Need help with screenshots #3 & #4, and then help on screen shot #8 (two pictures, same problem. Had to take two because taking only one would not fit the entire question). If anymore information is needed, please do not hesitate to inform me! I will try to get back to you as soon as I can if this is the case. Also, a lot of the information has already been filled, so it should not be too difficult. Let me know! Thanks.
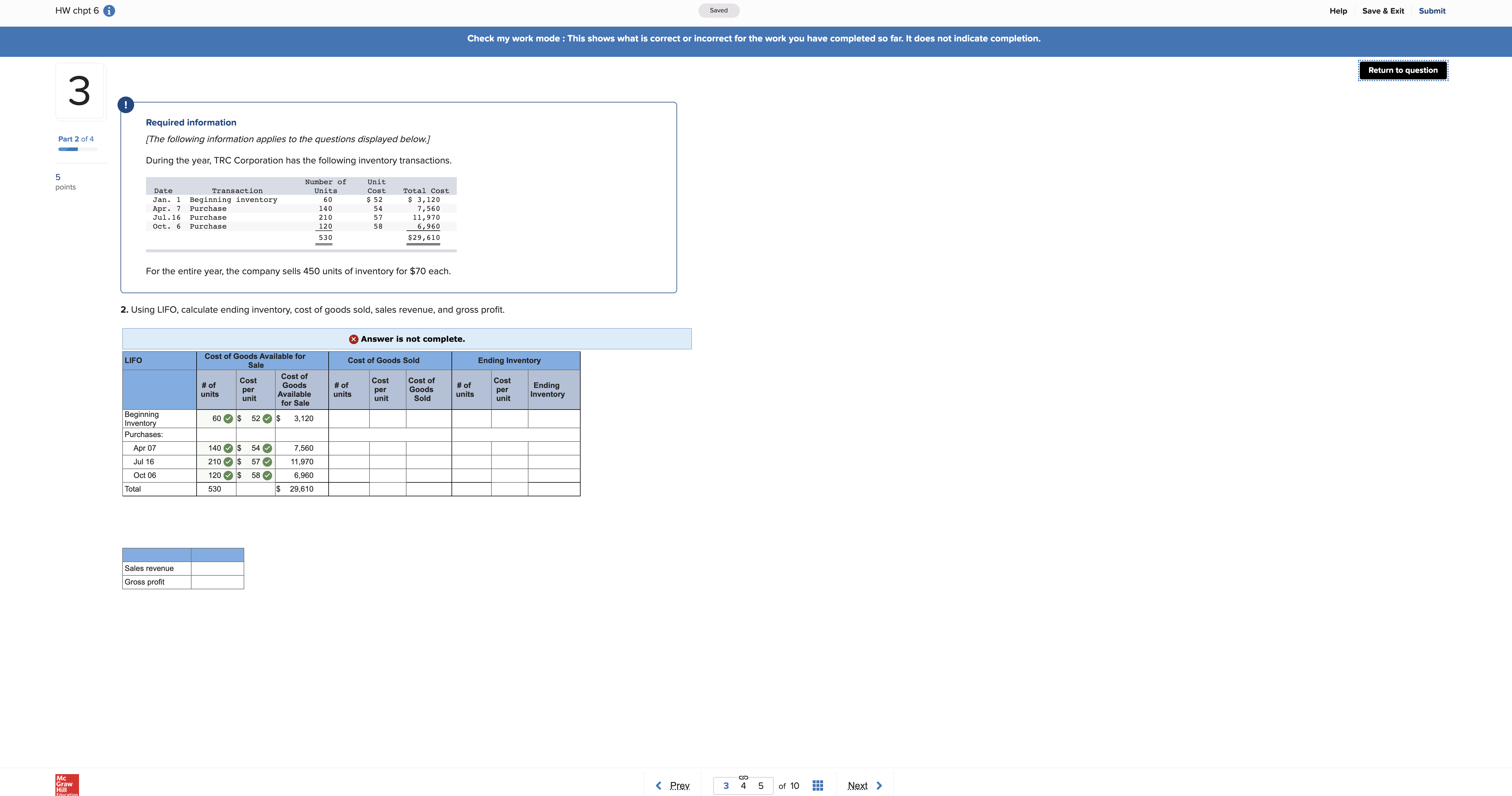
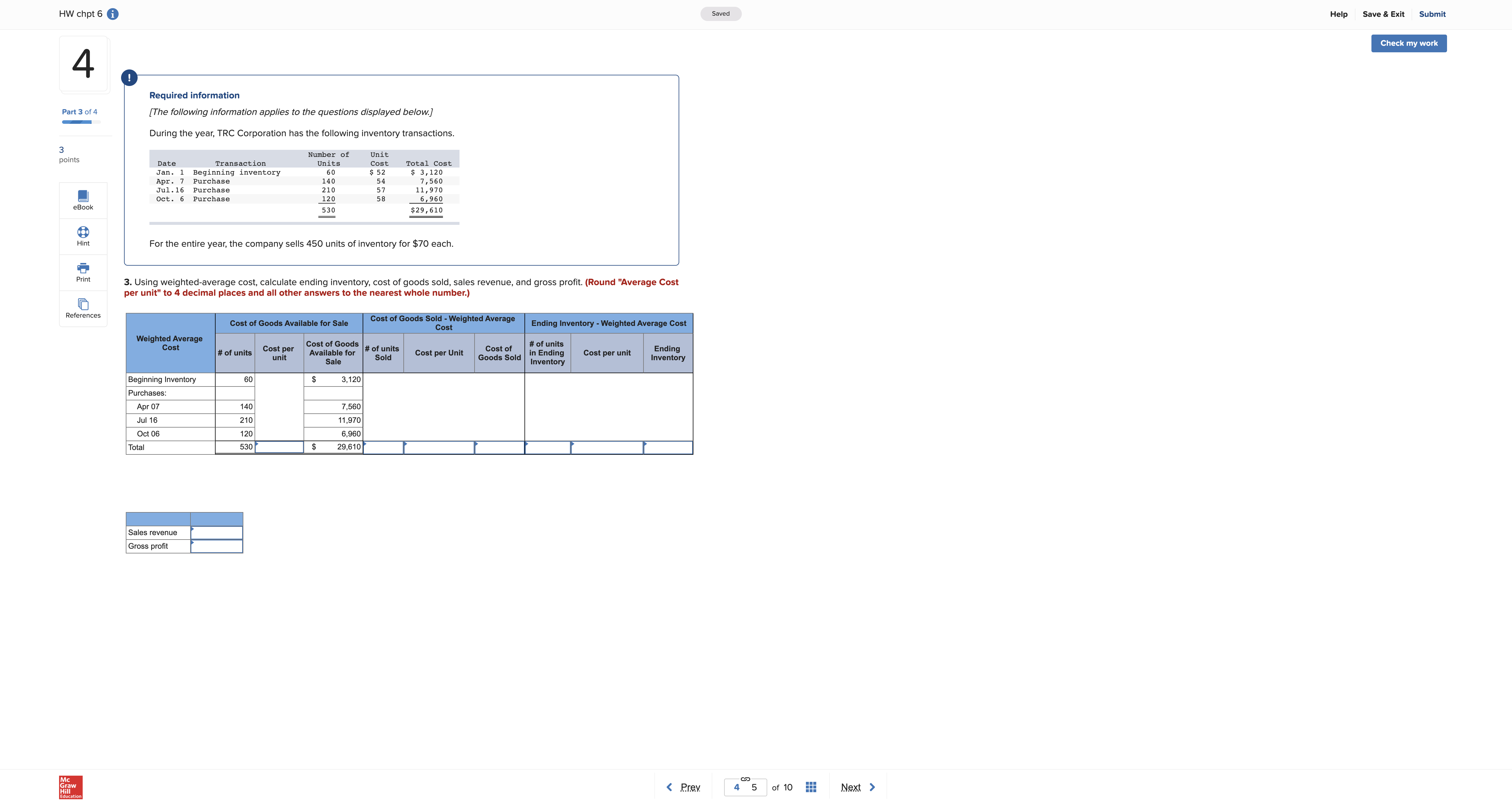
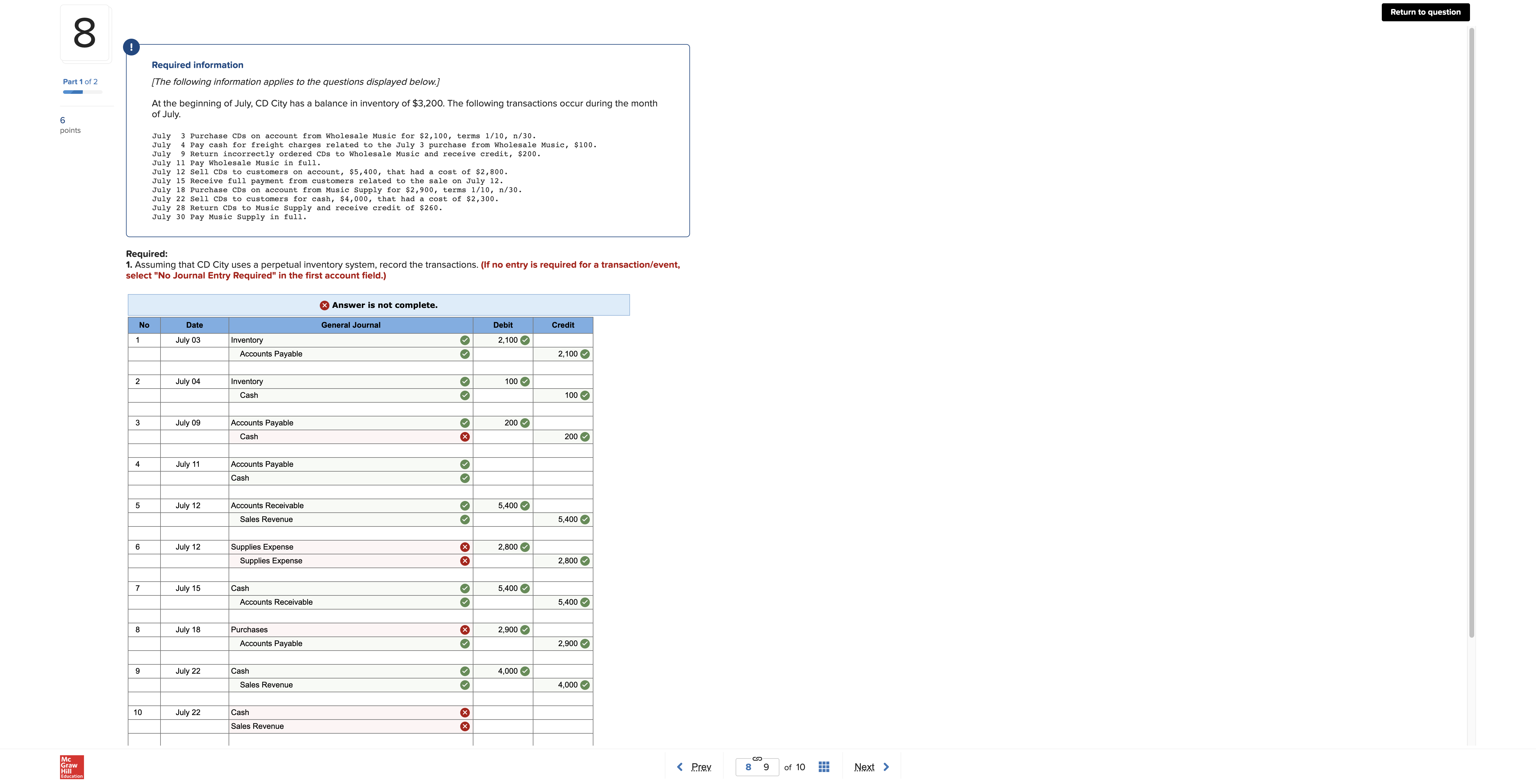
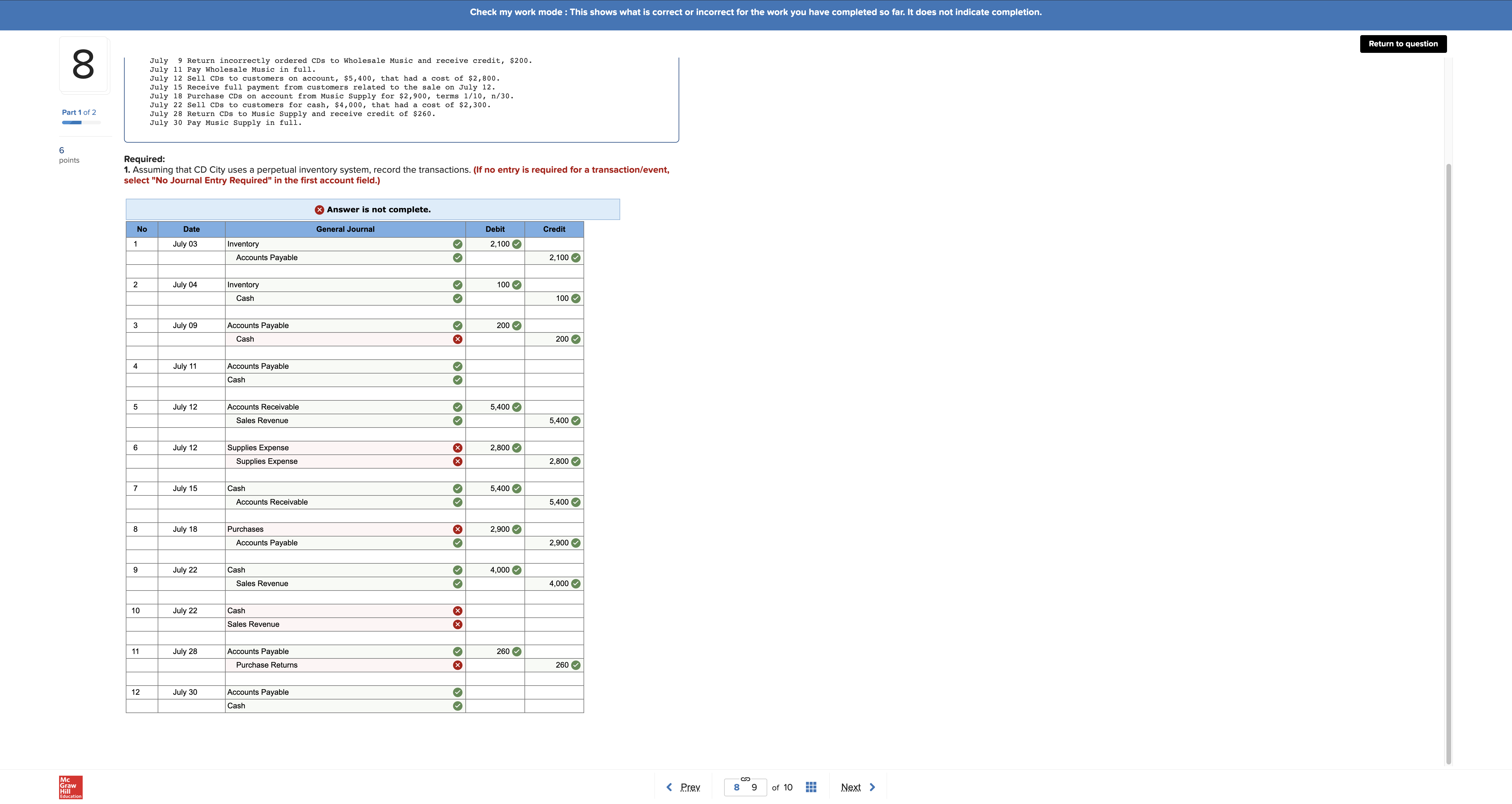
Help Save & Exit Submit HW chpt 6 i Check my work mode : This shows what is correct or incorrect for the work you have completed so far. It does not indicate completion. Return to question 3 Required information Part 2 of 4 [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] During the year, TRC Corporation has the following inventory transactions. 5 Number of Unit points Date Transaction Units Cost Total Cost Jan. 1 Beginning inventory 60 $ 52 Apr. Purchase 140 54 $ 3, 120 Jul . 16 Purchase 210 57 1, 560 11,97 Oct. 6 Purchase 120 58 6, 960 530 $29 , 610 For the entire year, the company sells 450 units of inventory for $70 each. 2. Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory, cost of goods sold, sales revenue, and gross profit. x Answer is not complete. LIFO Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory Cost Cost of Goods # of Cost Cost of # of Goods # of Cost units per Ending unit Available units for Sale unit Sold units unit Inventory Beginning Inventory 60 $ 52 $ 3,120 Purchases: Apr 07 140 $ 54 7,560 Jul 16 210 $ 57 11,970 Oct 06 120 $ 58 6,960 Total 530 29,010 Sales revenue Gross profit row HW chpt 6 i Saved Help Save & Exit Submit Check my work 4 ! Required information Part 3 of 4 [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] During the year, TRC Corporation has the following inventory transactions. 3 point Number of Units Unit Date Transaction Total Cost Jan. Beginning inventory Purchase 60 Cost 140 $ 52 54 $ 3, 120 210 7 , 560 Jul . 16 Purchase Oct. 6 Purchase 120 57 58 1, 970 eBook 6, 960 530 $29 , 610 Hint For the entire year, the company sells 450 units of inventory for $70 each. Print 3. Using weighted-average cost, calculate ending inventory, cost of goods sold, sales revenue, and gross profit. (Round "Average Cost per unit" to 4 decimal places and all other answers to the nearest whole number.) References Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Goods Sold - Weighted Average Cost Ending Inventory - Weighted Average Cost Weighted Average Cost # of units Cost per Cost of Goods # of units unit Available for # of units Cost per Unit Cost of Sale Sold Goods Sold In in Ending Inventory Cost per unit Ending Inventory Beginning Inventory 60 3,120 Purchases Apr 0 140 7,560 Jul 16 210 11,970 Oct 06 120 6,960 Total 530 29,610 Sales revenue Gross profit Return to question 8 Required information Part 1 of 2 [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] At the beginning of July, CD City has a balance in inventory of $3,200. The following transactions occur during the month 6 of July. points July 3 Purchase CDs on account from Wholesale Music for $2, 100, terms 1/10, n/30. July 4 Pay cash for freight charges related to the July 3 purchase from Wholesale Music, $100. July 9 Return incorrectly ordered CDs to Wholesale Music and receive credit, $200. July 11 Pay Wholesale Music in full. July 12 sell CDs to customers on account, $5,400, that had a cost of $2, 800. July 15 Receive full payment