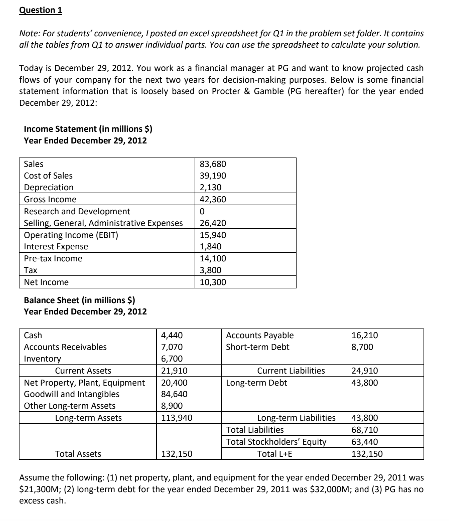
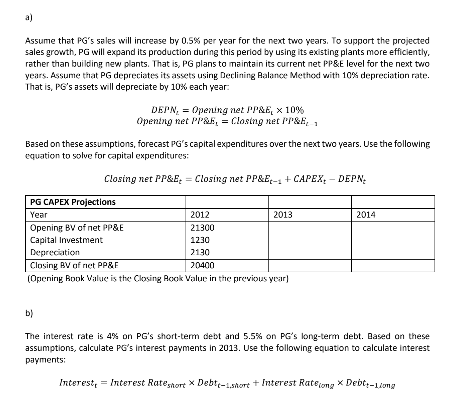
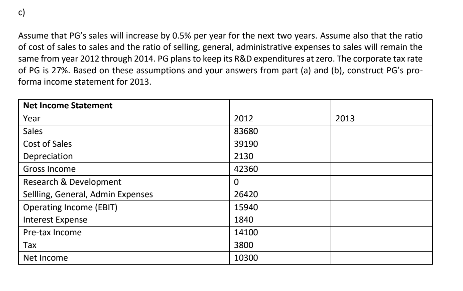



Note: For stucdents'converiice, I posted an excel spreodshen the prabiem setfokier. It contains ali the tabies from Q1 to answer individual parts. You can use the spreodsheet to calkulate your solution. Today is December 29, 2012. You work as a financial manager at PG and want to know projected cash flows of your company for the next two years for decision-making purposes. Below is some financial statement infarmation that is loosely based on Procter & Gamble (PG hereafter) for the year ended December 29, 2012: Income Statementin millions 5) Year Ended December 29, 2012 Sales Cost of Sales Decaon Gross Income Resah ad Developrnent Selling, General. Administrative Expenses 26,420 Operating Income (EGIT) Interest Fxpmsr Pre tax Incomic 83,68D 39,190 2,130 42,360 15,94D 14,100 3,300 10,300 Net Income Balance Sheet (in millions s) Year Ended December 29, 2012 Cash Accounts Recelvables Invento 4,440 ,070 6,P00 Accournts Payable Short-term Debt 16,210 8,7DD 24.910 13,800 Current Assets Current Liabilities Net Property, Plant, Equipment Goodwill and Intangibles Other Long-tern Assets 20,A00 Long-term Debt 84,540 8,900 Lona-term Assets Long-tenm Liabilities 3.800 Total Labilities 68,710 63.110 132,150 Total Stockholders Total Assets Assume the following: (1) net property, plant, and equipment for the year ended December 29, 2011 was $21,300M; (2) long-term debt for the year ended December 29, 2011 was $32,000M; and (3) PG has no excess cash a) Assume that PG's sales will increase by 0.5% per year for the next two years. To support the projected sales growth, PG will expand its production during this periad by using its existing plants more efficiently rather than building new plants. That is, PG plans to maintain its current net PP&E level for the next two years. Assume that PG depreciates its assets using Declining Balance Method with 10% depreciation rate. That is, PG's assets will depreciate by 10% each year DEPN: 0perung net PP&E, x 10% Opening net PP&F -Closng netP&hz1 Based on these assumptions, forecast PG's capital expenditures over the next two years. Use the following equation to solve for capital expenditures Closing net PP&E Closing net PP&Et-i CAPEXt - DEPN. PG CAPEX Projections ear Opening BV ofnet PP&E Capital Investment 21300 1230 130 0400 Closing BV f et PPRF (Op Bok Value is the Ckng Aook Value in te prevus yearl bl The interest rate is 4% on PG's short-term debt and 5.5% on PG's long-term debt. Based on these assumptions, calculate PG's interest payments in 2013. Use the following equation to calculate interest payments: Interest,-Interest Ratestort x Debtt-LstortT Interest Rate,ong Debt-llong c) Assume that PG's sales will increase by 0.5% per year for the next two years. Assume also that the ratio of cost of sales to sales and the ratio of selling, general, administrative expenses to sales will remain the same from year 2012 through 2014. PG plans to keep its R&D expenditures atzero. The corporate tax rate of PG is 27%. Based on these assumptions and your answers from part (a) and lb], construct PG's pro- forma income statement for 2013. Net Incomc Statement Year Sales Cost of Sales Depreciation Gross Income Research & Development Selling, General, Admin Expenses Operating Income (EBIT) Interest Expense Pre-tax Income 012 3680 39190 2130 42360 013 26420 15940 1840 14100 3800 10300 Net Income d) The table belows lists PG's current operating working capital as a fraction of sales and cost of sales. To utilize their operating working capital more efficiently, PG plans to tighten its credit policy, speed up customer