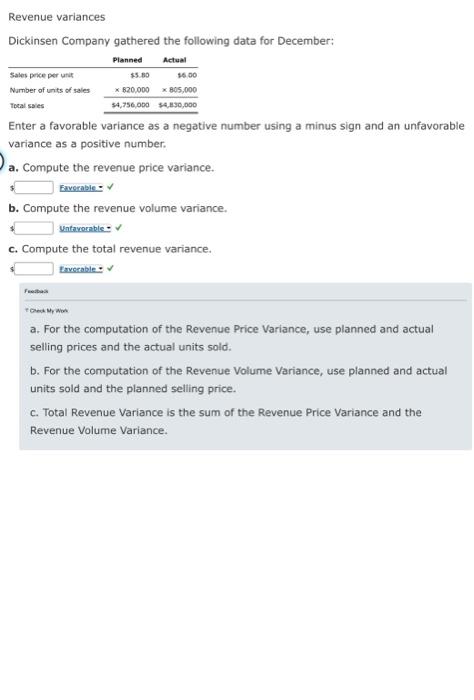
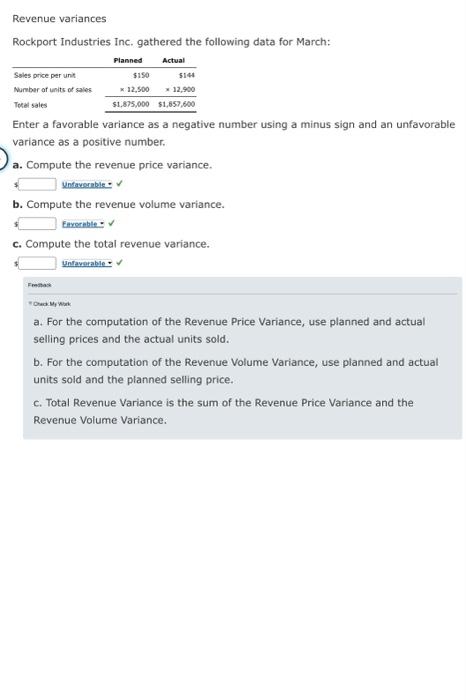
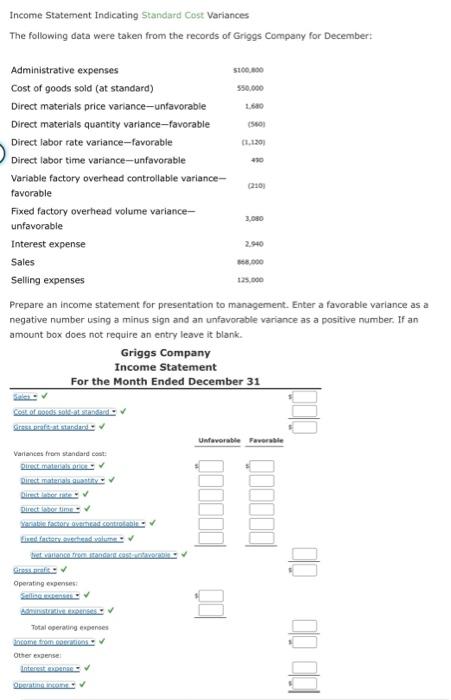
Revenue variances Lowell Manufacturing Inc. has a normal selling price of $20 per unit and has been selling 125,000 units per month. In November, Lowell Manufacturing decided to lower its price to $19 per unit expecting it can increase the units sold by 16%. a. Compute the normal revenue with a $20 selling price. b. Compute the planned revenue with a $19 selling price. $ c. Compute the actual revenue for November, assuming 135,000 units were sold in November at $19 per unit. d. Compute the revenue price variance, assuming 135,000 units were sold in November at $19 per unit. e. Compute the revenue volume variance, assuming 135,000 units were sold in November at $19 per unit. Unfavorable f. Analyze and interpret the lowering of the price to $19. Decreasing the selling price to $19 did increase total revenue, but it did not increase the revenues by 16% as planned. Revenue variances Rosenberry Company computed the following revenue variances for January: Revenue price variance Revenue volume variance $(350,000) Favorable 50,000 Unfavorable Assuming that the planned selling price per unit was $10 and that actual sales were 175,000 units, determine the following: a. Actual selling price of January. b. Planned number of units that were to be sold in January. units Revenue variances Dickinsen Company gathered the following data for December: Sales price per unit Number of units of sales Total sales Planned Actual $5.80 16.00 * 820,000 805,000 $4,756,000 $4,830,000 Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positive number. a. Compute the revenue price variance. Favorable b. Compute the revenue volume variance. Unfavorable c. Compute the total revenue variance. Favorable Check My Work a. For the computation of the Revenue Price Variance, use planned and actual selling prices and the actual units sold. b. For the computation of the Revenue Volume Variance, use planned and actual units sold and the planned selling price. c. Total Revenue Variance is the sum of the Revenue Price Variance and the Revenue Volume Variance. Revenue variances Rockport Industries Inc. gathered the following data for March: Sales price per unit Number of units of sales Total sales Planned Actual $150 5144 x12,500 12,900 $1,875,000 $1,657,600 Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positive number. a. Compute the revenue price variance. Unfavorable b. Compute the revenue volume variance. Eavorable c. Compute the total revenue variance. Unfavorable a. For the computation of the Revenue Price Variance, use planned and actual selling prices and the actual units sold. b. For the computation of the Revenue Volume Variance, use planned and actual units sold and the planned selling price. c. Total Revenue Variance is the sum of the Revenue Price Variance and the Revenue Volume Variance. Income Statement Indicating Standard Cost Variances The following data were taken from the records of Griggs Company for December: Administrative expenses Cost of goods sold (at standard) Direct materials price variance-unfavorable Direct materials quantity variance-favorable Direct labor rate variance-favorable Direct labor time variance-unfavorable Variable factory overhead controllable variance- favorable Fixed factory overhead volume variance- $100,000 550,000 1,680 (560) (1,120) 430 (210 3,080 unfavorable Interest expense Sales Selling expenses 2,940 868,000 125,000 Prepare an income statement for presentation to management. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positive number. If an amount box does not require an entry leave it blank. Griggs Company Income Statement For the Month Ended December 31 Cost of goods sold at standard Gress grafit:at standar Variances from standard cost: Direct materials pric Direct material quantity." Direct labor time Yanable factory overhead controlable Fixed factory schedu feet variance from standard cast-infavorab Grass cafi Operating expenses: Selling extenses Administrative exam Total operating expenses income from operations Other expense: Interest expense Operating income. Unfavorable Favorable 0000-00 Recording Standards in Accounts The Assembly Department produced 2,000 units of product during March. Each unit required 1.5 standard direct labor hours. There were 3,200 actual hours used in the Assembly Department during March at an actual rate of $13 per hour. The standard direct labor rate is $14 per hour. Assuming direct labor for a month is paid on the fifth day of the following month, journalize the direct labor in the Assembly Department on March 31. For a compound transaction, if an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. March 31 Work in Process Direct Labor Time Variance Direct Labor Rate Variance Wages Payable Feedback Check My Work Debit (unfavorable) or credit (favorable) direct labor rate and direct labor time variances.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Sure lets break this down Dickinsen Company Revenue Variances a Compute the Revenue Price Variance Formula Revenue Price Variance Actual Selling Price Planned Selling Price Actual Units Sold Revenue P...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