from customers related to the sale on July 12. July 18 Purchase CDs on account from Music Supply for $2,900, terms 1/10, n/30. July 22 Sell CDs to customers for cash, $4,000, that had a cost of $2, 300. July 28 Return CDs to Music Supply and receive credit of $260. July 30 Pay Music Supply in full. Required: 1. Assuming that CD City uses a perpetual inventory system, record the transactions. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.) x Answer is not complete. No Date General Journal Debit Credit July 03 Inventory 2, 100 Accounts Payable 2,100 2 July 04 Inventory 100 Cash 100 3 July 09 Accounts Payable O 200 Cash 200 July 1 Accounts Payable O Cash 5 July 12 Accounts Receivable 5,400 Sales Revenue 5,400 6 July 12 Supplies Expense 2,800 Supplies Expense 2,800 July 15 Cash 5,400 Accounts Receivable 5,400 8 July 18 Purchases 2,900 Accounts Payable 2,900 9 July 22 Cash 4,000 Sales Revenue 4,000 10 July 22 Cash Sales Revenue Grav Check my work mode : This shows what is correct or incorrect for the work you have completed so far. It does not indicate completion. 8 Return to question July 9 Return incorrectly ordered CDs to Wholesale Music and receive credit, $200. July 11 Pay Wholesale Music in full. July 12 Sell CDs to customers on account, $5,400, that had a cost of $2,800. July 15 Receive full payment from customers related to the sale on July 12. July 18 Purchase CDs on account from Music Supply for $2,900, terms 1/10, n/30. Part 1 of 2 July 22 Sell CDs to customers for cash, $4,000, that had a cost of $2,300. July 28 Return CDs to Music Supply and receive credit of $260. July 30 Pay Music Supply in full. 5 points Required: 1. Assuming that CD City uses a perpetual inventory system, record the transactions. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.) x Answer is not complete. No Date General Journal Debit Credit July 03 Inventory 2,100 Accounts Payable 2,100 July 04 Inventory O 100 Cash 100 July 09 Accounts Payable 200 Cash x 200 July 11 Accounts Payable O Cash July 12 Accounts Receivable 5,400 Sales Revenue 5,400 July 12 Supplies Expense x 2,800 Supplies Expense 2,800 July 15 Cash O 5,400 Accounts Receivable 5,400 8 July 18 Purchases 2,900 Accounts Payable 2,900 9 July 22 Cash O 4,000 Sales Revenue O 4,000 10 July 22 Cash Sales Revenue 11 July 28 Accounts Payable O 260 Purchase Returns 260 12 July 30 Accounts Payable O Cash