Need help.
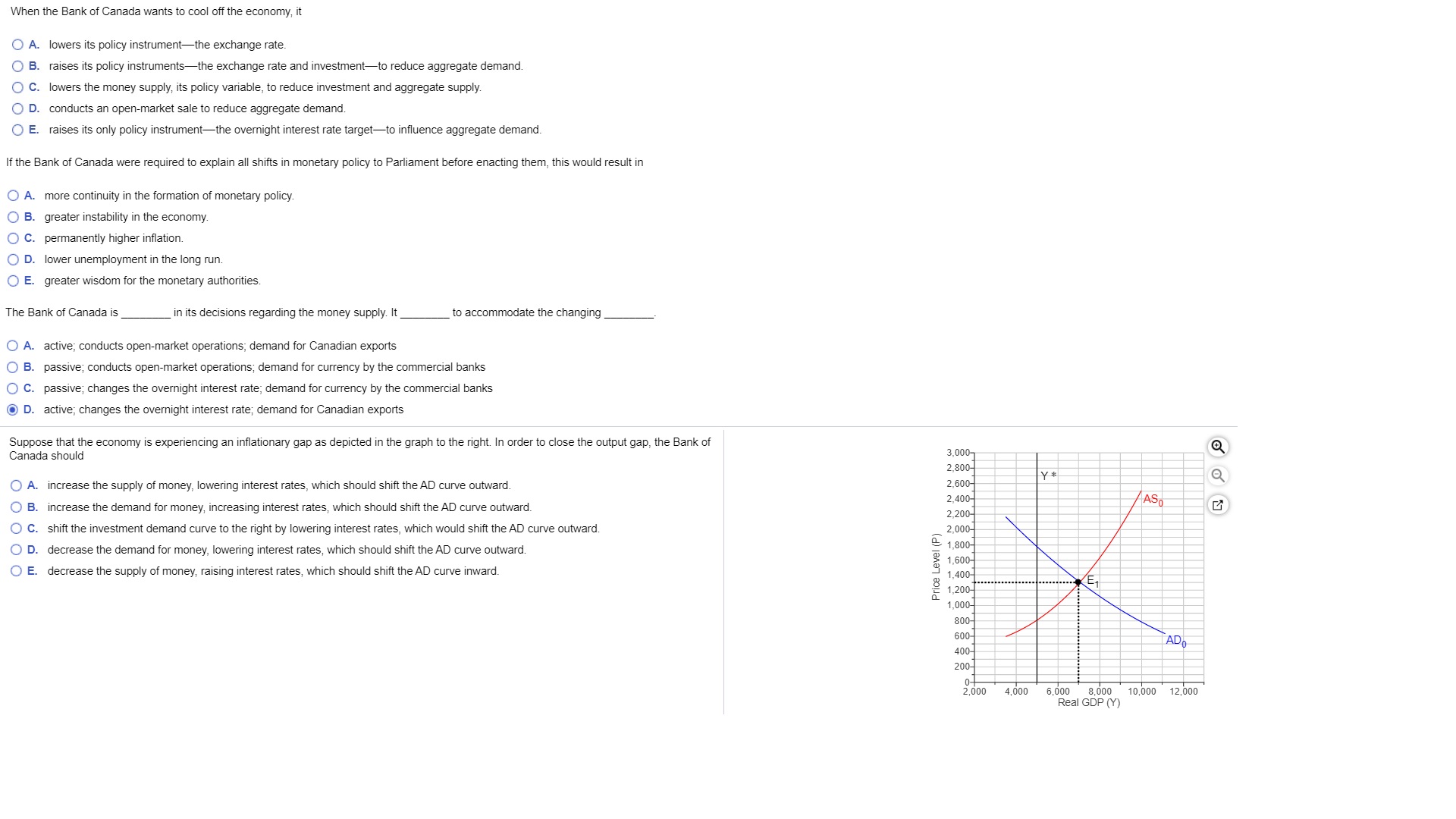
When the Bank of Canada wants to cool off the economy, it O A. lowers its policy instrument-the exchange rate. O B. raises its policy instruments-the exchange rate and investment-to reduce aggregate demand. O C. lowers the money supply, its policy variable, to reduce investment and aggregate supply O D. conducts an open-market sale to reduce aggregate demand. O E. raises its only policy instrument-the overnight interest rate target-to influence aggregate demand. If the Bank of Canada were required to explain all shifts in monetary policy to Parliament before enacting them, this would result in O A. more continuity in the formation of monetary policy. O B. greater instability in the economy O C. permanently higher inflation. O D. lower unemployment in the long run. O E. greater wisdom for the monetary authorities. The Bank of Canada is in its decisions regarding the money supply. It to accommodate the changing O A. active; conducts open-market operations; demand for Canadian exports O B. passive; conducts open-market operations; demand for currency by the commercial banks O C. passive; changes the overnight interest rate; demand for currency by the commercial banks D. active, changes the overnight interest rate; demand for Canadian exports Suppose that the economy is experiencing an inflationary gap as depicted in the graph to the right. In order to close the output gap, the Bank of Canada should 3,000- 2,800- O A. increase the supply of money, lowering interest rates, which should shift the AD curve outward. 2,600- Y * O B. increase the demand for money, increasing interest rates, which should shift the AD curve outward. 2,400- AS 2,200- O C. shift the investment demand curve to the right by lowering interest rates, which would shift the AD curve outward. 2,000- O D. decrease the demand for money, lowering interest rates, which should shift the AD curve outward. 2 1,800- O E. decrease the supply of money, raising interest rates, which should shift the AD curve inward. 1,600- Price L 1,400- 1,200-" E1 1,000- 800- 600- 400- ADo 200- 2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 10,000 12,000 Real GDP (Y)