Question: NOW. HERE ARE GIVEN PIECES OF THE CODE. FROM THAT BinaryTrees FILE. I WILL PROVIDE THEM IN TEXT FILE FORMAT SO ITS EASIER FOR YOU

NOW. HERE ARE GIVEN PIECES OF THE CODE. FROM THAT BinaryTrees FILE.
I WILL PROVIDE THEM IN TEXT FILE FORMAT SO ITS EASIER FOR YOU TO COPY THEM.
1)
public class BinaryTree extends BinaryTreeBasis {
public BinaryTree() { } // end default constructor
public BinaryTree(T rootItem) { super(rootItem); } // end constructor
public BinaryTree(T rootItem, BinaryTree leftTree, BinaryTree rightTree) { root = new TreeNode(rootItem, null, null); attachLeftSubtree(leftTree); attachRightSubtree(rightTree); } // end constructor
public void setRootItem(T newItem) { if (root != null) { root.setItem(newItem); } else { root = new TreeNode(newItem, null, null); } // end if } // end setRootItem
public void attachLeft(T newItem) { if (!isEmpty() && root.getLeft() == null) { // assertion: nonempty tree; no left child root.setLeft(new TreeNode(newItem, null, null)); } // end if } // end attachLeft
public void attachRight(T newItem) { if (!isEmpty() && root.getRight() == null) { // assertion: nonempty tree; no right child root.setRight(new TreeNode(newItem, null, null)); } // end if } // end attachRight
public void attachLeftSubtree(BinaryTree leftTree) throws TreeException { if (isEmpty()) { throw new TreeException("TreeException: Empty tree"); } else if (root.getLeft() != null) { // a left subtree already exists; it should have been // deleted first throw new TreeException("TreeException: " + "Cannot overwrite left subtree"); } else { // assertion: nonempty tree; no left child root.setLeft(leftTree.root); // don't want to leave multiple entry points into // our tree leftTree.makeEmpty(); } // end if } // end attachLeftSubtree
public void attachRightSubtree(BinaryTree rightTree) throws TreeException { if (isEmpty()) { throw new TreeException("TreeException: Empty tree"); } else if (root.getRight() != null) { // a right subtree already exists; it should have been // deleted first throw new TreeException("TreeException: " + "Cannot overwrite right subtree"); } else { // assertion: nonempty tree; no right child root.setRight(rightTree.root); // don't want to leave multiple entry points into // our tree rightTree.makeEmpty(); } // end if } // end attachRightSubtree protected BinaryTree(TreeNode rootNode) { root = rootNode; } // end protected constructor
public BinaryTree detachLeftSubtree() throws TreeException { if (isEmpty()) { throw new TreeException("TreeException: Empty tree"); } else { // create a new binary tree that has root's left // node as its root BinaryTree leftTree; leftTree = new BinaryTree(root.getLeft()); root.setLeft(null); return leftTree; } // end if } // end detachLeftSubtree
public BinaryTree detachRightSubtree() throws TreeException { if (isEmpty()) { throw new TreeException("TreeException: Empty tree"); } else { BinaryTree rightTree; rightTree = new BinaryTree(root.getRight()); root.setRight(null); return rightTree; } // end if } // end detachRightSubtree } // end BinaryTree
2)
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class TreeIterator implements java.util.Iterator { private BinaryTreeBasis binTree; private TreeNode currentNode; private LinkedList > queue; // from JCF
