Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
need help with the journal Materials Direct Materials Price Variance Direct materials (5 lbs. @ $2.60) Accounts Payable $13.00 Work in Process Direct labor (0.75
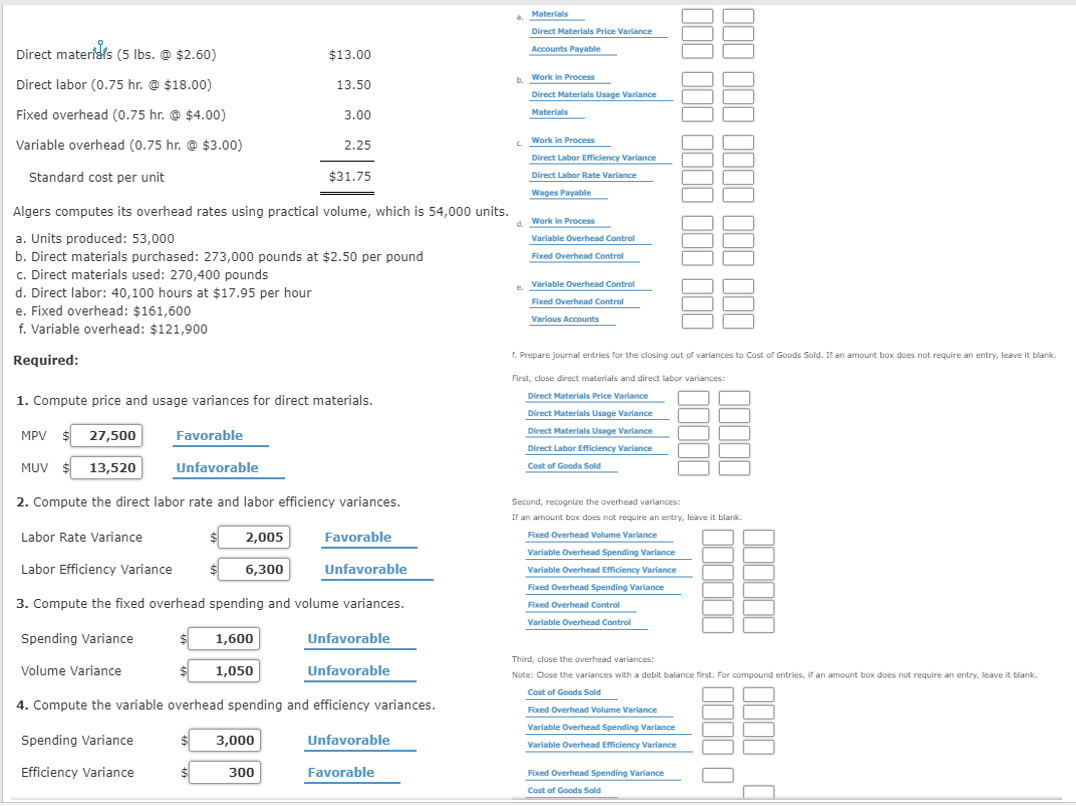
need help with the journal
Materials Direct Materials Price Variance Direct materials (5 lbs. @ $2.60) Accounts Payable $13.00 Work in Process Direct labor (0.75 hr. @ $18.00) 13.50 Direct Materials Usage Variance Materials Fixed overhead (0.75 hr. @ $4.00) 3.00 Variable overhead (0.75 hr. @ $3.00) 2.25 Work in Process Direct Labor Efficiency Variance Direct Labor Rate Variance Wages Payable Standard cost per unit $31.75 Work in Process Variable Overhead Control Fixed Overhead Control Algers computes its overhead rates using practical volume, which is 54,000 units. a. Units produced: 53,000 b. Direct materials purchased: 273,000 pounds at $2.50 per pound c. Direct materials used: 270,400 pounds d. Direct labor: 40,100 hours at $17.95 per hour e. Fixed overhead: $161,600 f. Variable overhead: $121,900 U V W IL 001 III III. II. II. 1,01111 e Variable Overhead Control Fixed Overhead Control Various Accounts 1. Prepare journal entries for the closing out of variances to Cost of Goods Sold. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank Required: 1. Compute price and usage variances for direct materials. First, close direct materials and direct labor variances: Direct Materials Price Variance Direct Materials Usage Variance Direct Materials Usage Variance Direct Labor Efficiency Variance Favorable MPV $ MUV $ 27,500 13,520 Unfavorable Cost of Goods Sold 2. Compute the direct labor rate and labor efficiency variances. m Labor Rate Variance $ 2,005 Favorable Labor Efficiency Variance $ 6,300 Unfavorable Second, recognize the overhead variances: If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. Fixed Overhead Volume Variance Variable Overhead Spending Variance Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance Fixed Overhead Spending Variance Fixed Overhead Control Variable Overhead Control 3. Compute the fixed overhead spending and volume variances. Spending Variance Unfavorable $ $ 1,600 1,050 Volume Variance Unfavorable Third, close the overhead variances: Note: Close the variances with a debit balance first. For compound entries, if an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. Cost of Goods Sold Fixed Overhead Volume Variance Variable Overhead Spending Variance 4. Compute the variable overhead spending and efficiency variances. Unfavorable Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance Spending Variance Efficiency Variance $ $ 3,000 300 0111 0 Favorable Fixed Overhead Spending Variance Cost of Goods SoldStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


