Need Help With 3&4!
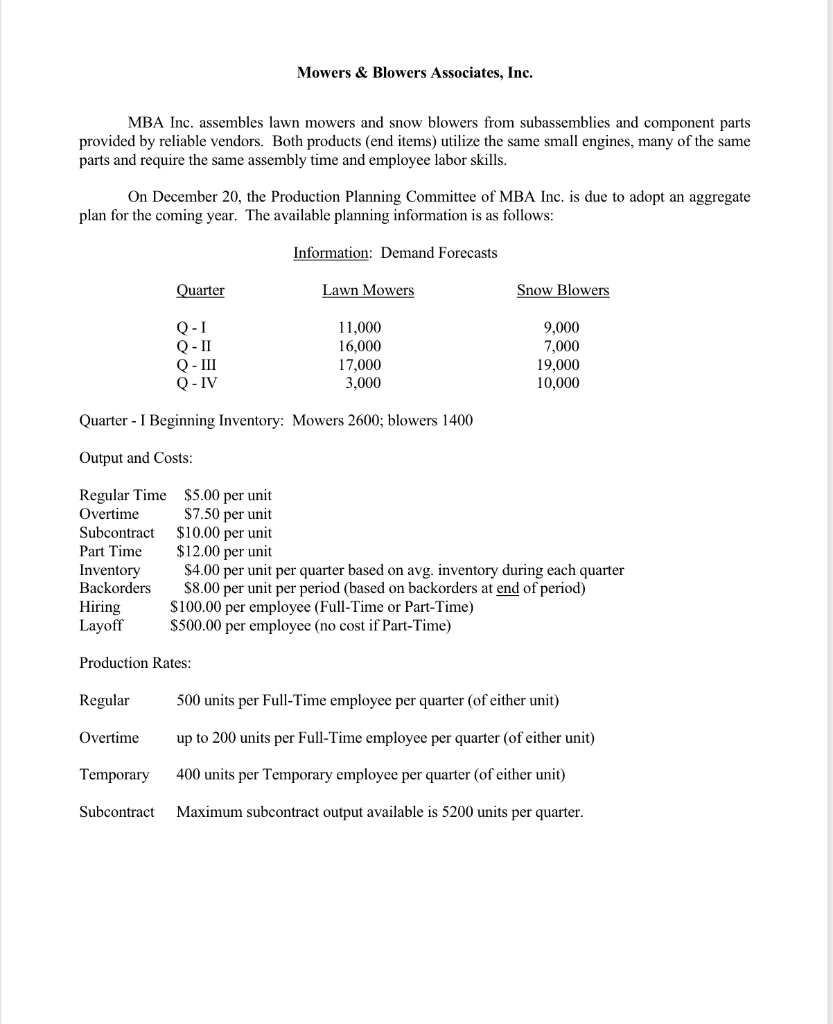


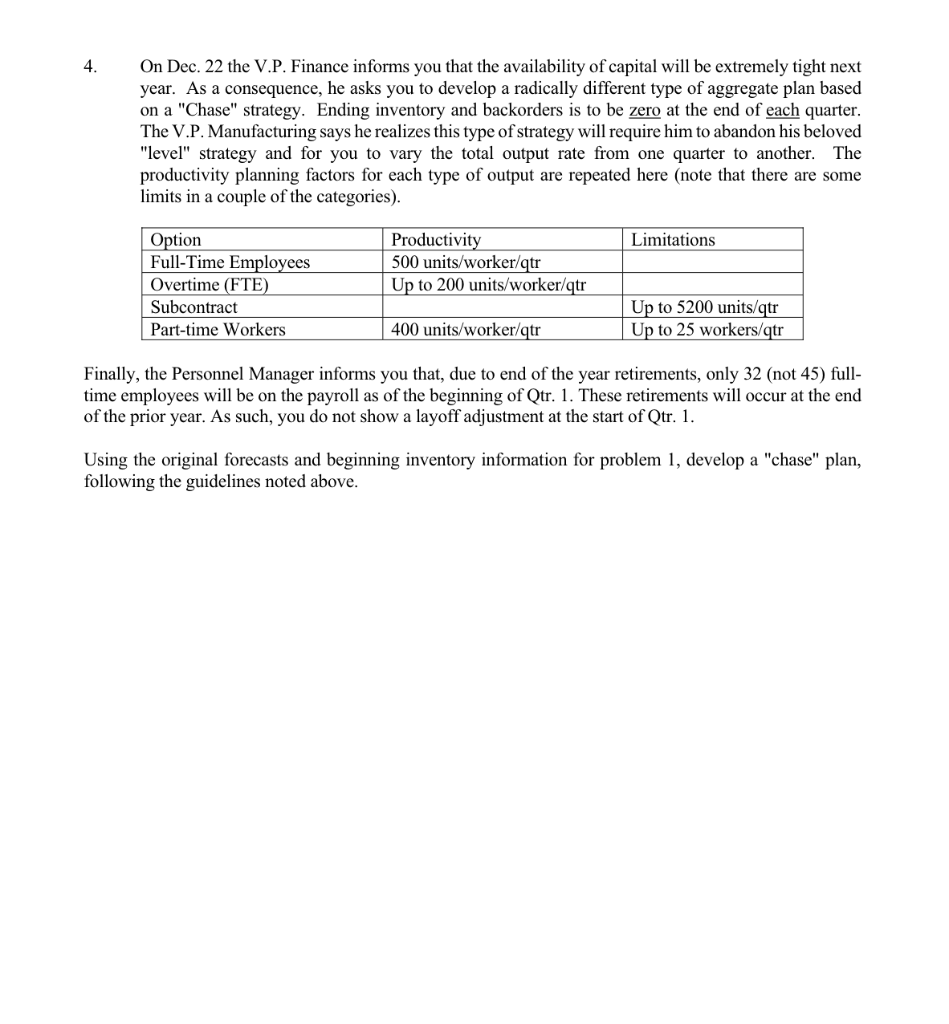
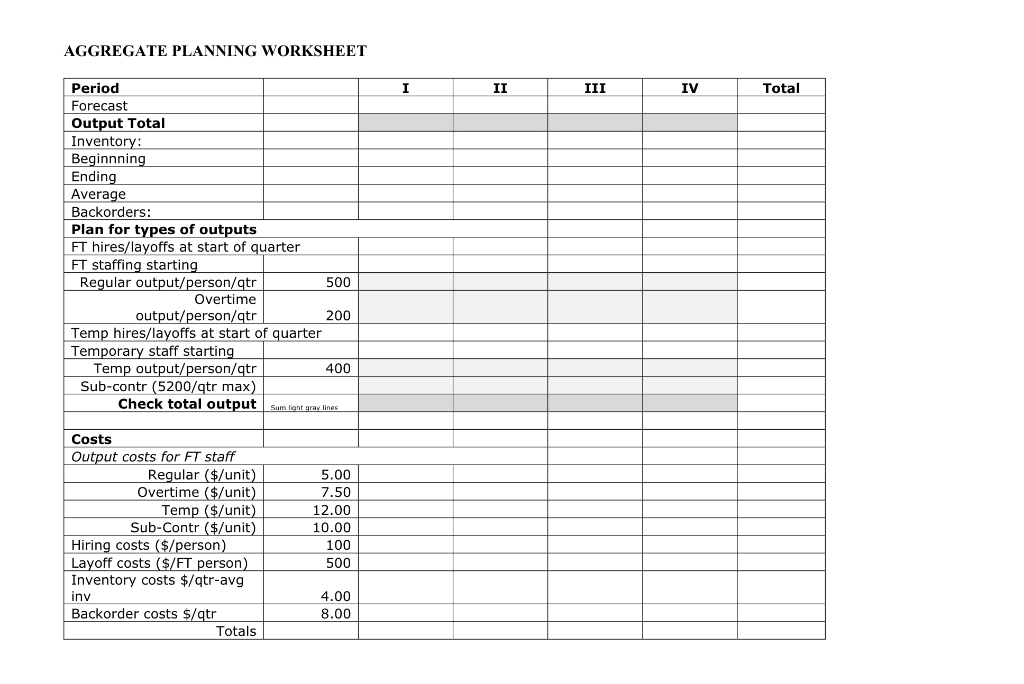
MBA Inc. assembles lawn mowers and snow blowers from subassemblies and component parts provided by reliable vendors. Both products (end items) utilize the same small engines, many of the same parts and require the same assembly time and employee labor skills. On December 20, the Production Planning Committee of MBA Inc. is due to adopt an aggregate plan for the coming year. The available planning information is as follows: Quarter - I Beginning Inventory: Mowers 2600; blowers 1400 Output and Costs: Regular Time $5.00 per unit Overtime $7.50 per unit Subcontract $10.00 per unit Part Time $12.00 per unit Inventory $4.00 per unit per quarter based on avg. inventory during each quarter Backorders $8.00 per unit per period (based on backorders at end of period) Hiring $100.00 per employee (Full-Time or Part-Time) Layoff $500.00 per employee (no cost if Part-Time) Production Rates: Regular 500 units per Full-Time employee per quarter (of either unit) Overtime up to 200 units per Full-Time employee per quarter (of either unit) Temporary 400 units per Temporary employee per quarter (of either unit) Subcontract Maximum subcontract output available is 5200 units per quarter. Production work force: As of the first of the year, the production work force consists of 45 Full-Time employees. Additional Assumptions: 1) Temporary employees may not work overtime 2) Assume 100\% utilization of Full-Time employees on regular time and of Temporary employees at all times (i.e., all such employees on the payroll during a period produce at the rates shown under Production Rates). 3) Overtime utilization of Full-Time employees can be on an as needed basis subject to the limitation on maximum overtime output shown under Production Rates. Given all of this planning information, develop a series of aggregate plans to meet the criteria presented in the following series of problems. All plans must include full costs and hiring/layoff actions, as needed. Show all plans using one of the worksheets at the end of this document. 1. A. Develop an aggregate plan which utilizes a level (constant) rate of output each quarter using only full-time employees without overtime. Ending inventory for quarter IV is 2000 ; this means, of course, that there will be no backorders at the end of quarter IV. Backorders may occur at the end of the other quarters. B. If each shipping container for a completed mower or blower requires 6cu. ft. of space, what is the maximum amount of cubic feet of space that would be needed in the finished goods warehouse if your plan 1-A is adopted? (Assume that sales and production occur at a steady, daily rate within each quarter.) C. If the cost of each completed end item is $200.00, what is the maximum