public TreeIterator(BinaryTreeBasis bTree) { binTree = bTree; currentNode = null; // empty queue indicates no traversal type currently // selected or end of current traversal has been reached queue = new LinkedList >(); } // end constructor
public boolean hasNext() { return !queue.isEmpty(); } // end hasNext
public T next() throws java.util.NoSuchElementException { currentNode = queue.remove(); return currentNode.getItem(); } // end next
public void remove() throws UnsupportedOperationException { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } // end remove
public void setPreorder() { queue.clear(); preorder(binTree.root); } // setPreOrder
public void setInorder() { queue.clear(); inorder(binTree.root); } // end setInorder
public void setPostorder() { queue.clear(); postorder(binTree.root); } // end setPostorder
private void preorder(TreeNode treeNode) { if (treeNode != null) { queue.add(treeNode); preorder(treeNode.getLeft()); preorder(treeNode.getRight()); } // end if } // end preorder
private void inorder(TreeNode treeNode) { if (treeNode != null) { inorder(treeNode.getLeft()); queue.add(treeNode); inorder(treeNode.getRight()); } // end if } // end inorder
private void postorder(TreeNode treeNode) { if (treeNode != null) { postorder(treeNode.getLeft()); postorder(treeNode.getRight()); queue.add(treeNode); } // end if } // end postorder } // end TreeIterator
3)
public class TreeTraversal { public static void main(String[] args){ // Create a tree called tree1 BinaryTree tree1 = new BinaryTree("H"); BinaryTree rightsubtree1 = new BinaryTree("X"); rightsubtree1.attachRight('Y'); BinaryTree leftsubtree1 = new BinaryTree("D"); leftsubtree1.attachLeft('B'); BinaryTree leftsubtree2 = new BinaryTree("F"); leftsubtree2.attachRight('G'); leftsubtree2.attachLeft('E'); leftsubtree1.attachRightSubtree(leftsubtree2); tree1.attachLeftSubtree(leftsubtree1); tree1.attachRightSubtree(rightsubtree1);
BinaryTree tree2 = new BinaryTree("F"); // // BUILD tree2 HERE // System.out.println(checkSkipped(tree1)); // Should return false System.out.println(checkSkipped(tree2)); // Should return true } public static boolean checkSkipped(BinaryTree tree){ /* // To Iterate a tree using Inorder Traversal TreeIterator iter = new TreeIterator(tree); iter.setInorder(); while (iter.hasNext()){ System.out.print (iter.next()); } */
// INSERT CODE HERE return false; }
}
4)
class TreeException extends RuntimeException { public TreeException(String s) { super(s); } // end constructor } // end TreeException
5)
public abstract class BinaryTreeBasis { protected TreeNode root;
public BinaryTreeBasis() { root = null; } // end default constructor
public BinaryTreeBasis(T rootItem) { root = new TreeNode(rootItem, null, null); } // end constructor
public boolean isEmpty() { // Returns true if the tree is empty, else returns false. return root == null; } // end isEmpty
public void makeEmpty() { // Removes all nodes from the tree. root = null; } // end makeEmpty
public T getRootItem() throws TreeException { // Returns the item in the trees root. if (root == null) { throw new TreeException("TreeException: Empty tree"); } else { return root.getItem(); } // end if } // end getRootItem
