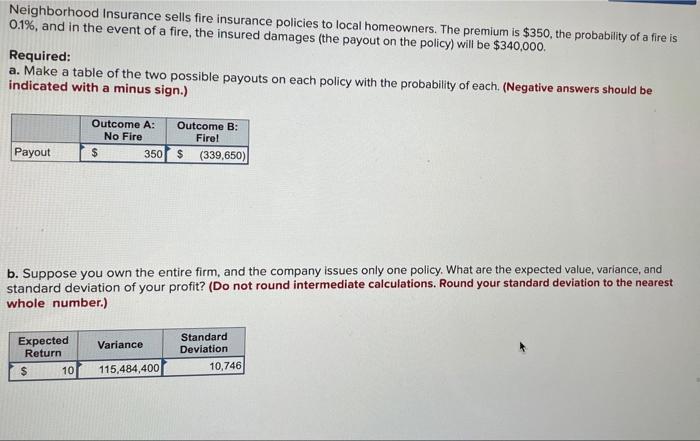
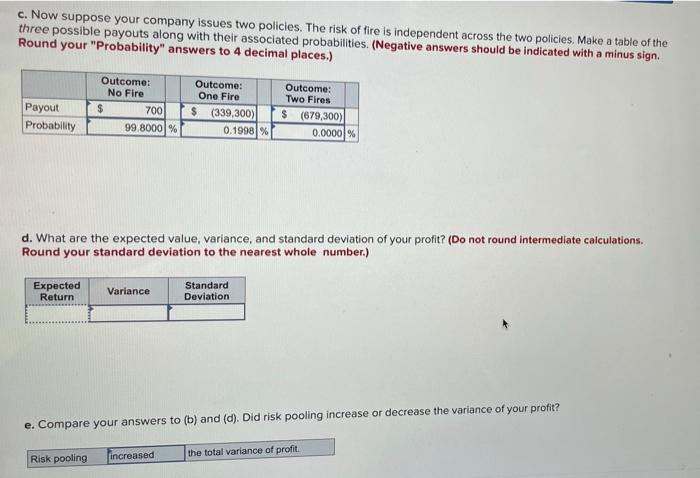
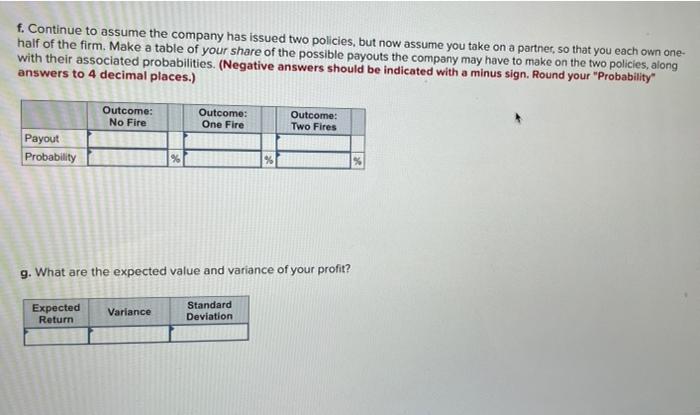
Neighborhood Insurance sells fire insurance policies to local homeowners. The premium is $350, the probability of a fire is 0.1%, and in the event of a fire, the insured damages (the payout on the policy) will be $340,000. Required: a. Make a table of the two possible payouts on each policy with the probability of each (Negative answers should be indicated with a minus sign.) Outcome A: No Fire 350 Outcome B: Fire! $ (339,650) Payout b. Suppose you own the entire firm, and the company issues only one policy. What are the expected value, variance, and standard deviation of your profit? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your standard deviation to the nearest whole number.) Variance Expected Return $ 10 Standard Deviation 10.746 115,484,400 c. Now suppose your company issues two policies. The risk of fire is independent across the two policies. Make a table of the three possible payouts along with their associated probabilities. (Negative answers should be indicated with a minus sign. Round your "Probability" answers to 4 decimal places.) Payout Probability Outcome: No Fire 700 99.80001% Outcome: One Fire $ (339,300) 0.1998 % Outcome: Two Fires $ (679,300) 0.0000 % d. What are the expected value, variance, and standard deviation of your profit? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your standard deviation to the nearest whole number.) Expected Return Variance Standard Deviation e. Compare your answers to (b) and (d). Did risk pooling increase or decrease the variance of your profit? Risk pooling increased the total variance of profit f. Continue to assume the company has issued two policies, but now assume you take on a partner, so that you each own one- half of the firm. Make a table of your share of the possible payouts the company may have to make on the two policies, along with their associated probabilities. (Negative answers should be indicated with a minus sign. Round your "Probability" answers to 4 decimal places.) Outcome: No Fire Outcome: One Fire Outcome: Two Fires Payout Probability % g. What are the expected value and variance of your profit? Expected Return Variance Standard Deviation