amount of capital that will be tied up in finished goods inventory during the year? (Continue with the assumption given for 1B.) 2. Suppose that on December 21 the long-range weather forecast is released by the weather service and more snow than normal is predicted. As a result, the Marketing Dept. raises their forecast for Quarter I sales of blowers from 9,000 to 11,000 units (all other forecasts remain unchanged). You will now have to develop and analyze several alternative plans for next year. Each of these plans must meet the other criteria listed in problem 1 with the same starting inventory and Full-Time work force. a) Total beginning inventory of 4000 units. b) Ending Qtr. IV inventory of 2000 units (which means no backorders; backorders can occur at the end of other quarters). c) Each plan must have the same level total output rate each quarter. A. Develop a plan that uses overtime by regular, full-time employees to meet the new demand conditions. B. Plan 2-B will use full time employees for regular output (no overtime) plus subcontracting to meet the new demand conditions. C. Hire an additional full-time employee (or employees) at the start of Qtr. I and employ those hires for the full year. 3. The V.P of Marketing is not all that happy with the large volume of backorders in your plan from question 1A. She asks that you develop a plan that results in no backorders at any time during the year. The V.P. of manufacturing says that he will insist that any such plan specify level output each quarter. The V.P. of Finance states that you no longer need to have a Qtr. IV ending inventory of 2000 units. Using the original forecast data, beginning inventory, starting number of full time employees, etc. from problem 1, develop a plan that will meet the requirements of all three V.P.'s. 4. On Dec. 22 the V.P. Finance informs you that the availability of capital will be extremely tight next year. As a consequence, he asks you to develop a radically different type of aggregate plan based on a "Chase" strategy. Ending inventory and backorders is to be zero at the end of each quarter. The V.P. Manufacturing says he realizes this type of strategy will require him to abandon his beloved "level" strategy and for you to vary the total output rate from one quarter to another. The productivity planning factors for each type of output are repeated here (note that there are some limits in a couple of the categories). Finally, the Personnel Manager informs you that, due to end of the year retirements, only 32 (not 45) fulltime employees will be on the payroll as of the beginning of Qtr. 1. These retirements will occur at the end of the prior year. As such, you do not show a layoff adjustment at the start of Qtr. 1. Using the original forecasts and beginning inventory information for problem 1, develop a "chase" plan, following the guidelines noted