payments and reduce PG's inventory. Specifically, PG plans to reduce the ratios of operating cash to sales, accounts recevables to sales, inventory to sales by 0.5% each year for the next two years. For example, cash will be 5.306-05-4.806% of 2013 sales in 2013. Likewise, accounts receivables will be 8.4490.57.949 of 2013 saes in 2013. At the se, PG will als reduc the ratio of accounts payable to cost of sales by 2% each year for the next two years, for example, accounts payable will be 11363-2-39.363% of 2013 cost of sales in 2013. Based on these projections, calculate PG's operating working capital requirements in 2013 Current Assets 2012 of 2012 sales 5.306% 8.449% 8.007% Operating Cash Accounts Receivables 7070 5700 1440 83680 -7070/83680 67C0/83680 Operating Current Li Accounts Payable 2012 1621D % of 2012 cost of sales 41 .363% -15210/3919D PG OWC Requirements Year Operating Current Assets Operating Cash 2012 2013 4440 7070 6700 Inventony Operating Current Liability Accournts Payable 16210 el Assume that PG has a non-flexible dividend policy, That is, PG pays $8 cash dividend per share each year regardless of its net income. PG has 100OM stack shares outstanding. Calculate tockholders equity for PG in 2013. Assume that PG will not issue or repurchase stocks in 2013, Use the followine equation to calculate stockholders equity ISE SEr SEt-1 1 Vet Income Diviiendsr I Stock Issuance- Stock Repurchasec Based on parts la) through (el construct a pro-forma balance sheet for 2013. Assume that goodwill and intangibles and other long term assets remain unchangrd from 2012. Assume also that PG will have no short-term debt outstanding in 2013. If total assets are greater than total liabilities plus equity, correct this imbalance by adding to long-term debt. If total assets are less than total liabilities plus equity, correct this inbalarice by etiring long-term debt. Pro-forma Balance Sheet (Asset Side) 2012 Cash-Operating Cash-Excess Cash) | 4440 TO70 Currernt Assets 1910 Net Property, Plant, Equipment Goodwill and Intangibles Other Long-Term Assets Term Assets Total Assets 13215D Pro-forma Balance Sheet (L+E) 2012 2013 2013 Accourts Payable Short-Term Debt 8700 Current Liabilities Term Deit 43800 43800 68710 63440 132150 lon Term liabilitics Total Liabilities Total Stockholders' Equi Total LtE EFN 8) The interest rate is 4% on PG's short-term debt and 5.5% on PG's long-term debt. Based on the short-term and long-term debt projections for 2013 from part ), calculate PG's interest payments in 2014. Use the following equation to caculate interest payments: Interestt Interest Ratestort x Debtc-Lshort Interest Rateiong X Debtiong Now, youare rady to calulat PG's pro forma iircome statement for 2014. Note that you caalsorepeat steps le) and ( to calculate stockholders' equity and a pra-forma balance sheet for 2014 (luckily, that is not a part of this assigriment). As this example shows, you cannot in gereral calculate, say, pro forna income statements af next five years all at once. You first calculate an income statement for 2013, and then calculate a balance sheet for 2013 using the income statement for 2013. Next you calculate an income statement for 2014 using the balance shee o 2013, and then calculate a halance sheet or 2014 using the income statement for 2014, and so on. Hold on though. We are not done wih this question yet. Let's now calculate the firm's free cash flow in 2013. h) What is the projected free cash flowCr) for December 29, 2013? Use the following equation to solve for FCh: FCF = EBIT(1-tax rate) + DEPN-CAPEX-NWC Make sure to show the individual numbers used in this equation. The free cash fows are the cash flows avallable for distribution