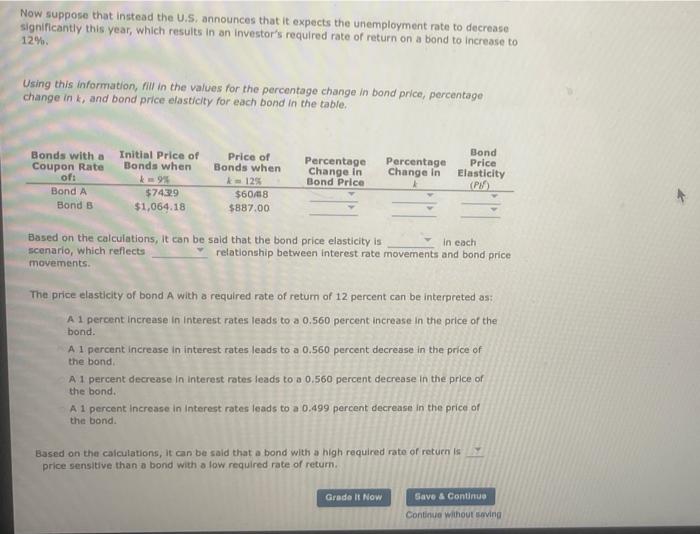
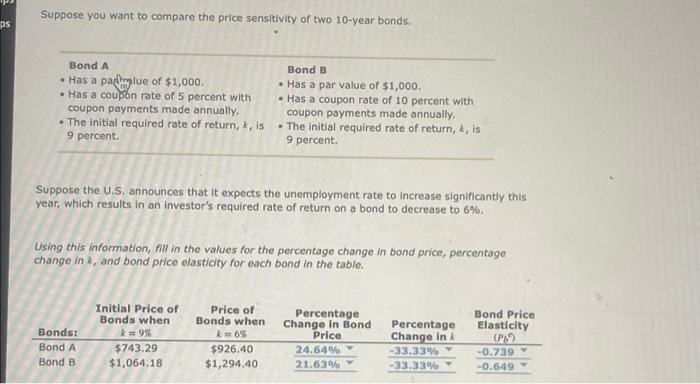
Now suppose that instead the U.S. announces that it expects the unemployment rate to decrease significantly this year, which results in an investor's required rate of return on a bond to increase to 12% Using this information, fill in the values for the percentage change in bond price, percentage change in k, and bond price elasticity for each bond in the table. Based on the calculations, it can be sald that the bond price elasticity is in each scenario, which refiects relationship between interest rate movements and bond price movements. The price elasticity of bond A with a required rate of retum of 12 percent can be interpreted as: A 1 percent increase in interest rates leads to a 0.560 percent increase in the price of the bond. A 1 percent increase in interest rates leads to a 0.560 percent decrease in the price of the bond. A 1 percent decrease in interest rates leads to a 0.560 percent decrease in the price of the bond. A 1 percent increase in interest rates leads to a 0.499 percent decrease in the price of the bond. Based on the calculations, it can be said that a bond with a high required rate of retuen is price sensitive than a bond with a low required rate of return. Suppose you want to compare the price sensitivity of two 10 -year bonds. Suppose the U.S. announces that it expects the unemployment rate to increase significantly this year, which results in an investor's required rate of return on a bond to decrease to 6%. Using this information, fill in the values for the percentage change in bond price, percentage change in k, and bond price elasticity for each bond in the table. Now suppose that instead the U.S. announces that it expects the unemployment rate to decrease significantly this year, which results in an investor's required rate of return on a bond to increase to 12%. Using this information, fill in the values for the percentage change in bond price, percentage change in k, and bond price elasticity for each bond in the table. Based on the calculations, it can be said that the bond price elasticity is scenario, which reflects price movements. The price elasticity of bons A with a required rate of return of 12 percent can be interpreted as: bond. A 1 percent increase in interest rates leads to a 0.560 percent decrease in the price of the bond. A 1 percent decrease in interest rates leads to a 0.560 percent decrease in the price of the bond. A 1 percent increase in interest rates leads to a 0.499 percent decrease in the price of the bond. Based on the calculations, it can be sald that a bond with a high required rate of return is price sensitive than a bond with a low required rate of return