above. AGGREGATE PLANNING WORKSHEET AGGREGATE PLANNING WORKSHEET MBA Inc. assembles lawn mowers and snow blowers from subassemblies and component parts provided by reliable vendors. Both products (end items) utilize the same small engines, many of the same parts and require the same assembly time and employee labor skills. On December 20, the Production Planning Committee of MBA Inc. is due to adopt an aggregate plan for the coming year. The available planning information is as follows: Quarter - I Beginning Inventory: Mowers 2600; blowers 1400 Output and Costs: Regular Time $5.00 per unit Overtime $7.50 per unit Subcontract $10.00 per unit Part Time $12.00 per unit Inventory $4.00 per unit per quarter based on avg. inventory during each quarter Backorders $8.00 per unit per period (based on backorders at end of period) Hiring $100.00 per employee (Full-Time or Part-Time) Layoff $500.00 per employee (no cost if Part-Time) Production Rates: Regular 500 units per Full-Time employee per quarter (of either unit) Overtime up to 200 units per Full-Time employee per quarter (of either unit) Temporary 400 units per Temporary employee per quarter (of either unit) Subcontract Maximum subcontract output available is 5200 units per quarter. Production work force: As of the first of the year, the production work force consists of 45 Full-Time employees. Additional Assumptions: 1) Temporary employees may not work overtime 2) Assume 100\% utilization of Full-Time employees on regular time and of Temporary employees at all times (i.e., all such employees on the payroll during a period produce at the rates shown under Production Rates). 3) Overtime utilization of Full-Time employees can be on an as needed basis subject to the limitation on maximum overtime output shown under Production Rates. Given all of this planning information, develop a series of aggregate plans to meet the criteria presented in the following series of problems. All plans must include full costs and hiring/layoff actions, as needed. Show all plans using one of the worksheets at the end of this document. 1. A. Develop an aggregate plan which utilizes a level (constant) rate of output each quarter using only full-time employees without overtime. Ending inventory for quarter IV is 2000 ; this means, of course, that there will be no backorders at the end of quarter IV. Backorders may occur at the end of the other quarters. B. If each shipping container for a completed mower or blower requires 6cu. ft. of space, what is the maximum amount of cubic feet of space that would be needed in the finished goods warehouse if your plan 1-A is adopted? (Assume that sales and production occur at a steady, daily rate within each quarter.) C. If the cost of each completed end item is $200.00, what is the maximum amount of capital that will be tied up in finished goods inventory during the