to the firm's investors (stackholders and bondholders]. Note: For stucdents'converiice, I posted an excel spreodshen the prabiem setfokier. It contains ali the tabies from Q1 to answer individual parts. You can use the spreodsheet to calkulate your solution. Today is December 29, 2012. You work as a financial manager at PG and want to know projected cash flows of your company for the next two years for decision-making purposes. Below is some financial statement infarmation that is loosely based on Procter & Gamble (PG hereafter) for the year ended December 29, 2012: Income Statementin millions 5) Year Ended December 29, 2012 Sales Cost of Sales Decaon Gross Income Resah ad Developrnent Selling, General. Administrative Expenses 26,420 Operating Income (EGIT) Interest Fxpmsr Pre tax Incomic 83,68D 39,190 2,130 42,360 15,94D 14,100 3,300 10,300 Net Income Balance Sheet (in millions s) Year Ended December 29, 2012 Cash Accounts Recelvables Invento 4,440 ,070 6,P00 Accournts Payable Short-term Debt 16,210 8,7DD 24.910 13,800 Current Assets Current Liabilities Net Property, Plant, Equipment Goodwill and Intangibles Other Long-tern Assets 20,A00 Long-term Debt 84,540 8,900 Lona-term Assets Long-tenm Liabilities 3.800 Total Labilities 68,710 63.110 132,150 Total Stockholders Total Assets Assume the following: (1) net property, plant, and equipment for the year ended December 29, 2011 was $21,300M; (2) long-term debt for the year ended December 29, 2011 was $32,000M; and (3) PG has no excess cash a) Assume that PG's sales will increase by 0.5% per year for the next two years. To support the projected sales growth, PG will expand its production during this periad by using its existing plants more efficiently rather than building new plants. That is, PG plans to maintain its current net PP&E level for the next two years. Assume that PG depreciates its assets using Declining Balance Method with 10% depreciation rate. That is, PG's assets will depreciate by 10% each year DEPN: 0perung net PP&E, x 10% Opening net PP&F -Closng netP&hz1 Based on these assumptions, forecast PG's capital expenditures over the next two years. Use the following equation to solve for capital expenditures Closing net PP&E Closing net PP&Et-i CAPEXt - DEPN. PG CAPEX Projections ear Opening BV ofnet PP&E Capital Investment 21300 1230 130 0400 Closing BV f et PPRF (Op Bok Value is the Ckng Aook Value in te prevus yearl bl The interest rate is 4% on PG's short-term debt and 5.5% on PG's long-term debt. Based on these assumptions, calculate PG's interest payments in 2013. Use the following equation to calculate interest payments: Interest,-Interest Ratestort x Debtt-LstortT Interest Rate,ong Debt-llong c) Assume that PG's sales will increase by 0.5% per year for the next two years. Assume also that the ratio of cost of sales to sales and the ratio of selling, general, administrative expenses to sales will remain the same from year 2012 through 2014. PG plans to keep its R&D expenditures atzero. The corporate tax rate of PG is 27%. Based on these assumptions and your answers from part (a) and lb], construct PG's pro- forma income statement for 2013. Net Incomc Statement Year Sales Cost of Sales Depreciation Gross Income Research & Development Selling, General, Admin Expenses Operating Income (EBIT) Interest Expense Pre-tax Income 012 3680 39190 2130 42360 013 26420 15940 1840 14100 3800 10300 Net Income d) The table belows lists PG's current operating working capital as a fraction of sales and cost of sales. To utilize their operating working capital more efficiently, PG plans to tighten its credit policy, speed up customer payments and reduce PG's inventory. Specifically, PG plans to reduce