Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Notation fo P. R Rech RC R Ruch S W.. L G G L L. K LM M Parameter Carrier frequency Transmitter power Data (bit)
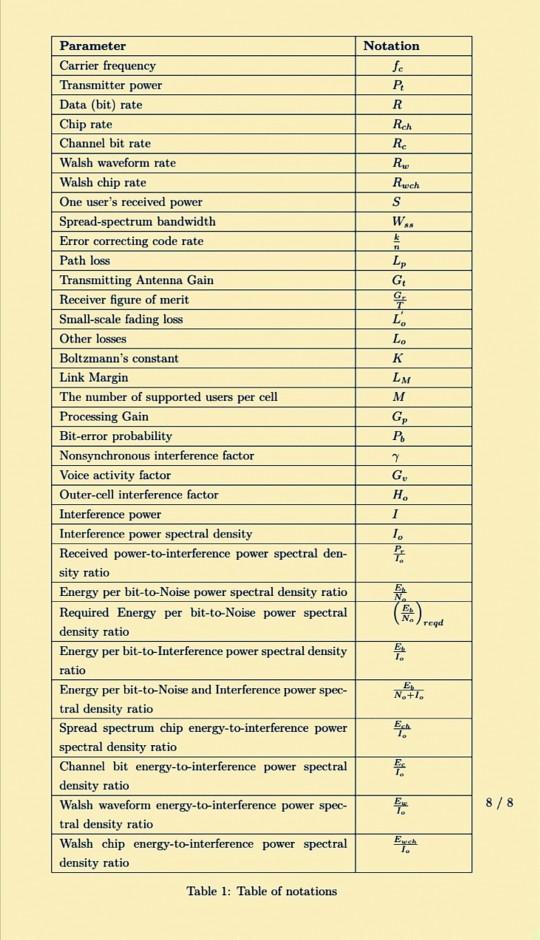

Notation fo P. R Rech RC R Ruch S W.. L G G L L. K LM M Parameter Carrier frequency Transmitter power Data (bit) rate Chip rate Channel bit rate Walsh waveform rate Walsh chip rate One user's received power Spread-spectrum bandwidth Error correcting code rate Path loss Transmitting Antenna Gain Receiver figure of merit Small-scale fading loss Other losses Boltzmann's constant Link Margin The number of supported users per cell Processing Gain Bit-error probability Nonsynchronous interference factor Voice activity factor Outer-cell interference factor Interference power Interference power spectral density Received power-to-interference power spectral den- sity ratio Energy per bit-to-Noise power spectral density ratio Required Energy per bit-to-Noise power spectral density ratio Energy per bit-to-Interference power spectral density ratio Energy per bit-to-Noise and Interference power spec- tral density ratio Spread spectrum chip energy-to-interference power spectral density ratio Channel bit energy-to-interference power spectral density ratio Walsh waveform energy-to-interference power spec- tral density ratio Walsh chip energy-to-interference power spectral density ratio G P 7 G H. 1 1. NA red EN E NA+T. EA E 8/8 E Table 1: Table of notations 7. A direct-sequence spread-spectrum system uses QPSK modulation for transmitting data. It is required that the bit-error probability (P) be 10-5 and that chip energy-to-interference power spectral density ratio, Ech/I.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