year? (Continue with the assumption given for 1B.) 2. Suppose that on December 21 the long-range weather forecast is released by the weather service and more snow than normal is predicted. As a result, the Marketing Dept. raises their forecast for Quarter I sales of blowers from 9,000 to 11,000 units (all other forecasts remain unchanged). You will now have to develop and analyze several alternative plans for next year. Each of these plans must meet the other criteria listed in problem 1 with the same starting inventory and Full-Time work force. a) Total beginning inventory of 4000 units. b) Ending Qtr. IV inventory of 2000 units (which means no backorders; backorders can occur at the end of other quarters). c) Each plan must have the same level total output rate each quarter. A. Develop a plan that uses overtime by regular, full-time employees to meet the new demand conditions. B. Plan 2-B will use full time employees for regular output (no overtime) plus subcontracting to meet the new demand conditions. C. Hire an additional full-time employee (or employees) at the start of Qtr. I and employ those hires for the full year. 3. The V.P of Marketing is not all that happy with the large volume of backorders in your plan from question 1A. She asks that you develop a plan that results in no backorders at any time during the year. The V.P. of manufacturing says that he will insist that any such plan specify level output each quarter. The V.P. of Finance states that you no longer need to have a Qtr. IV ending inventory of 2000 units. Using the original forecast data, beginning inventory, starting number of full time employees, etc. from problem 1, develop a plan that will meet the requirements of all three V.P.'s. 4. On Dec. 22 the V.P. Finance informs you that the availability of capital will be extremely tight next year. As a consequence, he asks you to develop a radically different type of aggregate plan based on a "Chase" strategy. Ending inventory and backorders is to be zero at the end of each quarter. The V.P. Manufacturing says he realizes this type of strategy will require him to abandon his beloved "level" strategy and for you to vary the total output rate from one quarter to another. The productivity planning factors for each type of output are repeated here (note that there are some limits in a couple of the categories). Finally, the Personnel Manager informs you that, due to end of the year retirements, only 32 (not 45) fulltime employees will be on the payroll as of the beginning of Qtr. 1. These retirements will occur at the end of the prior year. As such, you do not show a layoff adjustment at the start of Qtr. 1. Using the original forecasts and beginning inventory information for problem 1, develop a "chase" plan, following the guidelines noted above. AGGREGATE PLANNING WORKSHEET AGGREGATE PLANNING WORKSHEET