the ratios of operating cash to sales, accounts recevables to sales, inventory to sales by 0.5% each year for the next two years. For example, cash will be 5.306-05-4.806% of 2013 sales in 2013. Likewise, accounts receivables will be 8.4490.57.949 of 2013 saes in 2013. At the se, PG will als reduc the ratio of accounts payable to cost of sales by 2% each year for the next two years, for example, accounts payable will be 11363-2-39.363% of 2013 cost of sales in 2013. Based on these projections, calculate PG's operating working capital requirements in 2013 Current Assets 2012 of 2012 sales 5.306% 8.449% 8.007% Operating Cash Accounts Receivables 7070 5700 1440 83680 -7070/83680 67C0/83680 Operating Current Li Accounts Payable 2012 1621D % of 2012 cost of sales 41 .363% -15210/3919D PG OWC Requirements Year Operating Current Assets Operating Cash 2012 2013 4440 7070 6700 Inventony Operating Current Liability Accournts Payable 16210 el Assume that PG has a non-flexible dividend policy, That is, PG pays $8 cash dividend per share each year regardless of its net income. PG has 100OM stack shares outstanding. Calculate tockholders equity for PG in 2013. Assume that PG will not issue or repurchase stocks in 2013, Use the followine equation to calculate stockholders equity ISE SEr SEt-1 1 Vet Income Diviiendsr I Stock Issuance- Stock Repurchasec Based on parts la) through (el construct a pro-forma balance sheet for 2013. Assume that goodwill and intangibles and other long term assets remain unchangrd from 2012. Assume also that PG will have no short-term debt outstanding in 2013. If total assets are greater than total liabilities plus equity, correct this imbalance by adding to long-term debt. If total assets are less than total liabilities plus equity, correct this inbalarice by etiring long-term debt. Pro-forma Balance Sheet (Asset Side) 2012 Cash-Operating Cash-Excess Cash) | 4440 TO70 Currernt Assets 1910 Net Property, Plant, Equipment Goodwill and Intangibles Other Long-Term Assets Term Assets Total Assets 13215D Pro-forma Balance Sheet (L+E) 2012 2013 2013 Accourts Payable Short-Term Debt 8700 Current Liabilities Term Deit 43800 43800 68710 63440 132150 lon Term liabilitics Total Liabilities Total Stockholders' Equi Total LtE EFN 8) The interest rate is 4% on PG's short-term debt and 5.5% on PG's long-term debt. Based on the short-term and long-term debt projections for 2013 from part ), calculate PG's interest payments in 2014. Use the following equation to caculate interest payments: Interestt Interest Ratestort x Debtc-Lshort Interest Rateiong X Debtiong Now, youare rady to calulat PG's pro forma iircome statement for 2014. Note that you caalsorepeat steps le) and ( to calculate stockholders' equity and a pra-forma balance sheet for 2014 (luckily, that is not a part of this assigriment). As this example shows, you cannot in gereral calculate, say, pro forna income statements af next five years all at once. You first calculate an income statement for 2013, and then calculate a balance sheet for 2013 using the income statement for 2013. Next you calculate an income statement for 2014 using the balance shee o 2013, and then calculate a halance sheet or 2014 using the income statement for 2014, and so on. Hold on though. We are not done wih this question yet. Let's now calculate the firm's free cash flow in 2013. h) What is the projected free cash flowCr) for December 29, 2013? Use the following equation to solve for FCh: FCF = EBIT(1-tax rate) + DEPN-CAPEX-NWC Make sure to show the individual numbers used in this equation. The free cash fows are the cash flows avallable for distribution to the firm's investors (stackholders and bondholders]