public abstract void setRootItem(T newItem); // Throws UnsupportedOperationException if operation // is not supported. } // end BinaryTreeBasis
6)
public class TreeNode { private T item; private TreeNode leftChild; private TreeNode rightChild;
public TreeNode(T newItem) { // Initializes tree node with item and no children. item = newItem; leftChild = null; rightChild = null; } // end constructor public TreeNode(T newItem, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { // Initializes tree node with item and // the left and right children references. item = newItem; leftChild = left; rightChild = right; } // end constructor
public T getItem() { // Returns the item field. return item; } // end getItem
public void setItem(T newItem) { // Sets the item field to the new value newItem. item = newItem; } // end setItem
public TreeNode getLeft() { // Returns the reference to the left child. return leftChild; } // end getLeft
public void setLeft(TreeNode left) { // Sets the left child reference to left. leftChild = left; } // end setLeft
public TreeNode getRight() { // Returns the reference to the right child. return rightChild; } // end getRight
public void setRight(TreeNode right) { // Sets the right child reference to right. rightChild = right; } // end setRight } // end TreeNode
NOW. THIS IS ALL THE INFORMATION PROVIDED. PLEASE READ THE ASSIGNMENT CAREFULLY AND DO WHAT IT ASKS. THANK YOU FOR YOUR WORK
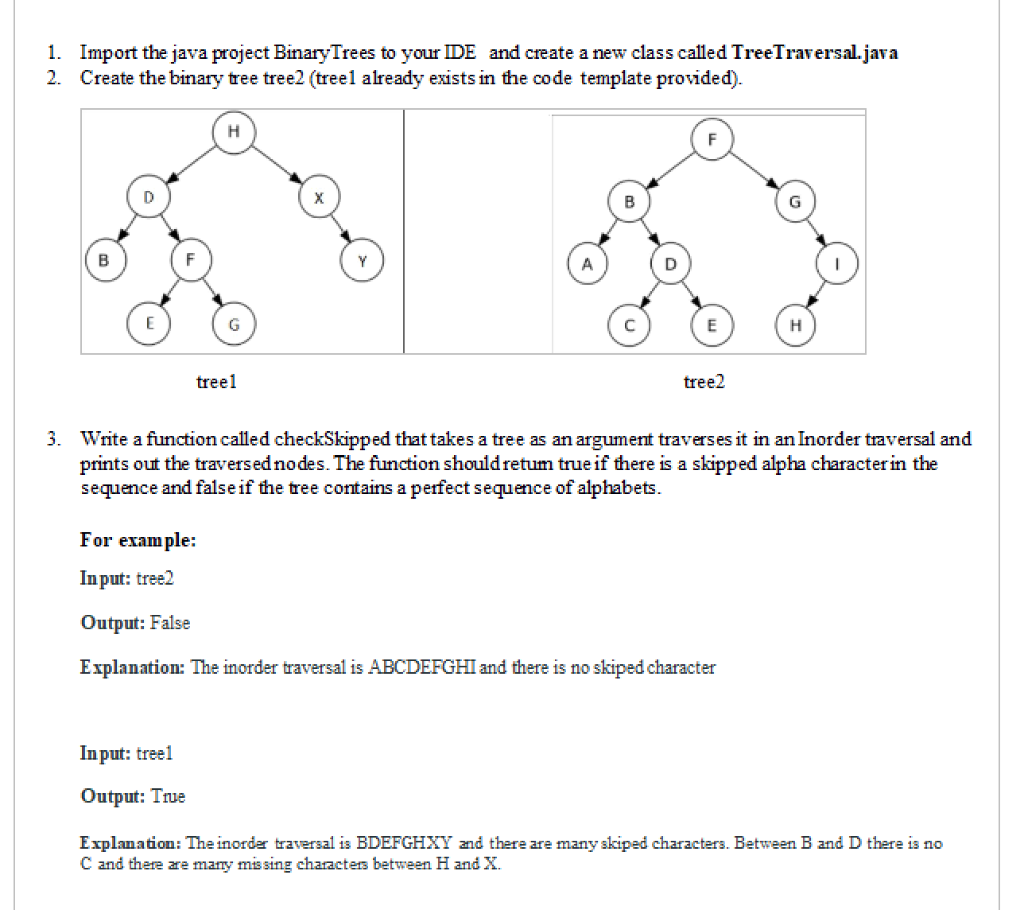
1. Import the java project Binary Trees to your IDE and create a new class called TreeTraversal.java 2. Create the binary tree tree2 (treel already exists in the code template provided). H D X B Y E G E H tree1 tree2 3. Write a function called checkSkipped that takes a tree as an argument traverses it in an Inorder traversal and prints out the trave The function hould here a skipped alpha chara the sequence and false if the tree contains a perfect sequence of alphabets. For example: Input: tree2 Output: False Explanation: The inorder traversal is ABCDEFGHI and there is no skiped character Input: tree1 Output: True Explanation: The inorde traversal is BDEFGHXY and there are many skiped characters. Between B and D there is no C and there are many missing characters between H and X. public class Tree Traversal { public static void main(String[] args) { 1 Create a tree called treel Binary Tree Character> treel = new BinaryTreel "H"); BinaryTreec Character> right subtree l = new Binary Tree ( "X"); rightsubtreel.attachRight('Y'); BinaryTree leftsubtreel = new BinaryTreel "D"); left subtree1.attachLeft( 'B'); Binaryl reecCharacters Lettsubtree2 = new BinaryTree F1 left subtree2.attachRight( 'G'); left subtree2.attachLeft( 'E'); leftsub treei.attachRight Subtree(left subtree2); treel.attachLeft Subtree(leftsubt reel); treel.attachRightSubtree (rightsubtreen); BinaryTree Character> tree2 = new Binary Tree ("F"); BUILD tree2 HERE 1 System.out.println(checkSkipped(tree)); // Should return true System.out.println(checkSkipped (tree2)); // Should return false } public static boolean checkSkipped(Binary Tree
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


