 Need part a
Need part a
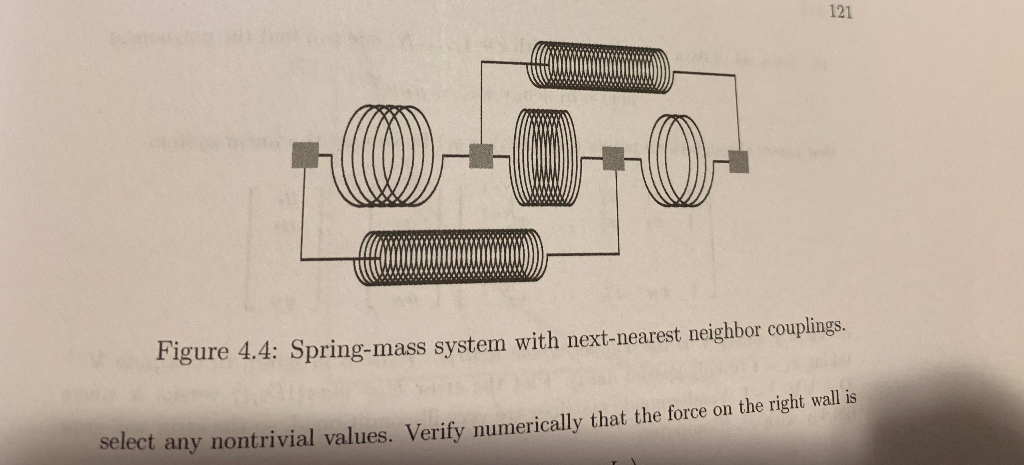
Computer 13. Consider ~ [ ] the spring-mass system in Figure 4.4 (a simple model of a short poly- mer molecule). The blocks are free to move but only along the r-axis. The springs connecting adjacent blocks have spring constant ki, while the two outer springs have stiffness k2. All the springs have a rest length of one. (a) Write the matrix equation for the equilibrium positions of the blocks. [Pencil (b) Write a program that plots the total length of the system as a function of ki/k2. [Computer) 14. Consider a system of coupled masses (such as in Figure 4.3) with N -1 blocks. The spring constants are Compute the condition number of K using MATLAB's cond function, and plot it as a function of N. Estimate the value of N for which cond(K) exceeds 1012. [MATLAB 121 Figure 4.4: Spring-mass system with next-nearest neighbor couplings. selec t any nontrivial values. Verify numerically that the force on the right wall is Question 3) Turn in a single m format MATLAB program and a single JPG format figure for this question: exercise 13 on page 121 of the textbook. This problem asks you to simulate a short polymer molecule as a system of springs and of masses which are free to move only in the a-direction. For ease of marking, in Figure 4.4 on page 121: * Label the masses 0 to 3 from left to right. * Assume that mass 0 is always located at ro 0. * Label the springs as follows: * spring 1 connects masses 0 and 1; * spring 2 connects masses 0 and 2; * spring 3 connects masses 1 and 2; *spring 4 connects masses 1 and 3; *spring 5 connects masses 2 and 3. a) [1 point] As discussed in section 4.2, set up the system of equations for , r, and t given that all springs have rest length 1, that springs 1, 3 and 5 have spring constant ki, and that springs 2 and 4 have spring constant k2. (In matrix notation, this system of equations is abbreviated as F- Kx -b.) Computer 13. Consider ~ [ ] the spring-mass system in Figure 4.4 (a simple model of a short poly- mer molecule). The blocks are free to move but only along the r-axis. The springs connecting adjacent blocks have spring constant ki, while the two outer springs have stiffness k2. All the springs have a rest length of one. (a) Write the matrix equation for the equilibrium positions of the blocks. [Pencil (b) Write a program that plots the total length of the system as a function of ki/k2. [Computer) 14. Consider a system of coupled masses (such as in Figure 4.3) with N -1 blocks. The spring constants are Compute the condition number of K using MATLAB's cond function, and plot it as a function of N. Estimate the value of N for which cond(K) exceeds 1012. [MATLAB 121 Figure 4.4: Spring-mass system with next-nearest neighbor couplings. selec t any nontrivial values. Verify numerically that the force on the right wall is Question 3) Turn in a single m format MATLAB program and a single JPG format figure for this question: exercise 13 on page 121 of the textbook. This problem asks you to simulate a short polymer molecule as a system of springs and of masses which are free to move only in the a-direction. For ease of marking, in Figure 4.4 on page 121: * Label the masses 0 to 3 from left to right. * Assume that mass 0 is always located at ro 0. * Label the springs as follows: * spring 1 connects masses 0 and 1; * spring 2 connects masses 0 and 2; * spring 3 connects masses 1 and 2; *spring 4 connects masses 1 and 3; *spring 5 connects masses 2 and 3. a) [1 point] As discussed in section 4.2, set up the system of equations for , r, and t given that all springs have rest length 1, that springs 1, 3 and 5 have spring constant ki, and that springs 2 and 4 have spring constant k2. (In matrix notation, this system of equations is abbreviated as F- Kx -b.)


 Need part a
Need part a





